Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [5]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- NBP2-32356 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Novus Biologicals
- Proper citation
- Novus Cat#NBP2-32356, RRID:AB_2687926
- Product name
- Rabbit Polyclonal HOXA9 Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Immunogen affinity purified. Specificity of human HOXA9 antibody verified on a Protein Array containing target protein plus 383 other non-specific proteins.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 0.1 ml
- Storage
- Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Submitted references Modulation of HOXA9 after skeletal muscle denervation and reinnervation.
Upregulated HOXA9 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Hoxa9 and Meis1 Cooperatively Induce Addiction to Syk Signaling by Suppressing miR-146a in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Gene expression comparison reveals distinct basal expression of HOX members and differential TNF-induced response between brain- and spinal cord-derived microvascular endothelial cells.
Lu X, Liang B, Li S, Chen Z, Chang W
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2020 Jun 1;318(6):C1154-C1165
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2020 Jun 1;318(6):C1154-C1165
Upregulated HOXA9 expression is associated with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Watanabe Y, Saito M, Saito K, Matsumoto Y, Kanke Y, Onozawa H, Hayase S, Sakamoto W, Ishigame T, Momma T, Ohki S, Takenoshita S
Oncology letters 2018 Mar;15(3):2756-2762
Oncology letters 2018 Mar;15(3):2756-2762
Hoxa9 and Meis1 Cooperatively Induce Addiction to Syk Signaling by Suppressing miR-146a in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
Mohr S, Doebele C, Comoglio F, Berg T, Beck J, Bohnenberger H, Alexe G, Corso J, Ströbel P, Wachter A, Beissbarth T, Schnütgen F, Cremer A, Haetscher N, Göllner S, Rouhi A, Palmqvist L, Rieger MA, Schroeder T, Bönig H, Müller-Tidow C, Kuchenbauer F, Schütz E, Green AR, Urlaub H, Stegmaier K, Humphries RK, Serve H, Oellerich T
Cancer cell 2017 Apr 10;31(4):549-562.e11
Cancer cell 2017 Apr 10;31(4):549-562.e11
Gene expression comparison reveals distinct basal expression of HOX members and differential TNF-induced response between brain- and spinal cord-derived microvascular endothelial cells.
Molino Y, Jabès F, Bonnet A, Gaudin N, Bernard A, Benech P, Khrestchatisky M
Journal of neuroinflammation 2016 Nov 10;13(1):290
Journal of neuroinflammation 2016 Nov 10;13(1):290
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
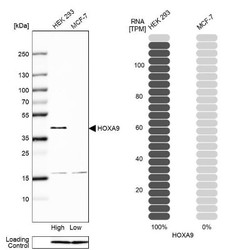
- Experimental details
- Western Blot: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Analysis in human cell line HEK 293 and human cell line MCF-7.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
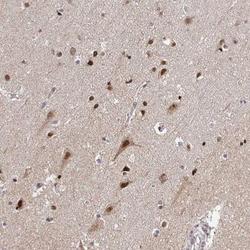
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Staining of human cerebral cortex shows moderate nuclear and cytoplasmic positivity in neuronal cells, glial cells were strongly stained..
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
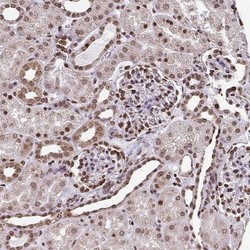
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Staining of human kidney shows strong nuclear positivity in cells in glomeruli.
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
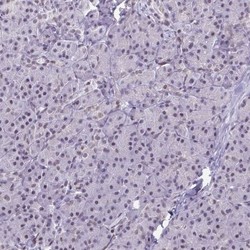
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Staining of human pancreas shows no positivity in exocrine glandular cells as expected.
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
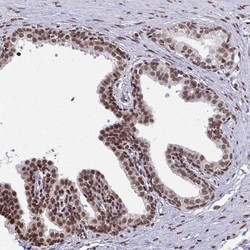
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Staining of human prostate shows moderate nuclear positivity in glandular cells.
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
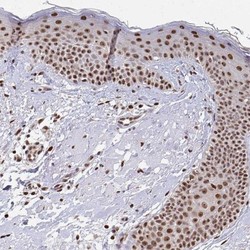
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: HOXA9 Antibody [NBP2-32356] - Staining of human skin shows moderate to strong nuclear positivity in squamous epithelial cells.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry