Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [6]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA3-113 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- VIPR1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- PA3-113 detects VPAC1 Receptor in human samples. PA3-113 has been successfully used in Western blot, immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry (paraffin) procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects an ~55-70 kDa protein representing VPAC1 Receptor in human samples. In immunohistochemistry, VPAC1 Receptor immunoreactivity is predominantly localized at the level of the plasma membrane. PA3-113 immunizing peptide corresponds to amino acid residues 438-457 from human VPAC1 Receptor.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- Conc. Not Determined
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Comprehensive Profiling Reveals Distinct Microenvironment and Metabolism Characterization of Lung Adenocarcinoma.
Expression and localization of VPAC1, the major receptor of vasoactive intestinal peptide along the length of the intestine.
Atypical nuclear localization of VIP receptors in glioma cell lines and patients.
The vasoactive intestinal peptide-receptor system is involved in human glioblastoma cell migration.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) induces malignant transformation of the human prostate epithelial cell line RWPE-1.
Immunocytochemical identification of VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptors in normal and neoplastic human tissues with subtype-specific antibodies.
Li C, Tian C, Liu Y, Liang J, Zeng Y, Yang Q, Liu Y, Wu D, Wu J, Wang J, Zhang K, Gu F, Hu Y, Liu L
Frontiers in genetics 2021;12:619821
Frontiers in genetics 2021;12:619821
Expression and localization of VPAC1, the major receptor of vasoactive intestinal peptide along the length of the intestine.
Jayawardena D, Guzman G, Gill RK, Alrefai WA, Onyuksel H, Dudeja PK
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology 2017 Jul 1;313(1):G16-G25
American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology 2017 Jul 1;313(1):G16-G25
Atypical nuclear localization of VIP receptors in glioma cell lines and patients.
Barbarin A, Séité P, Godet J, Bensalma S, Muller JM, Chadéneau C
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2014 Nov 28;454(4):524-30
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2014 Nov 28;454(4):524-30
The vasoactive intestinal peptide-receptor system is involved in human glioblastoma cell migration.
Cochaud S, Chevrier L, Meunier AC, Brillet T, Chadéneau C, Muller JM
Neuropeptides 2010 Oct;44(5):373-83
Neuropeptides 2010 Oct;44(5):373-83
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) induces malignant transformation of the human prostate epithelial cell line RWPE-1.
Fernández-Martínez AB, Bajo AM, Isabel Arenas M, Sánchez-Chapado M, Prieto JC, Carmena MJ
Cancer letters 2010 Dec 18;299(1):11-21
Cancer letters 2010 Dec 18;299(1):11-21
Immunocytochemical identification of VPAC1, VPAC2, and PAC1 receptors in normal and neoplastic human tissues with subtype-specific antibodies.
Schulz S, Röcken C, Mawrin C, Weise W, Höllt V, Schulz S
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2004 Dec 15;10(24):8235-42
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2004 Dec 15;10(24):8235-42
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
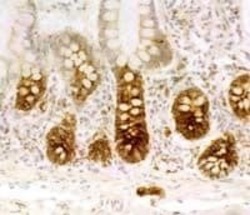
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical staining of VPAC1 Receptor in human intestine samples using Product # PA3-113.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
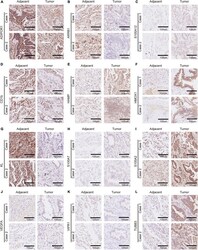
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 10 Immunohistochemistry of 12 selected genes expression in two lung adenocarcinoma cases. (A-L) Representative pictures of an IHC staining with paraffin-embedded tissue sections demonstrate the selected genes' protein expression patterns (brown signal) in adjacent tissue (left panel) and matched malignant tumor tissue (right panel). The 12 selected genes were in order as follows: ADIPOR1, ARRB1, S100A12, CD1b, HAMP, HMOX1, KL, S100A7, S100A2, VEGFA, VIPR1, and TUBB3.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry