Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [3]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA006366 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA006366, RRID:AB_1079654
- Product name
- Anti-POLRMT
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human POLRMT, Gene description: polymerase (RNA) mitochondrial (DNA directed), Alternative Gene Names: APOLMT, h-mtRPOL, MTRNAP, MTRPOL, Validated applications: IHC, ICC, Uniprot ID: O00411, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.3 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references Comparative analysis of MACROD1, MACROD2 and TARG1 expression, localisation and interactome
Mitochondria “fuel” breast cancer metabolism: Fifteen markers of mitochondrial biogenesis label epithelial cancer cells, but are excluded from adjacent stromal cells
Mitochondrial biogenesis in epithelial cancer cells promotes breast cancer tumor growth and confers autophagy resistance
Žaja R, Aydin G, Lippok B, Feederle R, Lüscher B, Feijs K
Scientific Reports 2020;10(1)
Scientific Reports 2020;10(1)
Mitochondria “fuel” breast cancer metabolism: Fifteen markers of mitochondrial biogenesis label epithelial cancer cells, but are excluded from adjacent stromal cells
Sotgia F, Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn U, Salem A, Tsirigos A, Lamb R, Sneddon S, Hulit J, Howell A, Lisanti M
Cell Cycle 2014;11(23):4390-4401
Cell Cycle 2014;11(23):4390-4401
Mitochondrial biogenesis in epithelial cancer cells promotes breast cancer tumor growth and confers autophagy resistance
Salem A, Whitaker-Menezes D, Howell A, Sotgia F, Lisanti M
Cell Cycle 2014;11(22):4174-4180
Cell Cycle 2014;11(22):4174-4180
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
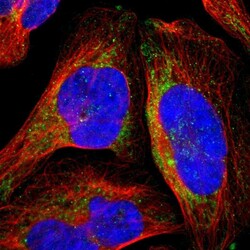
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line U-2 OS shows localization to mitochondria.
- Sample type
- Human
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry