Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [38]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [12]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA1-313 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Estrogen Receptor beta Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- PA1-313 has been successfully used in Western blot and immunohistochemistry procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects an ~55 kDa protein representing ER beta from rat brain homogenate. Immunohistochemical staining of ER beta in rat prostate with PA1-313 results in nuclear staining, whereas nuclear staining may not be observed in human tissue. The PA1-313 immunogen is a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues C(459) S P A E D S K S K E G S Q N P Q S Q(477) of human ER beta. PA1-313 immunizing peptide (Cat. # PEP-029) is available for use in neutralization and control experiments. Recombinant ER beta expressed in baculovirus system (Cat. # RP-311 and RP-312) can be purchased for control experiments in Western blot and gel shift assays.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 50 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references The absence of oestrogen receptor beta disturbs collagen I type deposition during Achilles tendon healing by regulating the IRF5-CCL3 axis.
Insights into the Role of Estrogen Receptor β in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Interaction Proteomics Identifies ERbeta Association with Chromatin Repressive Complexes to Inhibit Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exert An Oncosuppressive Role in Triple-negative Breast Cancer.
Absence of estrogen receptor beta leads to abnormal adipogenesis during early tendon healing by an up-regulation of PPARγ signalling.
Effect of estradiol on fibroblasts from postmenopausal idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome patients.
Targeting Estrogen Receptor Beta in a Phase 2 Study of High-Dose Estradiol in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Wisconsin Oncology Network Study.
Prognostic significance of full-length estrogen receptor beta expression in stage I-III triple negative breast cancer.
Histone H3 Lysine 27 demethylases Jmjd3 and Utx are required for T-cell differentiation.
Characterization of estrogen response element binding proteins as biomarkers of breast cancer behavior.
Estrogen receptor beta in cancer: an attractive target for therapy.
Amounts of an estrogen receptor β isoform increased in the theca of preovulatory follicles of sheep.
Morphologic transformation of human breast epithelial cells MCF-10A: dependence on an oxidative microenvironment and estrogen/epidermal growth factor receptors.
Estrogen increases survival in an orthotopic model of glioblastoma.
Prepubertal physical activity up-regulates estrogen receptor beta, BRCA1 and p53 mRNA expression in the rat mammary gland.
Estrogen receptor beta displays cell cycle-dependent expression and regulates the G1 phase through a non-genomic mechanism in prostate carcinoma cells.
Changes in biomarkers of estrogen receptor and growth factor signaling pathways in MCF-7 tumors after short- and long-term treatment with soy and flaxseed.
Differing transcriptional responses to pulsed or continuous estradiol exposure in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Changes in transcription profile and cytoskeleton morphology in pelvic ligament fibroblasts in response to stretch: the effects of estradiol and levormeloxifene.
Estrogen receptors in the uterus and ovarian follicles of gilts treated with dihydrotestosterone.
Nuclear estrogen receptor beta in lung cancer: expression and survival differences by sex.
Binding of estrogen receptor beta to estrogen response element in situ is independent of estradiol and impaired by its amino terminus.
Single-chain estrogen receptors (ERs) reveal that the ERalpha/beta heterodimer emulates functions of the ERalpha dimer in genomic estrogen signaling pathways.
Gonadal hormones and frontocortical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in male stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats, a model for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Prepubertal estradiol and genistein exposures up-regulate BRCA1 mRNA and reduce mammary tumorigenesis.
Oestrogen receptor beta: what it means for patients with breast cancer.
Estrogen receptor beta localization in the lizard (Podarcis s. sicula) testis.
Estrogen regulates adrenal angiotensin AT1 receptors by modulating AT1 receptor translation.
17Beta-estradiol up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression in human myometrial microvascular endothelial cells: role of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta.
17-Beta-estradiol regulates expression of genes that function in macrophage activation and cholesterol homeostasis.
17-Beta-estradiol regulates expression of genes that function in macrophage activation and cholesterol homeostasis.
Differences in the abilities of estrogen receptors to integrate activation functions are critical for subtype-specific transcriptional responses.
Expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the baboon fetal ovary.
Loss of estrogen receptor beta expression in malignant human prostate cells in primary cultures and in prostate cancer tissues.
Different regulation of oestrogen receptors alpha and beta in the human cervix at term pregnancy.
Estrogen receptors in the normal adult and developing human inner ear and in Turner's syndrome.
Estradiol acts as a germ cell survival factor in the human testis in vitro.
Estrogen receptor beta is coexpressed with ERalpha and PR and associated with nodal status, grade, and proliferation rate in breast cancer.
Identification and developmental expression of the estrogen receptor alpha and beta in the baboon fetal adrenal gland.
Bian X, Liu T, Yang M, Gu C, He G, Zhou M, Tang H, Lu K, Lai F, Wang F, Yang Q, Gustafsson JÅ, Fan X, Tang K
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2020 Sep;24(17):9925-9935
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2020 Sep;24(17):9925-9935
Insights into the Role of Estrogen Receptor β in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.
Sellitto A, D'Agostino Y, Alexandrova E, Lamberti J, Pecoraro G, Memoli D, Rocco D, Coviello E, Giurato G, Nassa G, Tarallo R, Weisz A, Rizzo F
Cancers 2020 Jun 5;12(6)
Cancers 2020 Jun 5;12(6)
Interaction Proteomics Identifies ERbeta Association with Chromatin Repressive Complexes to Inhibit Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exert An Oncosuppressive Role in Triple-negative Breast Cancer.
Alexandrova E, Giurato G, Saggese P, Pecoraro G, Lamberti J, Ravo M, Rizzo F, Rocco D, Tarallo R, Nyman TA, Collina F, Cantile M, Di Bonito M, Botti G, Nassa G, Weisz A
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2020 Feb;19(2):245-260
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2020 Feb;19(2):245-260
Absence of estrogen receptor beta leads to abnormal adipogenesis during early tendon healing by an up-regulation of PPARγ signalling.
Bian X, Liu T, Zhou M, He G, Ma Y, Shi Y, Wang Y, Tang H, Kang X, Yang M, Gustafsson JÅ, Fan X, Tang K
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2019 Nov;23(11):7406-7416
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2019 Nov;23(11):7406-7416
Effect of estradiol on fibroblasts from postmenopausal idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome patients.
Yamanaka Y, Menuki K, Tajima T, Okada Y, Kosugi K, Zenke Y, Sakai A
Journal of cellular physiology 2018 Nov;233(11):8723-8730
Journal of cellular physiology 2018 Nov;233(11):8723-8730
Targeting Estrogen Receptor Beta in a Phase 2 Study of High-Dose Estradiol in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Wisconsin Oncology Network Study.
Wisinski KB, Xu W, Tevaarwerk AJ, Saha S, Kim K, Traynor A, Dietrich L, Hegeman R, Patel D, Blank J, Harter J, Burkard ME
Clinical breast cancer 2016 Aug;16(4):256-61
Clinical breast cancer 2016 Aug;16(4):256-61
Prognostic significance of full-length estrogen receptor beta expression in stage I-III triple negative breast cancer.
Shanle EK, Onitilo AA, Huang W, Kim K, Zang C, Engel JM, Xu W, Wisinski KB
American journal of translational research 2015;7(7):1246-59
American journal of translational research 2015;7(7):1246-59
Histone H3 Lysine 27 demethylases Jmjd3 and Utx are required for T-cell differentiation.
Manna S, Kim JK, Baugé C, Cam M, Zhao Y, Shetty J, Vacchio MS, Castro E, Tran B, Tessarollo L, Bosselut R
Nature communications 2015 Sep 2;6:8152
Nature communications 2015 Sep 2;6:8152
Characterization of estrogen response element binding proteins as biomarkers of breast cancer behavior.
Kruer TL, Cummins TD, Powell DW, Wittliff JL
Clinical biochemistry 2013 Nov;46(16-17):1739-46
Clinical biochemistry 2013 Nov;46(16-17):1739-46
Estrogen receptor beta in cancer: an attractive target for therapy.
Gallo D, De Stefano I, Grazia Prisco M, Scambia G, Ferrandina G
Current pharmaceutical design 2012;18(19):2734-57
Current pharmaceutical design 2012;18(19):2734-57
Amounts of an estrogen receptor β isoform increased in the theca of preovulatory follicles of sheep.
Cárdenas H, Pope WF
Animal reproduction science 2012 Apr;131(3-4):143-52
Animal reproduction science 2012 Apr;131(3-4):143-52
Morphologic transformation of human breast epithelial cells MCF-10A: dependence on an oxidative microenvironment and estrogen/epidermal growth factor receptors.
Yusuf R, Frenkel K
Cancer cell international 2010 Sep 1;10:30
Cancer cell international 2010 Sep 1;10:30
Estrogen increases survival in an orthotopic model of glioblastoma.
Barone TA, Gorski JW, Greenberg SJ, Plunkett RJ
Journal of neuro-oncology 2009 Oct;95(1):37-48
Journal of neuro-oncology 2009 Oct;95(1):37-48
Prepubertal physical activity up-regulates estrogen receptor beta, BRCA1 and p53 mRNA expression in the rat mammary gland.
Wang M, Yu B, Westerlind K, Strange R, Khan G, Patil D, Boeneman K, Hilakivi-Clarke L
Breast cancer research and treatment 2009 May;115(1):213-20
Breast cancer research and treatment 2009 May;115(1):213-20
Estrogen receptor beta displays cell cycle-dependent expression and regulates the G1 phase through a non-genomic mechanism in prostate carcinoma cells.
Hurtado A, Pinós T, Barbosa-Desongles A, López-Avilés S, Barquinero J, Petriz J, Santamaria-Martínez A, Morote J, de Torres I, Bellmunt J, Reventós J, Munell F
Cellular oncology : the official journal of the International Society for Cellular Oncology 2008;30(4):349-65
Cellular oncology : the official journal of the International Society for Cellular Oncology 2008;30(4):349-65
Changes in biomarkers of estrogen receptor and growth factor signaling pathways in MCF-7 tumors after short- and long-term treatment with soy and flaxseed.
Power KA, Chen JM, Saarinen NM, Thompson LU
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2008 Nov;112(1-3):13-9
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2008 Nov;112(1-3):13-9
Differing transcriptional responses to pulsed or continuous estradiol exposure in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Li J, Wang H, Johnson SM, Horner-Glister E, Thompson J, White IN, Al-Azzawi F
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2008 Jul;111(1-2):41-9
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2008 Jul;111(1-2):41-9
Changes in transcription profile and cytoskeleton morphology in pelvic ligament fibroblasts in response to stretch: the effects of estradiol and levormeloxifene.
Ewies AA, Elshafie M, Li J, Stanley A, Thompson J, Styles J, White I, Al-Azzawi F
Molecular human reproduction 2008 Feb;14(2):127-35
Molecular human reproduction 2008 Feb;14(2):127-35
Estrogen receptors in the uterus and ovarian follicles of gilts treated with dihydrotestosterone.
Cárdenas H, Pope WF
Domestic animal endocrinology 2005 Oct;29(3):523-33
Domestic animal endocrinology 2005 Oct;29(3):523-33
Nuclear estrogen receptor beta in lung cancer: expression and survival differences by sex.
Schwartz AG, Prysak GM, Murphy V, Lonardo F, Pass H, Schwartz J, Brooks S
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2005 Oct 15;11(20):7280-7
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2005 Oct 15;11(20):7280-7
Binding of estrogen receptor beta to estrogen response element in situ is independent of estradiol and impaired by its amino terminus.
Huang J, Li X, Maguire CA, Hilf R, Bambara RA, Muyan M
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Nov;19(11):2696-712
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Nov;19(11):2696-712
Single-chain estrogen receptors (ERs) reveal that the ERalpha/beta heterodimer emulates functions of the ERalpha dimer in genomic estrogen signaling pathways.
Li X, Huang J, Yi P, Bambara RA, Hilf R, Muyan M
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Sep;24(17):7681-94
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Sep;24(17):7681-94
Gonadal hormones and frontocortical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in male stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats, a model for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
Jesmin S, Togashi H, Sakuma I, Mowa CN, Ueno K, Yamaguchi T, Yoshioka M, Kitabatake A
Endocrinology 2004 Sep;145(9):4330-43
Endocrinology 2004 Sep;145(9):4330-43
Prepubertal estradiol and genistein exposures up-regulate BRCA1 mRNA and reduce mammary tumorigenesis.
Cabanes A, Wang M, Olivo S, DeAssis S, Gustafsson JA, Khan G, Hilakivi-Clarke L
Carcinogenesis 2004 May;25(5):741-8
Carcinogenesis 2004 May;25(5):741-8
Oestrogen receptor beta: what it means for patients with breast cancer.
Speirs V, Carder PJ, Lane S, Dodwell D, Lansdown MR, Hanby AM
The Lancet. Oncology 2004 Mar;5(3):174-81
The Lancet. Oncology 2004 Mar;5(3):174-81
Estrogen receptor beta localization in the lizard (Podarcis s. sicula) testis.
Chieffi P, Varriale B
Zygote (Cambridge, England) 2004 Feb;12(1):39-42
Zygote (Cambridge, England) 2004 Feb;12(1):39-42
Estrogen regulates adrenal angiotensin AT1 receptors by modulating AT1 receptor translation.
Wu Z, Maric C, Roesch DM, Zheng W, Verbalis JG, Sandberg K
Endocrinology 2003 Jul;144(7):3251-61
Endocrinology 2003 Jul;144(7):3251-61
17Beta-estradiol up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression in human myometrial microvascular endothelial cells: role of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta.
Gargett CE, Zaitseva M, Bucak K, Chu S, Fuller PJ, Rogers PA
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2002 Sep;87(9):4341-9
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2002 Sep;87(9):4341-9
17-Beta-estradiol regulates expression of genes that function in macrophage activation and cholesterol homeostasis.
Kramer PR, Wray S
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2002 Jul;81(3):203-16
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2002 Jul;81(3):203-16
17-Beta-estradiol regulates expression of genes that function in macrophage activation and cholesterol homeostasis.
Kramer PR, Wray S
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2002 Jul;81(3):203-16
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 2002 Jul;81(3):203-16
Differences in the abilities of estrogen receptors to integrate activation functions are critical for subtype-specific transcriptional responses.
Yi P, Bhagat S, Hilf R, Bambara RA, Muyan M
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Aug;16(8):1810-27
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Aug;16(8):1810-27
Expression of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the baboon fetal ovary.
Pepe GJ, Billiar RB, Leavitt MG, Zachos NC, Gustafsson JA, Albrecht ED
Biology of reproduction 2002 Apr;66(4):1054-60
Biology of reproduction 2002 Apr;66(4):1054-60
Loss of estrogen receptor beta expression in malignant human prostate cells in primary cultures and in prostate cancer tissues.
Pasquali D, Rossi V, Esposito D, Abbondanza C, Puca GA, Bellastella A, Sinisi AA
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2001 May;86(5):2051-5
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2001 May;86(5):2051-5
Different regulation of oestrogen receptors alpha and beta in the human cervix at term pregnancy.
Wang H, Stjernholm Y, Ekman G, Eriksson H, Sahlin L
Molecular human reproduction 2001 Mar;7(3):293-300
Molecular human reproduction 2001 Mar;7(3):293-300
Estrogen receptors in the normal adult and developing human inner ear and in Turner's syndrome.
Stenberg AE, Wang H, Fish J 3rd, Schrott-Fischer A, Sahlin L, Hultcrantz M
Hearing research 2001 Jul;157(1-2):87-92
Hearing research 2001 Jul;157(1-2):87-92
Estradiol acts as a germ cell survival factor in the human testis in vitro.
Pentikäinen V, Erkkilä K, Suomalainen L, Parvinen M, Dunkel L
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2000 May;85(5):2057-67
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 2000 May;85(5):2057-67
Estrogen receptor beta is coexpressed with ERalpha and PR and associated with nodal status, grade, and proliferation rate in breast cancer.
Järvinen TA, Pelto-Huikko M, Holli K, Isola J
The American journal of pathology 2000 Jan;156(1):29-35
The American journal of pathology 2000 Jan;156(1):29-35
Identification and developmental expression of the estrogen receptor alpha and beta in the baboon fetal adrenal gland.
Albrecht ED, Babischkin JS, Davies WA, Leavitt MG, Pepe GJ
Endocrinology 1999 Dec;140(12):5953-61
Endocrinology 1999 Dec;140(12):5953-61
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
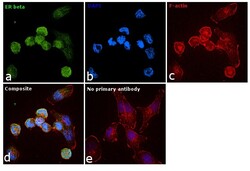
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Estrogen Receptor beta was performed using 70% confluent log phase T-47D cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Estrogen Receptor beta Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-313) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree Celsius overnight and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing predominant nuclear localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
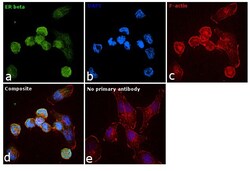
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Estrogen Receptor beta was performed using 70% confluent log phase T-47D cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Estrogen Receptor beta Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-313) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree Celsius overnight and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing predominant nuclear localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
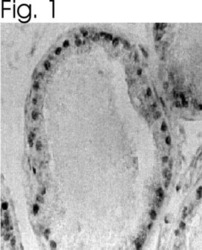
- Experimental details
- Immunolocalization of ER beta in rat prostate using Product # PA1-313.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
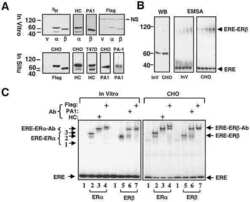
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
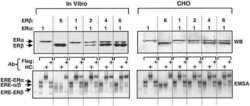
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
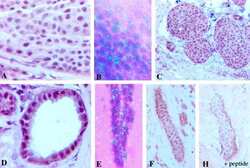
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
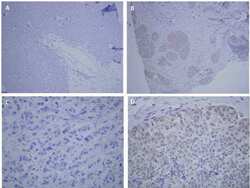
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
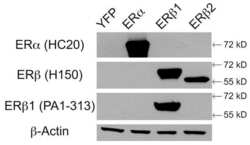
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
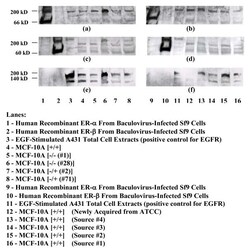
- Experimental details
- Figure 7 Analysis of MCF-10A Cells for ERalpha, ERbeta, and EGFR . Nuclear proteins extracted from MCF-10A cells that were exposed to differing culture conditions were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of ERalpha, ERbeta, and EGFR. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of passages in that particular type of medium. Proteins (42 mug/lane) were electrophoresed onto two 12% Tris-HCl gels (lanes 1-8 and 9-16 respectively) and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were probed with antibodies directed against ERalpha (a and b), stripped and re-probed with antibodies directed against ERbeta (c and d), and stripped a second time and re-probed with antibodies directed against EGFR (e and f). Results shown are those from one experiment.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
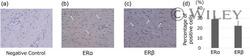
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of ERalpha and ERbeta in the SSCT derived from idiopathic patients (magnification x400). (a) Negative control. (b) ERalpha expression (indicated by an arrow). (c) ERbeta expression (indicated by an arrow). (d) ERalpha expression was higher than ERbeta expression, but this difference was not significant. All results are expressed as means +- standard error
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
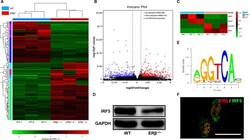
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 RNA-seq analysis of the gene expression profile of ERbeta -/- and WT control tendon scars revealed IRF5 down-regulation in the absence of ERbeta. A, Heatmap depicting the expression levels of genes in WT and ERbeta -/- tendons after 1 wk of repair. B, Volcano map of differentially expressed genes between WT and ERbeta -/- tendons after 1 wk of repair: 68 genes were up-regulated, and 51 genes were down-regulated. C, Heatmap of differentially expressed transcription factors. D, Immunoblots of IRF5 in WT and ERbeta -/- tendons after 1 wk of repair. E, Bioinformatic prediction of binding sites of ERbeta and IRF5 using JASPAR (chr6:29528943-29528949, AGGGCAG, length = 7). F, The immunofluorescence analysis of ERbeta and IRF5 revealed co-expression in macrophages. Scale bars: 50 mum
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
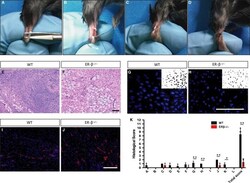
- Figure 1 ERbeta -/- tendon scars have an inferior tendon repair process. A-D, Surgery process of mouse Achilles tendon. E, F Low-magnification HE staining indicates a very different scar organization with clear adipocyte accumulation in ERbeta -/- mice. (G,H) Cell density in the healing region was significantly lower in ERbeta -/- mice compared with WT controls. (I,J) Number of CD34-labelled blood vessels was significantly higher in ERbeta -/- mice compared with WT controls. K, Evaluation of tendon healing using an established histological scoring system revealed that ERbeta -/- mice had a significantly lower histological score compared with WT controls. Data are represented as mean +- SEM (n = 5), * P < .05, ** P < .01. Scale Bars: 100mum
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
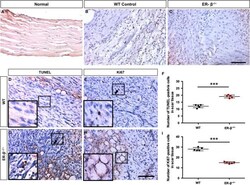
- Figure 2 ERbeta -/- tendon scars have reduced cell proliferation, whilst increased cell apoptosis. A-C, Immunohistochemistry of ERbeta revealed a little expression in normal mouse Achilles tendon (A), more expression in early healing of WT mouse Achilles tendon (B) and no expression in ER-beta -/- mouse injured Achilles tendon. ERbeta -/- mouse Achilles tendon (C). (D,G,F) TUNEL staining and statistical analysis showed more apoptotic cells in ERbeta -/- tendon scars. (E,H,I) Immunohistochemistry of Ki67 and statistical analysis revealed decreased cell proliferation in ERbeta -/- tendon scars. Data are represented as mean +- SEM (n = 5), *** P < .001. Scale Bars: 100mum
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry