Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA029308 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA029308, RRID:AB_10601923
- Product name
- Anti-KLF9
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human KLF9, Gene description: Kruppel-like factor 9, Alternative Gene Names: BTEB1, Validated applications: ChIP, ICC, WB, Uniprot ID: Q13886, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references RETRACTED ARTICLE: Interference of KLF9 relieved the development of gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating DDAH2
Chen W, Wang H, Liu J, Li K
Bioengineered 2021;13(1):395-406
Bioengineered 2021;13(1):395-406
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
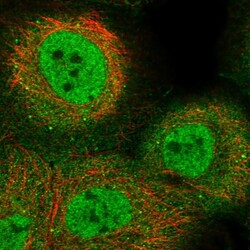
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line A-431 shows localization to nucleoplasm, plasma membrane & cytosol.
- Sample type
- Human
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
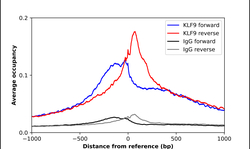
- Experimental details
- ChIP-Exo-Seq composite graph for Anti-KLF9 (HPA029308, Lot A106550) tested in K562 cells. Strand-specific reads (blue: forward, red: reverse) and IgG controls (black: forward, grey: reverse) are plotted against the distance from a composite set of reference binding sites. The antibody exhibits robust target enrichment compared to a non-specific IgG control and precisely reveals its structural organization around the binding site. Data generated by Prof. B. F. Pugh´s Lab at Cornell University.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry