MA1-510
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: NR3C1
GR, GRL
 Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry Gel shift
Gel shift Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [180]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [6]
- Flow cytometry [5]
- Other assay [14]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA1-510 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- MA1-510 detects glucocorticoid receptor (GR) from human, mouse, rat, guinea pig, rabbit, sheep and yeast samples. This antibody does not react with primate, avian or amphibian GR. MA1-510 has been successfully used in Western blot, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, and gel shift procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects a 97 kDa protein representing GR in L929 cell extract. Immunocytochemical staining of GR in L929 cells with MA1-510 results in staining of both the cytoplasm and nucleus, even in the presence of hormone. Using enzymatic digestion analysis, MA1-510 reacts with the undigested 97 kDa GR, a 17 kDa DNA-binding trypsin fragment, and a 45 kDa steroid- and DNA-binding chymotrypsin fragment. The MA1-510 immunogen is partially purified rat GR. Reconstitute with 100 µL distilled water.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Guinea Pig, Rabbit, Yeast
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- BuGR2
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Loss of central mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptors impacts auditory nerve processing in the cochlea.
Impaired glucocorticoid receptor expression in liver disrupts feeding-induced gene expression, glucose uptake, and glycogen storage.
Cardiomyocyte-restricted high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) deletion leads to small heart and glycolipid metabolic disorder through GR/PGC-1α signalling.
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the glucocorticoid receptor is influenced by tetratricopeptide repeat-containing proteins.
Chronic inflammatory pain alters alcohol-regulated frontocortical signaling and associations between alcohol drinking and thermal sensitivity.
Sex differences in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation after chronic unpredictable stress.
The glucocorticoid receptor interferes with progesterone receptor-dependent genomic regulation in breast cancer cells.
Developmental Lead Exposure and Prenatal Stress Result in Sex-Specific Reprograming of Adult Stress Physiology and Epigenetic Profiles in Brain.
Insulin signaling and reduced glucocorticoid receptor activity attenuate postprandial gene expression in liver.
Severe asthma in humans and mouse model suggests a CXCL10 signature underlies corticosteroid-resistant Th1 bias.
Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding Induces Rapid and Prolonged Large-Scale Chromatin Decompaction at Multiple Target Loci.
Anti-Inflammatory Chromatinscape Suggests Alternative Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Receptor Action.
Maternal Separation Induces Orofacial Mechanical Allodynia in Adulthood.
Forkhead box A3 mediates glucocorticoid receptor function in adipose tissue.
Disruption of the HPA-axis through corticosterone-release pellets induces robust depressive-like behavior and reduced BDNF levels in mice.
Development and validation of an immunohistochemistry assay to assess glucocorticoid receptor expression for clinical trials of mifepristone in breast cancer.
Effects of maternal dexamethasone treatment early in pregnancy on glucocorticoid receptors in the ovine placenta.
Dynamics of chromatin accessibility and long-range interactions in response to glucocorticoid pulsing.
Neurotrophic-priming of glucocorticoid receptor signaling is essential for neuronal plasticity to stress and antidepressant treatment.
Environmental enrichment mitigates the sex-specific effects of gestational inflammation on social engagement and the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis-feedback system.
A kinase-independent activity of Cdk9 modulates glucocorticoid receptor-mediated gene induction.
Specificity in the actions of the UBR1 ubiquitin ligase in the degradation of nuclear receptors.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling rewrites the glucocorticoid transcriptome via glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation.
Regulation of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone transcription by elevated glucocorticoids.
A conserved protein motif is required for full modulatory activity of negative elongation factor subunits NELF-A and NELF-B in modifying glucocorticoid receptor-regulated gene induction properties.
ZFP36L2 is required for self-renewal of early burst-forming unit erythroid progenitors.
PA1 protein, a new competitive decelerator acting at more than one step to impede glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transactivation.
Corticosterone modulates fear responses and the expression of glucocorticoid receptors in the brain of high-anxiety rats.
Brain region- and sex-specific modulation of mitochondrial glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in fluoxetine treated stressed rats: effects on energy metabolism.
Enhanced stimulus sequence-dependent repeated learning in male offspring after prenatal stress alone or in conjunction with lead exposure.
Identification of location and kinetically defined mechanism of cofactors and reporter genes in the cascade of steroid-regulated transactivation.
Separate regions of glucocorticoid receptor, coactivator TIF2, and comodulator STAMP modify different parameters of glucocorticoid-mediated gene induction.
Expression and regulation of human fetal-specific CYP3A7 in mice.
BDNF and glucocorticoids regulate corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) homeostasis in the hypothalamus.
Expression of human glucocorticoid receptor in T lymphocytes in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure.
Chromatin accessibility pre-determines glucocorticoid receptor binding patterns.
DNA methylation status predicts cell type-specific enhancer activity.
Interactions of lifetime lead exposure and stress: behavioral, neurochemical and HPA axis effects.
The 90-kDa heat-shock protein (Hsp90)-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is a mitochondrial protein that translocates to the nucleus to protect cells against oxidative stress.
Dynamic exchange at regulatory elements during chromatin remodeling underlies assisted loading mechanism.
Extensive chromatin remodelling and establishment of transcription factor 'hotspots' during early adipogenesis.
Subcellular rearrangement of hsp90-binding immunophilins accompanies neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth.
Suppressive effect of quercetin on acute stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response in Wistar rats.
Inhibition of hsp70 by methylene blue affects signaling protein function and ubiquitination and modulates polyglutamine protein degradation.
Hsp110 chaperones control client fate determination in the hsp70-Hsp90 chaperone system.
Association of the glucocorticoid receptor with STAT3, C/EBPbeta, and the hormone-responsive element within the rat haptoglobin gene promoter during the acute phase response.
The hsp90-FKBP52 complex links the mineralocorticoid receptor to motor proteins and persists bound to the receptor in early nuclear events.
HSD11B1, HSD11B2, PTGS2, and NR3C1 expression in the peri-implantation ovine uterus: effects of pregnancy, progesterone, and interferon tau.
Glucocorticoid-induced impairment of mammary gland involution is associated with STAT5 and STAT3 signaling modulation.
Localization of mineralocorticoid receptors at mammalian synapses.
Sexually dimorphic functional alterations of rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptor in response to fluoxetine.
Nuclear import of the glucocorticoid receptor-hsp90 complex through the nuclear pore complex is mediated by its interaction with Nup62 and importin beta.
The role of phosphorylated glucocorticoid receptor in mitochondrial functions and apoptotic signalling in brain tissue of stressed Wistar rats.
Corticosterone and related receptor expression are associated with increased beta-amyloid plaques in isolated Tg2576 mice.
Farnesylation of Ydj1 is required for in vivo interaction with Hsp90 client proteins.
Interaction and functional interference of glucocorticoid receptor and SOCS1.
Betamethasone-related acute alterations of microtubule-associated proteins in the fetal sheep brain are reversible and independent of age during the last one-third of gestation.
Amino-terminal domain of TIF2 is involved in competing for corepressor binding to glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors.
Dexamethasone treatment affects nuclear glucocorticoid receptor and glucocorticoid response element binding activity in liver of rats (Rattus norvegicus) during aging.
The dynamic pattern of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcriptional responses in neuronal PC12 cells.
The middle domain of Hsp90 acts as a discriminator between different types of client proteins.
Melatonin inhibits glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation in mouse thymocytes.
Mechanism of action of Hic-5/androgen receptor activator 55, a LIM domain-containing nuclear receptor coactivator.
Anthrax lethal toxin represses glucocorticoid receptor (GR) transactivation by inhibiting GR-DNA binding in vivo.
Interactions of chronic lead exposure and intermittent stress: consequences for brain catecholamine systems and associated behaviors and HPA axis function.
A Nuclear Receptor Atlas: macrophage activation.
TCR signaling inhibits glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in murine thymocytes depending on the stage of development.
Functional comparison of human and Drosophila Hop reveals novel role in steroid receptor maturation.
Glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain is sufficient for the modulation of glucocorticoid induction properties by homologous receptors, coactivator transcription intermediary factor 2, and Ubc9.
Mercury stimulates rat liver glucocorticoid receptor association with Hsp90 and Hsp70.
Corticosteroids but not pimecrolimus affect viability, maturation and immune function of murine epidermal Langerhans cells.
Steroid hormones induce bcl-X gene expression through direct activation of distal promoter P4.
Equilibrium interactions of corepressors and coactivators with agonist and antagonist complexes of glucocorticoid receptors.
The heat shock protein 70 cochaperone hip enhances functional maturation of glucocorticoid receptor.
The role of hsp90 in heme-dependent activation of apo-neuronal nitric-oxide synthase.
Involvement of Bax protein in the prevention of glucocorticoid-induced thymocytes apoptosis by melatonin.
Effects of three courses of maternally administered dexamethasone at 0.7, 0.75, and 0.8 of gestation on prenatal and postnatal growth in sheep.
Evidence for glucocorticoid receptor transport on microtubules by dynein.
Glucocorticoid receptor overexpression in forebrain: a mouse model of increased emotional lability.
Type II glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity in the mossy cells of the rat and the mouse hippocampus.
Glucocorticoid receptors are downregulated in hepatic T lymphocytes in rats with experimental cholangitis.
Nuclear export of the glucocorticoid receptor is accelerated by cell fusion-dependent release of calreticulin.
Visualization and mechanism of assembly of a glucocorticoid receptor.Hsp70 complex that is primed for subsequent Hsp90-dependent opening of the steroid binding cleft.
The Hsp90-binding peptidylprolyl isomerase FKBP52 potentiates glucocorticoid signaling in vivo.
CBP recruitment and histone acetylation in differential gene induction by glucocorticoids and progestins.
The hsp90 cochaperone p23 is the limiting component of the multiprotein hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone system in vivo where it acts to stabilize the client protein: hsp90 complex.
The Group 3 LIM domain protein paxillin potentiates androgen receptor transactivation in prostate cancer cell lines.
Nucleotide binding states of hsp70 and hsp90 during sequential steps in the process of glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly.
A new first step in activation of steroid receptors: hormone-induced switching of FKBP51 and FKBP52 immunophilins.
Modification of an essential amino group in the mineralocorticoid receptor evidences a differential conformational change of the receptor protein upon binding of antagonists, natural agonists and the synthetic agonist 11,19-oxidoprogesterone.
Modification of an essential amino group in the mineralocorticoid receptor evidences a differential conformational change of the receptor protein upon binding of antagonists, natural agonists and the synthetic agonist 11,19-oxidoprogesterone.
Attenuation of glucocorticoid signaling through targeted degradation of p300 via the 26S proteasome pathway.
Thymocyte apoptosis induced by T cell activation is mediated by glucocorticoids in vivo.
Decrements in nuclear glucocorticoid receptor (GR) protein levels and DNA binding in aged rat hippocampus.
All of the protein interactions that link steroid receptor.hsp90.immunophilin heterocomplexes to cytoplasmic dynein are common to plant and animal cells.
All of the protein interactions that link steroid receptor.hsp90.immunophilin heterocomplexes to cytoplasmic dynein are common to plant and animal cells.
Differential interactions of specific nuclear factor I isoforms with the glucocorticoid receptor and STAT5 in the cooperative regulation of WAP gene transcription.
High neonatal leptin exposure enhances brain GR expression and feedback efficacy on the adrenocortical axis of developing rats.
Physical interaction and functional synergy between glucocorticoid receptor and Ets2 proteins for transcription activation of the rat cytochrome P-450c27 promoter.
Heterodimerization between the glucocorticoid receptor and the unrelated DNA-binding protein, Xenopus glucocorticoid receptor accessory factor.
Hormone-induced nucleosome positioning in the MMTV promoter is reversible.
Interleukin-2 inhibits glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity through a mechanism involving STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5) but not AP-1.
Glucocorticoid receptor homodimers and glucocorticoid-mineralocorticoid receptor heterodimers form in the cytoplasm through alternative dimerization interfaces.
Cooperative effects of STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5) and C/EBPbeta (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta) on beta-casein gene transcription are mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor.
Activation and autoregulation of DNA-PK from structured single-stranded DNA and coding end hairpins.
Stoichiometry, abundance, and functional significance of the hsp90/hsp70-based multiprotein chaperone machinery in reticulocyte lysate.
hsp70 interacting protein Hip does not affect glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery except to oppose the effect of BAG-1.
hsp70 interacting protein Hip does not affect glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery except to oppose the effect of BAG-1.
A role for the Hsp40 Ydj1 in repression of basal steroid receptor activity in yeast.
The Hsp organizer protein hop enhances the rate of but is not essential for glucocorticoid receptor folding by the multiprotein Hsp90-based chaperone system.
The Hsp organizer protein hop enhances the rate of but is not essential for glucocorticoid receptor folding by the multiprotein Hsp90-based chaperone system.
The molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Hsc70 are both necessary and sufficient to activate hormone binding by glucocorticoid receptor.
Defense of adrenocorticosteroid receptor expression in rat hippocampus: effects of stress and strain.
Early maturation of T-cell progenitors in the absence of glucocorticoids.
Differential effects of the hsp70-binding protein BAG-1 on glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery.
Differential effects of the hsp70-binding protein BAG-1 on glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery.
Regulation of growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression by glucocorticoids in MtT-S cells and in the pituitary gland of fetal rats.
Inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor nucleocytoplasmic shuttling by okadaic acid requires intact cytoskeleton.
The glucocorticoid receptor is tethered to DNA-bound Oct-1 at the mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone distal negative glucocorticoid response element.
Neuronal nitric-oxide synthase is regulated by the Hsp90-based chaperone system in vivo.
Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor.
Glucocorticoid resistance in the squirrel monkey is associated with overexpression of the immunophilin FKBP51.
Discrimination between NL1- and NL2-mediated nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor.
Glucocorticoid receptor/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) interactions enhance STAT5 activation by prolonging STAT5 DNA binding and tyrosine phosphorylation.
Glucocorticoids downregulate cyclooxygenase-1 gene expression and prostacyclin synthesis in fetal pulmonary artery endothelium.
The seven amino acids (547-553) of rat glucocorticoid receptor required for steroid and hsp90 binding contain a functionally independent LXXLL motif that is critical for steroid binding.
Glucocorticoids stimulate the accumulation of lipids in the rat corpus luteum.
Glucocorticoid-mediated regulation of thymic dendritic cell function.
The DNA-binding and tau2 transactivation domains of the rat glucocorticoid receptor constitute a nuclear matrix-targeting signal.
Regulation of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor gene transcription and protein expression in vivo.
Analysis of FKBP51/FKBP52 chimeras and mutants for Hsp90 binding and association with progesterone receptor complexes.
The role of DnaJ-like proteins in glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly by the reconstituted hsp90.p60.hsp70 foldosome complex.
The role of DnaJ-like proteins in glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly by the reconstituted hsp90.p60.hsp70 foldosome complex.
A conserved proline in the hsp90 binding region of the glucocorticoid receptor is required for hsp90 heterocomplex stabilization and receptor signaling.
GRIP1, a transcriptional coactivator for the AF-2 transactivation domain of steroid, thyroid, retinoid, and vitamin D receptors.
GRIP1, a transcriptional coactivator for the AF-2 transactivation domain of steroid, thyroid, retinoid, and vitamin D receptors.
Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the reconstituted Hsp90-based chaperone machinery. The initial hsp90.p60.hsp70-dependent step is sufficient for creating the steroid binding conformation.
Protein phosphatase 5 is a major component of glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 complexes with properties of an FK506-binding immunophilin.
In vivo analysis of the Hsp90 cochaperone Sti1 (p60).
In vivo analysis of the Hsp90 cochaperone Sti1 (p60).
Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the heat shock protein (hsp) 90-based chaperone machinery. The role of p23 is to stabilize receptor.hsp90 heterocomplexes formed by hsp90.p60.hsp70.
Determinants of subcellular distribution of the glucocorticoid receptor.
Reconstitution of the steroid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly system of rabbit reticulocyte lysate.
Reconstitution of the steroid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly system of rabbit reticulocyte lysate.
Dexamethasone responsiveness of a major glucocorticoid-inducible CYP3A gene is mediated by elements unrelated to a glucocorticoid receptor binding motif.
The tetratricopeptide repeat domain of protein phosphatase 5 mediates binding to glucocorticoid receptor heterocomplexes and acts as a dominant negative mutant.
Use of the thiol-specific derivatizing agent N-iodoacetyl-3-[125I]iodotyrosine to demonstrate conformational differences between the unbound and hsp90-bound glucocorticoid receptor hormone binding domain.
The cyclosporin A-binding immunophilin CyP-40 and the FK506-binding immunophilin hsp56 bind to a common site on hsp90 and exist in independent cytosolic heterocomplexes with the untransformed glucocorticoid receptor.
The cyclosporin A-binding immunophilin CyP-40 and the FK506-binding immunophilin hsp56 bind to a common site on hsp90 and exist in independent cytosolic heterocomplexes with the untransformed glucocorticoid receptor.
Zinc ions antagonize the inhibitory effect of aurothiomalate on glucocorticoid receptor function at physiological concentrations.
Cyclosporin A potentiates the dexamethasone-induced mouse mammary tumor virus-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity in LMCAT cells: a possible role for different heat shock protein-binding immunophilins in glucocorticosteroid receptor-mediated gene expression.
Effect of stress on cochlear glucocorticoid protein: acoustic stress.
Effect of stress on cochlear glucocorticoid protein. II. Restraint.
The 23-kDa acidic protein in reticulocyte lysate is the weakly bound component of the hsp foldosome that is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a functional heterocomplex with hsp90.
BCL-2 expression and mitochondrial activity in leukemic cells with different sensitivity to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis.
High levels of non-activated receptors in glucocorticoid-sensitive S49wt mouse lymphoma cells incubated with dexamethasone.
Conservation of Hsp90 macromolecular complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Metal oxyanion stabilization of the rat glucocorticoid receptor is independent of thiols.
All of the factors required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a functional heterocomplex with heat shock protein 90 are preassociated in a self-sufficient protein folding structure, a "foldosome".
Absence of intramolecular disulfides in the structure and function of native rat glucocorticoid receptors.
Proof that hsp70 is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a heterocomplex with hsp90.
A functional glucocorticoid-responsive unit composed of two overlapping inactive receptor-binding sites: evidence for formation of a receptor tetramer.
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptors interact with insulin degrading enzyme.
Characterization of the protein-protein interactions determining the heat shock protein (hsp90.hsp70.hsp56) heterocomplex.
Raf exists in a native heterocomplex with hsp90 and p50 that can be reconstituted in a cell-free system.
Inhibition of mouse GATA-1 function by the glucocorticoid receptor: possible mechanism of steroid inhibition of erythroleukemia cell differentiation.
Comparison of the 90-kilodalton heat shock protein interaction with in vitro translated glucocorticoid and estrogen receptors.
Reconstitution of the multiprotein complex of pp60src, hsp90, and p50 in a cell-free system.
Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors.
Direct stoichiometric evidence that the untransformed Mr 300,000, 9S, glucocorticoid receptor is a core unit derived from a larger heteromeric complex.
Phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptor-associated and free forms of the approximately 90-kDa heat shock protein before and after receptor activation.
The glucocorticoid antagonist 17 alpha-methyltestosterone binds to the 10 S glucocorticoid receptor and blocks agonist-mediated dissociation of the 10 S oligomer to the 4 S deoxyribonucleic acid-binding subunit.
Kinetic pulse-chase labeling study of the glucocorticoid receptor in mouse lymphoma cells. Effect of glucocorticoid and antiglucocorticoid hormones on intracellular receptor half-life.
Relationship between glucocorticoid receptor steroid-binding capacity and association of the Mr 90,000 heat shock protein with the unliganded receptor.
Isolation of ribonucleic acid from the unactivated rat liver glucocorticoid receptor.
Immunocytochemical localization of glucocorticoid receptors in cells, cytoplasts, and nucleoplasts.
Evidence for intracellular association of the glucocorticoid receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein.
Analysis of the disruptive action of an epididymal protease and the stabilizing influence of molybdate on nondenatured and denatured glucocorticoid receptor.
Immunochemical comparison of mutant glucocorticoid receptors and wild type receptor fragments produced by neutrophil elastase and chymotrypsin.
Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor.
Marchetta P, Eckert P, Lukowski R, Ruth P, Singer W, Rüttiger L, Knipper M
iScience 2022 Mar 18;25(3):103981
iScience 2022 Mar 18;25(3):103981
Impaired glucocorticoid receptor expression in liver disrupts feeding-induced gene expression, glucose uptake, and glycogen storage.
Præstholm SM, Correia CM, Goitea VE, Siersbæk MS, Jørgensen M, Havelund JF, Pedersen TÅ, Færgeman NJ, Grøntved L
Cell reports 2021 Nov 2;37(5):109938
Cell reports 2021 Nov 2;37(5):109938
Cardiomyocyte-restricted high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) deletion leads to small heart and glycolipid metabolic disorder through GR/PGC-1α signalling.
Yu P, Liu M, Zhang B, Yu Y, Su E, Xie S, Zhang L, Yang X, Jiang H, Chen R, Zou Y, Ge J
Cell death discovery 2020;6:106
Cell death discovery 2020;6:106
Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the glucocorticoid receptor is influenced by tetratricopeptide repeat-containing proteins.
Mazaira GI, Echeverria PC, Galigniana MD
Journal of cell science 2020 Jun 16;133(12)
Journal of cell science 2020 Jun 16;133(12)
Chronic inflammatory pain alters alcohol-regulated frontocortical signaling and associations between alcohol drinking and thermal sensitivity.
Adrienne McGinn M, Edwards KN, Edwards S
Neurobiology of pain (Cambridge, Mass.) 2020 Aug-Dec;8:100052
Neurobiology of pain (Cambridge, Mass.) 2020 Aug-Dec;8:100052
Sex differences in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation after chronic unpredictable stress.
Palumbo MC, Dominguez S, Dong H
Brain and behavior 2020 Apr;10(4):e01586
Brain and behavior 2020 Apr;10(4):e01586
The glucocorticoid receptor interferes with progesterone receptor-dependent genomic regulation in breast cancer cells.
Ogara MF, Rodríguez-Seguí SA, Marini M, Nacht AS, Stortz M, Levi V, Presman DM, Vicent GP, Pecci A
Nucleic acids research 2019 Nov 18;47(20):10645-10661
Nucleic acids research 2019 Nov 18;47(20):10645-10661
Developmental Lead Exposure and Prenatal Stress Result in Sex-Specific Reprograming of Adult Stress Physiology and Epigenetic Profiles in Brain.
Sobolewski M, Varma G, Adams B, Anderson DW, Schneider JS, Cory-Slechta DA
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2018 Jun 1;163(2):478-489
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2018 Jun 1;163(2):478-489
Insulin signaling and reduced glucocorticoid receptor activity attenuate postprandial gene expression in liver.
Kalvisa A, Siersbæk MS, Præstholm SM, Christensen LJL, Nielsen R, Stohr O, Vettorazzi S, Tuckermann J, White M, Mandrup S, Grøntved L
PLoS biology 2018 Dec;16(12):e2006249
PLoS biology 2018 Dec;16(12):e2006249
Severe asthma in humans and mouse model suggests a CXCL10 signature underlies corticosteroid-resistant Th1 bias.
Gauthier M, Chakraborty K, Oriss TB, Raundhal M, Das S, Chen J, Huff R, Sinha A, Fajt M, Ray P, Wenzel SE, Ray A
JCI insight 2017 Jul 6;2(13)
JCI insight 2017 Jul 6;2(13)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding Induces Rapid and Prolonged Large-Scale Chromatin Decompaction at Multiple Target Loci.
Jubb AW, Boyle S, Hume DA, Bickmore WA
Cell reports 2017 Dec 12;21(11):3022-3031
Cell reports 2017 Dec 12;21(11):3022-3031
Anti-Inflammatory Chromatinscape Suggests Alternative Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Receptor Action.
Oh KS, Patel H, Gottschalk RA, Lee WS, Baek S, Fraser IDC, Hager GL, Sung MH
Immunity 2017 Aug 15;47(2):298-309.e5
Immunity 2017 Aug 15;47(2):298-309.e5
Maternal Separation Induces Orofacial Mechanical Allodynia in Adulthood.
Yasuda M, Shinoda M, Honda K, Fujita M, Kawata A, Nagashima H, Watanabe M, Shoji N, Takahashi O, Kimoto S, Iwata K
Journal of dental research 2016 Sep;95(10):1191-7
Journal of dental research 2016 Sep;95(10):1191-7
Forkhead box A3 mediates glucocorticoid receptor function in adipose tissue.
Ma X, Xu L, Mueller E
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Mar 22;113(12):3377-82
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Mar 22;113(12):3377-82
Disruption of the HPA-axis through corticosterone-release pellets induces robust depressive-like behavior and reduced BDNF levels in mice.
Demuyser T, Bentea E, Deneyer L, Albertini G, Massie A, Smolders I
Neuroscience letters 2016 Jul 28;626:119-25
Neuroscience letters 2016 Jul 28;626:119-25
Development and validation of an immunohistochemistry assay to assess glucocorticoid receptor expression for clinical trials of mifepristone in breast cancer.
Baker GM, Murphy T, Block T, Nguyen D, Lynch FJ
Cancer management and research 2015;7:361-8
Cancer management and research 2015;7:361-8
Effects of maternal dexamethasone treatment early in pregnancy on glucocorticoid receptors in the ovine placenta.
Shang H, Meng W, Sloboda DM, Li S, Ehrlich L, Plagemann A, Dudenhausen JW, Henrich W, Newnham JP, Challis JR, Braun T
Reproductive sciences (Thousand Oaks, Calif.) 2015 May;22(5):534-44
Reproductive sciences (Thousand Oaks, Calif.) 2015 May;22(5):534-44
Dynamics of chromatin accessibility and long-range interactions in response to glucocorticoid pulsing.
Stavreva DA, Coulon A, Baek S, Sung MH, John S, Stixova L, Tesikova M, Hakim O, Miranda T, Hawkins M, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Chow CC, Hager GL
Genome research 2015 Jun;25(6):845-57
Genome research 2015 Jun;25(6):845-57
Neurotrophic-priming of glucocorticoid receptor signaling is essential for neuronal plasticity to stress and antidepressant treatment.
Arango-Lievano M, Lambert WM, Bath KG, Garabedian MJ, Chao MV, Jeanneteau F
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2015 Dec 22;112(51):15737-42
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2015 Dec 22;112(51):15737-42
Environmental enrichment mitigates the sex-specific effects of gestational inflammation on social engagement and the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis-feedback system.
Connors EJ, Shaik AN, Migliore MM, Kentner AC
Brain, behavior, and immunity 2014 Nov;42:178-90
Brain, behavior, and immunity 2014 Nov;42:178-90
A kinase-independent activity of Cdk9 modulates glucocorticoid receptor-mediated gene induction.
Zhu R, Lu X, Pradhan M, Armstrong SP, Storchan GB, Chow CC, Simons SS Jr
Biochemistry 2014 Mar 25;53(11):1753-67
Biochemistry 2014 Mar 25;53(11):1753-67
Specificity in the actions of the UBR1 ubiquitin ligase in the degradation of nuclear receptors.
Sultana R, Theodoraki MA, Caplan AJ
FEBS open bio 2013;3:394-7
FEBS open bio 2013;3:394-7
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling rewrites the glucocorticoid transcriptome via glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation.
Lambert WM, Xu CF, Neubert TA, Chao MV, Garabedian MJ, Jeanneteau FD
Molecular and cellular biology 2013 Sep;33(18):3700-14
Molecular and cellular biology 2013 Sep;33(18):3700-14
Regulation of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone transcription by elevated glucocorticoids.
Evans AN, Liu Y, Macgregor R, Huang V, Aguilera G
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2013 Nov;27(11):1796-807
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2013 Nov;27(11):1796-807
A conserved protein motif is required for full modulatory activity of negative elongation factor subunits NELF-A and NELF-B in modifying glucocorticoid receptor-regulated gene induction properties.
Luo M, Lu X, Zhu R, Zhang Z, Chow CC, Li R, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Nov 22;288(47):34055-72
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Nov 22;288(47):34055-72
ZFP36L2 is required for self-renewal of early burst-forming unit erythroid progenitors.
Zhang L, Prak L, Rayon-Estrada V, Thiru P, Flygare J, Lim B, Lodish HF
Nature 2013 Jul 4;499(7456):92-6
Nature 2013 Jul 4;499(7456):92-6
PA1 protein, a new competitive decelerator acting at more than one step to impede glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transactivation.
Zhang Z, Sun Y, Cho YW, Chow CC, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Jan 4;288(1):42-58
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Jan 4;288(1):42-58
Corticosterone modulates fear responses and the expression of glucocorticoid receptors in the brain of high-anxiety rats.
Wisłowska-Stanek A, Lehner M, Skórzewska A, Maciejak P, Szyndler J, Turzyńska D, Sobolewska A, Płaźnik A
Neuroscience letters 2013 Jan 15;533:17-22
Neuroscience letters 2013 Jan 15;533:17-22
Brain region- and sex-specific modulation of mitochondrial glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation in fluoxetine treated stressed rats: effects on energy metabolism.
Adzic M, Lukic I, Mitic M, Djordjevic J, Elaković I, Djordjevic A, Krstic-Demonacos M, Matić G, Radojcic M
Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013 Dec;38(12):2914-24
Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013 Dec;38(12):2914-24
Enhanced stimulus sequence-dependent repeated learning in male offspring after prenatal stress alone or in conjunction with lead exposure.
Cory-Slechta DA, Virgolini MB, Liu S, Weston D
Neurotoxicology 2012 Oct;33(5):1188-202
Neurotoxicology 2012 Oct;33(5):1188-202
Identification of location and kinetically defined mechanism of cofactors and reporter genes in the cascade of steroid-regulated transactivation.
Blackford JA Jr, Guo C, Zhu R, Dougherty EJ, Chow CC, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Nov 30;287(49):40982-95
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Nov 30;287(49):40982-95
Separate regions of glucocorticoid receptor, coactivator TIF2, and comodulator STAMP modify different parameters of glucocorticoid-mediated gene induction.
Awasthi S, Simons SS Jr
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2012 May 15;355(1):121-34
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2012 May 15;355(1):121-34
Expression and regulation of human fetal-specific CYP3A7 in mice.
Pang XY, Cheng J, Kim JH, Matsubara T, Krausz KW, Gonzalez FJ
Endocrinology 2012 Mar;153(3):1453-63
Endocrinology 2012 Mar;153(3):1453-63
BDNF and glucocorticoids regulate corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) homeostasis in the hypothalamus.
Jeanneteau FD, Lambert WM, Ismaili N, Bath KG, Lee FS, Garabedian MJ, Chao MV
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012 Jan 24;109(4):1305-10
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012 Jan 24;109(4):1305-10
Expression of human glucocorticoid receptor in T lymphocytes in acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure.
Gao L, Wang JF, Xiang M, Fan YC, Zhang ZG, Wang K
Digestive diseases and sciences 2011 Sep;56(9):2605-12
Digestive diseases and sciences 2011 Sep;56(9):2605-12
Chromatin accessibility pre-determines glucocorticoid receptor binding patterns.
John S, Sabo PJ, Thurman RE, Sung MH, Biddie SC, Johnson TA, Hager GL, Stamatoyannopoulos JA
Nature genetics 2011 Mar;43(3):264-8
Nature genetics 2011 Mar;43(3):264-8
DNA methylation status predicts cell type-specific enhancer activity.
Wiench M, John S, Baek S, Johnson TA, Sung MH, Escobar T, Simmons CA, Pearce KH, Biddie SC, Sabo PJ, Thurman RE, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Hager GL
The EMBO journal 2011 Jun 24;30(15):3028-39
The EMBO journal 2011 Jun 24;30(15):3028-39
Interactions of lifetime lead exposure and stress: behavioral, neurochemical and HPA axis effects.
Rossi-George A, Virgolini MB, Weston D, Thiruchelvam M, Cory-Slechta DA
Neurotoxicology 2011 Jan;32(1):83-99
Neurotoxicology 2011 Jan;32(1):83-99
The 90-kDa heat-shock protein (Hsp90)-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is a mitochondrial protein that translocates to the nucleus to protect cells against oxidative stress.
Gallo LI, Lagadari M, Piwien-Pilipuk G, Galigniana MD
The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 Aug 26;286(34):30152-60
The Journal of biological chemistry 2011 Aug 26;286(34):30152-60
Dynamic exchange at regulatory elements during chromatin remodeling underlies assisted loading mechanism.
Voss TC, Schiltz RL, Sung MH, Yen PM, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Biddie SC, Johnson TA, Miranda TB, John S, Hager GL
Cell 2011 Aug 19;146(4):544-54
Cell 2011 Aug 19;146(4):544-54
Extensive chromatin remodelling and establishment of transcription factor 'hotspots' during early adipogenesis.
Siersbæk R, Nielsen R, John S, Sung MH, Baek S, Loft A, Hager GL, Mandrup S
The EMBO journal 2011 Apr 20;30(8):1459-72
The EMBO journal 2011 Apr 20;30(8):1459-72
Subcellular rearrangement of hsp90-binding immunophilins accompanies neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth.
Quintá HR, Maschi D, Gomez-Sanchez C, Piwien-Pilipuk G, Galigniana MD
Journal of neurochemistry 2010 Nov;115(3):716-34
Journal of neurochemistry 2010 Nov;115(3):716-34
Suppressive effect of quercetin on acute stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response in Wistar rats.
Kawabata K, Kawai Y, Terao J
The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2010 May;21(5):374-80
The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2010 May;21(5):374-80
Inhibition of hsp70 by methylene blue affects signaling protein function and ubiquitination and modulates polyglutamine protein degradation.
Wang AM, Morishima Y, Clapp KM, Peng HM, Pratt WB, Gestwicki JE, Osawa Y, Lieberman AP
The Journal of biological chemistry 2010 May 21;285(21):15714-23
The Journal of biological chemistry 2010 May 21;285(21):15714-23
Hsp110 chaperones control client fate determination in the hsp70-Hsp90 chaperone system.
Mandal AK, Gibney PA, Nillegoda NB, Theodoraki MA, Caplan AJ, Morano KA
Molecular biology of the cell 2010 May 1;21(9):1439-48
Molecular biology of the cell 2010 May 1;21(9):1439-48
Association of the glucocorticoid receptor with STAT3, C/EBPbeta, and the hormone-responsive element within the rat haptoglobin gene promoter during the acute phase response.
Arambasić J, Poznanović G, Ivanović-Matić S, Bogojević D, Mihailović M, Uskoković A, Grigorov I
IUBMB life 2010 Mar;62(3):227-36
IUBMB life 2010 Mar;62(3):227-36
The hsp90-FKBP52 complex links the mineralocorticoid receptor to motor proteins and persists bound to the receptor in early nuclear events.
Galigniana MD, Erlejman AG, Monte M, Gomez-Sanchez C, Piwien-Pilipuk G
Molecular and cellular biology 2010 Mar;30(5):1285-98
Molecular and cellular biology 2010 Mar;30(5):1285-98
HSD11B1, HSD11B2, PTGS2, and NR3C1 expression in the peri-implantation ovine uterus: effects of pregnancy, progesterone, and interferon tau.
Simmons RM, Satterfield MC, Welsh TH Jr, Bazer FW, Spencer TE
Biology of reproduction 2010 Jan;82(1):35-43
Biology of reproduction 2010 Jan;82(1):35-43
Glucocorticoid-induced impairment of mammary gland involution is associated with STAT5 and STAT3 signaling modulation.
Bertucci PY, Quaglino A, Pozzi AG, Kordon EC, Pecci A
Endocrinology 2010 Dec;151(12):5730-40
Endocrinology 2010 Dec;151(12):5730-40
Localization of mineralocorticoid receptors at mammalian synapses.
Prager EM, Brielmaier J, Bergstrom HC, McGuire J, Johnson LR
PloS one 2010 Dec 15;5(12):e14344
PloS one 2010 Dec 15;5(12):e14344
Sexually dimorphic functional alterations of rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptor in response to fluoxetine.
Elaković I, Vasiljević D, Adzic M, Djordjevic A, Djordjevic J, Radojcić M, Matić G
European journal of pharmacology 2010 Apr 25;632(1-3):79-85
European journal of pharmacology 2010 Apr 25;632(1-3):79-85
Nuclear import of the glucocorticoid receptor-hsp90 complex through the nuclear pore complex is mediated by its interaction with Nup62 and importin beta.
Echeverría PC, Mazaira G, Erlejman A, Gomez-Sanchez C, Piwien Pilipuk G, Galigniana MD
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Sep;29(17):4788-97
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Sep;29(17):4788-97
The role of phosphorylated glucocorticoid receptor in mitochondrial functions and apoptotic signalling in brain tissue of stressed Wistar rats.
Adzic M, Djordjevic A, Demonacos C, Krstic-Demonacos M, Radojcic MB
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2009 Nov;41(11):2181-8
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2009 Nov;41(11):2181-8
Corticosterone and related receptor expression are associated with increased beta-amyloid plaques in isolated Tg2576 mice.
Dong H, Yuede CM, Yoo HS, Martin MV, Deal C, Mace AG, Csernansky JG
Neuroscience 2008 Jul 31;155(1):154-63
Neuroscience 2008 Jul 31;155(1):154-63
Farnesylation of Ydj1 is required for in vivo interaction with Hsp90 client proteins.
Flom GA, Lemieszek M, Fortunato EA, Johnson JL
Molecular biology of the cell 2008 Dec;19(12):5249-58
Molecular biology of the cell 2008 Dec;19(12):5249-58
Interaction and functional interference of glucocorticoid receptor and SOCS1.
Haffner MC, Jurgeit A, Berlato C, Geley S, Parajuli N, Yoshimura A, Doppler W
The Journal of biological chemistry 2008 Aug 8;283(32):22089-96
The Journal of biological chemistry 2008 Aug 8;283(32):22089-96
Betamethasone-related acute alterations of microtubule-associated proteins in the fetal sheep brain are reversible and independent of age during the last one-third of gestation.
Antonow-Schlorke I, Müller T, Brodhun M, Wicher C, Schubert H, Nathanielsz PW, Witte OW, Schwab M
American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 2007 Jun;196(6):553.e1-6
American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 2007 Jun;196(6):553.e1-6
Amino-terminal domain of TIF2 is involved in competing for corepressor binding to glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors.
Wang D, Wang Q, Awasthi S, Simons SS Jr
Biochemistry 2007 Jul 10;46(27):8036-49
Biochemistry 2007 Jul 10;46(27):8036-49
Dexamethasone treatment affects nuclear glucocorticoid receptor and glucocorticoid response element binding activity in liver of rats (Rattus norvegicus) during aging.
Vujcić MT, Velicković N, Ruzdijić S
Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & molecular biology 2007 Dec;148(4):463-9
Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & molecular biology 2007 Dec;148(4):463-9
The dynamic pattern of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcriptional responses in neuronal PC12 cells.
Morsink MC, Joëls M, Sarabdjitsingh RA, Meijer OC, De Kloet ER, Datson NA
Journal of neurochemistry 2006 Nov;99(4):1282-98
Journal of neurochemistry 2006 Nov;99(4):1282-98
The middle domain of Hsp90 acts as a discriminator between different types of client proteins.
Hawle P, Siepmann M, Harst A, Siderius M, Reusch HP, Obermann WM
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Nov;26(22):8385-95
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Nov;26(22):8385-95
Melatonin inhibits glucocorticoid receptor nuclear translocation in mouse thymocytes.
Presman DM, Hoijman E, Ceballos NR, Galigniana MD, Pecci A
Endocrinology 2006 Nov;147(11):5452-9
Endocrinology 2006 Nov;147(11):5452-9
Mechanism of action of Hic-5/androgen receptor activator 55, a LIM domain-containing nuclear receptor coactivator.
Heitzer MD, DeFranco DB
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2006 Jan;20(1):56-64
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2006 Jan;20(1):56-64
Anthrax lethal toxin represses glucocorticoid receptor (GR) transactivation by inhibiting GR-DNA binding in vivo.
Webster JI, Sternberg EM
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2005 Sep 28;241(1-2):21-31
Molecular and cellular endocrinology 2005 Sep 28;241(1-2):21-31
Interactions of chronic lead exposure and intermittent stress: consequences for brain catecholamine systems and associated behaviors and HPA axis function.
Virgolini MB, Chen K, Weston DD, Bauter MR, Cory-Slechta DA
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2005 Oct;87(2):469-82
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2005 Oct;87(2):469-82
A Nuclear Receptor Atlas: macrophage activation.
Barish GD, Downes M, Alaynick WA, Yu RT, Ocampo CB, Bookout AL, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Oct;19(10):2466-77
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Oct;19(10):2466-77
TCR signaling inhibits glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in murine thymocytes depending on the stage of development.
Erlacher M, Knoflach M, Stec IE, Böck G, Wick G, Wiegers GJ
European journal of immunology 2005 Nov;35(11):3287-96
European journal of immunology 2005 Nov;35(11):3287-96
Functional comparison of human and Drosophila Hop reveals novel role in steroid receptor maturation.
Carrigan PE, Riggs DL, Chinkers M, Smith DF
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Mar 11;280(10):8906-11
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Mar 11;280(10):8906-11
Glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain is sufficient for the modulation of glucocorticoid induction properties by homologous receptors, coactivator transcription intermediary factor 2, and Ubc9.
Cho S, Kagan BL, Blackford JA Jr, Szapary D, Simons SS Jr
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Feb;19(2):290-311
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2005 Feb;19(2):290-311
Mercury stimulates rat liver glucocorticoid receptor association with Hsp90 and Hsp70.
Brkljacić J, Milutinović DV, Dundjerski J, Matić G
Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology 2004;18(5):257-60
Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology 2004;18(5):257-60
Corticosteroids but not pimecrolimus affect viability, maturation and immune function of murine epidermal Langerhans cells.
Hoetzenecker W, Meingassner JG, Ecker R, Stingl G, Stuetz A, Elbe-Bürger A
The Journal of investigative dermatology 2004 Mar;122(3):673-84
The Journal of investigative dermatology 2004 Mar;122(3):673-84
Steroid hormones induce bcl-X gene expression through direct activation of distal promoter P4.
Viegas LR, Vicent GP, Barañao JL, Beato M, Pecci A
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Mar 12;279(11):9831-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Mar 12;279(11):9831-9
Equilibrium interactions of corepressors and coactivators with agonist and antagonist complexes of glucocorticoid receptors.
Wang Q, Blackford JA Jr, Song LN, Huang Y, Cho S, Simons SS Jr
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Jun;18(6):1376-95
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Jun;18(6):1376-95
The heat shock protein 70 cochaperone hip enhances functional maturation of glucocorticoid receptor.
Nelson GM, Prapapanich V, Carrigan PE, Roberts PJ, Riggs DL, Smith DF
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Jul;18(7):1620-30
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Jul;18(7):1620-30
The role of hsp90 in heme-dependent activation of apo-neuronal nitric-oxide synthase.
Billecke SS, Draganov DI, Morishima Y, Murphy PJ, Dunbar AY, Pratt WB, Osawa Y
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jul 16;279(29):30252-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jul 16;279(29):30252-8
Involvement of Bax protein in the prevention of glucocorticoid-induced thymocytes apoptosis by melatonin.
Hoijman E, Rocha Viegas L, Keller Sarmiento MI, Rosenstein RE, Pecci A
Endocrinology 2004 Jan;145(1):418-25
Endocrinology 2004 Jan;145(1):418-25
Effects of three courses of maternally administered dexamethasone at 0.7, 0.75, and 0.8 of gestation on prenatal and postnatal growth in sheep.
Kutzler MA, Ruane EK, Coksaygan T, Vincent SE, Nathanielsz PW
Pediatrics 2004 Feb;113(2):313-9
Pediatrics 2004 Feb;113(2):313-9
Evidence for glucocorticoid receptor transport on microtubules by dynein.
Harrell JM, Murphy PJ, Morishima Y, Chen H, Mansfield JF, Galigniana MD, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54647-54
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54647-54
Glucocorticoid receptor overexpression in forebrain: a mouse model of increased emotional lability.
Wei Q, Lu XY, Liu L, Schafer G, Shieh KR, Burke S, Robinson TE, Watson SJ, Seasholtz AF, Akil H
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2004 Aug 10;101(32):11851-6
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2004 Aug 10;101(32):11851-6
Type II glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity in the mossy cells of the rat and the mouse hippocampus.
Patel A, Bulloch K
Hippocampus 2003;13(1):59-66
Hippocampus 2003;13(1):59-66
Glucocorticoid receptors are downregulated in hepatic T lymphocytes in rats with experimental cholangitis.
Tjandra K, Le T, Swain MG
Gut 2003 Sep;52(9):1363-70
Gut 2003 Sep;52(9):1363-70
Nuclear export of the glucocorticoid receptor is accelerated by cell fusion-dependent release of calreticulin.
Walther RF, Lamprecht C, Ridsdale A, Groulx I, Lee S, Lefebvre YA, Haché RJ
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 26;278(39):37858-64
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 26;278(39):37858-64
Visualization and mechanism of assembly of a glucocorticoid receptor.Hsp70 complex that is primed for subsequent Hsp90-dependent opening of the steroid binding cleft.
Murphy PJ, Morishima Y, Chen H, Galigniana MD, Mansfield JF, Simons SS Jr, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 12;278(37):34764-73
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Sep 12;278(37):34764-73
The Hsp90-binding peptidylprolyl isomerase FKBP52 potentiates glucocorticoid signaling in vivo.
Riggs DL, Roberts PJ, Chirillo SC, Cheung-Flynn J, Prapapanich V, Ratajczak T, Gaber R, Picard D, Smith DF
The EMBO journal 2003 Mar 3;22(5):1158-67
The EMBO journal 2003 Mar 3;22(5):1158-67
CBP recruitment and histone acetylation in differential gene induction by glucocorticoids and progestins.
Lambert JR, Nordeen SK
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2003 Jun;17(6):1085-94
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2003 Jun;17(6):1085-94
The hsp90 cochaperone p23 is the limiting component of the multiprotein hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone system in vivo where it acts to stabilize the client protein: hsp90 complex.
Morishima Y, Kanelakis KC, Murphy PJ, Lowe ER, Jenkins GJ, Osawa Y, Sunahara RK, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 5;278(49):48754-63
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 5;278(49):48754-63
The Group 3 LIM domain protein paxillin potentiates androgen receptor transactivation in prostate cancer cell lines.
Kasai M, Guerrero-Santoro J, Friedman R, Leman ES, Getzenberg RH, DeFranco DB
Cancer research 2003 Aug 15;63(16):4927-35
Cancer research 2003 Aug 15;63(16):4927-35
Nucleotide binding states of hsp70 and hsp90 during sequential steps in the process of glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly.
Kanelakis KC, Shewach DS, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Sep 13;277(37):33698-703
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Sep 13;277(37):33698-703
A new first step in activation of steroid receptors: hormone-induced switching of FKBP51 and FKBP52 immunophilins.
Davies TH, Ning YM, Sánchez ER
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4597-600
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4597-600
Modification of an essential amino group in the mineralocorticoid receptor evidences a differential conformational change of the receptor protein upon binding of antagonists, natural agonists and the synthetic agonist 11,19-oxidoprogesterone.
Piwien-Pilipuk G, Kanelakis KC, Ghini AA, Lantos CP, Litwack G, Burton G, Galigniana MD
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2002 Feb 13;1589(1):31-48
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2002 Feb 13;1589(1):31-48
Modification of an essential amino group in the mineralocorticoid receptor evidences a differential conformational change of the receptor protein upon binding of antagonists, natural agonists and the synthetic agonist 11,19-oxidoprogesterone.
Piwien-Pilipuk G, Kanelakis KC, Ghini AA, Lantos CP, Litwack G, Burton G, Galigniana MD
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2002 Feb 13;1589(1):31-48
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2002 Feb 13;1589(1):31-48
Attenuation of glucocorticoid signaling through targeted degradation of p300 via the 26S proteasome pathway.
Li Q, Su A, Chen J, Lefebvre YA, Haché RJ
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Dec;16(12):2819-27
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2002 Dec;16(12):2819-27
Thymocyte apoptosis induced by T cell activation is mediated by glucocorticoids in vivo.
Brewer JA, Kanagawa O, Sleckman BP, Muglia LJ
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2002 Aug 15;169(4):1837-43
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2002 Aug 15;169(4):1837-43
Decrements in nuclear glucocorticoid receptor (GR) protein levels and DNA binding in aged rat hippocampus.
Murphy EK, Spencer RL, Sipe KJ, Herman JP
Endocrinology 2002 Apr;143(4):1362-70
Endocrinology 2002 Apr;143(4):1362-70
All of the protein interactions that link steroid receptor.hsp90.immunophilin heterocomplexes to cytoplasmic dynein are common to plant and animal cells.
Harrell JM, Kurek I, Breiman A, Radanyi C, Renoir JM, Pratt WB, Galigniana MD
Biochemistry 2002 Apr 30;41(17):5581-7
Biochemistry 2002 Apr 30;41(17):5581-7
All of the protein interactions that link steroid receptor.hsp90.immunophilin heterocomplexes to cytoplasmic dynein are common to plant and animal cells.
Harrell JM, Kurek I, Breiman A, Radanyi C, Renoir JM, Pratt WB, Galigniana MD
Biochemistry 2002 Apr 30;41(17):5581-7
Biochemistry 2002 Apr 30;41(17):5581-7
Differential interactions of specific nuclear factor I isoforms with the glucocorticoid receptor and STAT5 in the cooperative regulation of WAP gene transcription.
Mukhopadhyay SS, Wyszomierski SL, Gronostajski RM, Rosen JM
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Oct;21(20):6859-69
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Oct;21(20):6859-69
High neonatal leptin exposure enhances brain GR expression and feedback efficacy on the adrenocortical axis of developing rats.
Proulx K, Clavel S, Nault G, Richard D, Walker CD
Endocrinology 2001 Nov;142(11):4607-16
Endocrinology 2001 Nov;142(11):4607-16
Physical interaction and functional synergy between glucocorticoid receptor and Ets2 proteins for transcription activation of the rat cytochrome P-450c27 promoter.
Mullick J, Anandatheerthavarada HK, Amuthan G, Bhagwat SV, Biswas G, Camasamudram V, Bhat NK, Reddy SE, Rao V, Avadhani NG
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 May 25;276(21):18007-17
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 May 25;276(21):18007-17
Heterodimerization between the glucocorticoid receptor and the unrelated DNA-binding protein, Xenopus glucocorticoid receptor accessory factor.
Morin B, Woodcock GR, Nichols LA, Holland LJ
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Mar;15(3):458-66
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Mar;15(3):458-66
Hormone-induced nucleosome positioning in the MMTV promoter is reversible.
Belikov S, Gelius B, Wrange O
The EMBO journal 2001 Jun 1;20(11):2802-11
The EMBO journal 2001 Jun 1;20(11):2802-11
Interleukin-2 inhibits glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity through a mechanism involving STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5) but not AP-1.
Biola A, Lefebvre P, Perrin-Wolff M, Sturm M, Bertoglio J, Pallardy M
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Jul;15(7):1062-76
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Jul;15(7):1062-76
Glucocorticoid receptor homodimers and glucocorticoid-mineralocorticoid receptor heterodimers form in the cytoplasm through alternative dimerization interfaces.
Savory JG, Préfontaine GG, Lamprecht C, Liao M, Walther RF, Lefebvre YA, Haché RJ
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Feb;21(3):781-93
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Feb;21(3):781-93
Cooperative effects of STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5) and C/EBPbeta (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta) on beta-casein gene transcription are mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor.
Wyszomierski SL, Rosen JM
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Feb;15(2):228-40
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001 Feb;15(2):228-40
Activation and autoregulation of DNA-PK from structured single-stranded DNA and coding end hairpins.
Soubeyrand S, Torrance H, Giffin W, Gong W, Schild-Poulter C, Haché RJ
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9605-10
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9605-10
Stoichiometry, abundance, and functional significance of the hsp90/hsp70-based multiprotein chaperone machinery in reticulocyte lysate.
Murphy PJ, Kanelakis KC, Galigniana MD, Morishima Y, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Aug 10;276(32):30092-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Aug 10;276(32):30092-8
hsp70 interacting protein Hip does not affect glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery except to oppose the effect of BAG-1.
Kanelakis KC, Murphy PJ, Galigniana MD, Morishima Y, Takayama S, Reed JC, Toft DO, Pratt WB
Biochemistry 2000 Nov 21;39(46):14314-21
Biochemistry 2000 Nov 21;39(46):14314-21
hsp70 interacting protein Hip does not affect glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery except to oppose the effect of BAG-1.
Kanelakis KC, Murphy PJ, Galigniana MD, Morishima Y, Takayama S, Reed JC, Toft DO, Pratt WB
Biochemistry 2000 Nov 21;39(46):14314-21
Biochemistry 2000 Nov 21;39(46):14314-21
A role for the Hsp40 Ydj1 in repression of basal steroid receptor activity in yeast.
Johnson JL, Craig EA
Molecular and cellular biology 2000 May;20(9):3027-36
Molecular and cellular biology 2000 May;20(9):3027-36
The Hsp organizer protein hop enhances the rate of but is not essential for glucocorticoid receptor folding by the multiprotein Hsp90-based chaperone system.
Morishima Y, Kanelakis KC, Silverstein AM, Dittmar KD, Estrada L, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 10;275(10):6894-900
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 10;275(10):6894-900
The Hsp organizer protein hop enhances the rate of but is not essential for glucocorticoid receptor folding by the multiprotein Hsp90-based chaperone system.
Morishima Y, Kanelakis KC, Silverstein AM, Dittmar KD, Estrada L, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 10;275(10):6894-900
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 10;275(10):6894-900
The molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Hsc70 are both necessary and sufficient to activate hormone binding by glucocorticoid receptor.
Rajapandi T, Greene LE, Eisenberg E
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22597-604
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Jul 21;275(29):22597-604
Defense of adrenocorticosteroid receptor expression in rat hippocampus: effects of stress and strain.
Herman JP, Watson SJ, Spencer RL
Endocrinology 1999 Sep;140(9):3981-91
Endocrinology 1999 Sep;140(9):3981-91
Early maturation of T-cell progenitors in the absence of glucocorticoids.
Sacedón R, Vicente A, Varas A, Jiménez E, Muñoz JJ, Zapata AG
Blood 1999 Oct 15;94(8):2819-26
Blood 1999 Oct 15;94(8):2819-26
Differential effects of the hsp70-binding protein BAG-1 on glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery.
Kanelakis KC, Morishima Y, Dittmar KD, Galigniana MD, Takayama S, Reed JC, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Nov 26;274(48):34134-40
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Nov 26;274(48):34134-40
Differential effects of the hsp70-binding protein BAG-1 on glucocorticoid receptor folding by the hsp90-based chaperone machinery.
Kanelakis KC, Morishima Y, Dittmar KD, Galigniana MD, Takayama S, Reed JC, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Nov 26;274(48):34134-40
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Nov 26;274(48):34134-40
Regulation of growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression by glucocorticoids in MtT-S cells and in the pituitary gland of fetal rats.
Nogami H, Inoue K, Moriya H, Ishida A, Kobayashi S, Hisano S, Katayama M, Kawamura K
Endocrinology 1999 Jun;140(6):2763-70
Endocrinology 1999 Jun;140(6):2763-70
Inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor nucleocytoplasmic shuttling by okadaic acid requires intact cytoskeleton.
Galigniana MD, Housley PR, DeFranco DB, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jun 4;274(23):16222-7
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jun 4;274(23):16222-7
The glucocorticoid receptor is tethered to DNA-bound Oct-1 at the mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone distal negative glucocorticoid response element.
Chandran UR, Warren BS, Baumann CT, Hager GL, DeFranco DB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 22;274(4):2372-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 22;274(4):2372-8
Neuronal nitric-oxide synthase is regulated by the Hsp90-based chaperone system in vivo.
Bender AT, Silverstein AM, Demady DR, Kanelakis KC, Noguchi S, Pratt WB, Osawa Y
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 15;274(3):1472-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 15;274(3):1472-8
Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor.
Haché RJ, Tse R, Reich T, Savory JG, Lefebvre YA
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 15;274(3):1432-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Jan 15;274(3):1432-9
Glucocorticoid resistance in the squirrel monkey is associated with overexpression of the immunophilin FKBP51.
Reynolds PD, Ruan Y, Smith DF, Scammell JG
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 1999 Feb;84(2):663-9
The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 1999 Feb;84(2):663-9
Discrimination between NL1- and NL2-mediated nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor.
Savory JG, Hsu B, Laquian IR, Giffin W, Reich T, Haché RJ, Lefebvre YA
Molecular and cellular biology 1999 Feb;19(2):1025-37
Molecular and cellular biology 1999 Feb;19(2):1025-37
Glucocorticoid receptor/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) interactions enhance STAT5 activation by prolonging STAT5 DNA binding and tyrosine phosphorylation.
Wyszomierski SL, Yeh J, Rosen JM
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1999 Feb;13(2):330-43
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1999 Feb;13(2):330-43
Glucocorticoids downregulate cyclooxygenase-1 gene expression and prostacyclin synthesis in fetal pulmonary artery endothelium.
Jun SS, Chen Z, Pace MC, Shaul PW
Circulation research 1999 Feb 5;84(2):193-200
Circulation research 1999 Feb 5;84(2):193-200
The seven amino acids (547-553) of rat glucocorticoid receptor required for steroid and hsp90 binding contain a functionally independent LXXLL motif that is critical for steroid binding.
Giannoukos G, Silverstein AM, Pratt WB, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Dec 17;274(51):36527-36
The Journal of biological chemistry 1999 Dec 17;274(51):36527-36
Glucocorticoids stimulate the accumulation of lipids in the rat corpus luteum.
Towns R, Menon KM, Brabec RK, Silverstein AM, Cohen JM, Bowen JM, Keyes PL
Biology of reproduction 1999 Aug;61(2):416-21
Biology of reproduction 1999 Aug;61(2):416-21
Glucocorticoid-mediated regulation of thymic dendritic cell function.
Sacedón R, Vicente A, Varas A, Jiménez E, Muñoz JJ, Zapata AG
International immunology 1999 Aug;11(8):1217-24
International immunology 1999 Aug;11(8):1217-24
The DNA-binding and tau2 transactivation domains of the rat glucocorticoid receptor constitute a nuclear matrix-targeting signal.
Tang Y, Getzenberg RH, Vietmeier BN, Stallcup MR, Eggert M, Renkawitz R, DeFranco DB
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1998 Sep;12(9):1420-31
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1998 Sep;12(9):1420-31
Regulation of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor gene transcription and protein expression in vivo.
Herman JP, Spencer R
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 1998 Sep 15;18(18):7462-73
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 1998 Sep 15;18(18):7462-73
Analysis of FKBP51/FKBP52 chimeras and mutants for Hsp90 binding and association with progesterone receptor complexes.
Barent RL, Nair SC, Carr DC, Ruan Y, Rimerman RA, Fulton J, Zhang Y, Smith DF
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1998 Mar;12(3):342-54
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1998 Mar;12(3):342-54
The role of DnaJ-like proteins in glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly by the reconstituted hsp90.p60.hsp70 foldosome complex.
Dittmar KD, Banach M, Galigniana MD, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Mar 27;273(13):7358-66
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Mar 27;273(13):7358-66
The role of DnaJ-like proteins in glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly by the reconstituted hsp90.p60.hsp70 foldosome complex.
Dittmar KD, Banach M, Galigniana MD, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Mar 27;273(13):7358-66
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Mar 27;273(13):7358-66
A conserved proline in the hsp90 binding region of the glucocorticoid receptor is required for hsp90 heterocomplex stabilization and receptor signaling.
Caamaño CA, Morano MI, Dalman FC, Pratt WB, Akil H
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Aug 7;273(32):20473-80
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Aug 7;273(32):20473-80
GRIP1, a transcriptional coactivator for the AF-2 transactivation domain of steroid, thyroid, retinoid, and vitamin D receptors.
Hong H, Kohli K, Garabedian MJ, Stallcup MR
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 May;17(5):2735-44
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 May;17(5):2735-44
GRIP1, a transcriptional coactivator for the AF-2 transactivation domain of steroid, thyroid, retinoid, and vitamin D receptors.
Hong H, Kohli K, Garabedian MJ, Stallcup MR
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 May;17(5):2735-44
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 May;17(5):2735-44
Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the reconstituted Hsp90-based chaperone machinery. The initial hsp90.p60.hsp70-dependent step is sufficient for creating the steroid binding conformation.
Dittmar KD, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 May 16;272(20):13047-54
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 May 16;272(20):13047-54
Protein phosphatase 5 is a major component of glucocorticoid receptor.hsp90 complexes with properties of an FK506-binding immunophilin.
Silverstein AM, Galigniana MD, Chen MS, Owens-Grillo JK, Chinkers M, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Jun 27;272(26):16224-30
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Jun 27;272(26):16224-30
In vivo analysis of the Hsp90 cochaperone Sti1 (p60).
Chang HC, Nathan DF, Lindquist S
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 Jan;17(1):318-25
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 Jan;17(1):318-25
In vivo analysis of the Hsp90 cochaperone Sti1 (p60).
Chang HC, Nathan DF, Lindquist S
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 Jan;17(1):318-25
Molecular and cellular biology 1997 Jan;17(1):318-25
Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the heat shock protein (hsp) 90-based chaperone machinery. The role of p23 is to stabilize receptor.hsp90 heterocomplexes formed by hsp90.p60.hsp70.
Dittmar KD, Demady DR, Stancato LF, Krishna P, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21213-20
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21213-20
Determinants of subcellular distribution of the glucocorticoid receptor.
Sackey FN, Haché RJ, Reich T, Kwast-Welfeld J, Lefebvre YA
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1996 Oct;10(10):1191-205
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1996 Oct;10(10):1191-205
Reconstitution of the steroid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly system of rabbit reticulocyte lysate.
Dittmar KD, Hutchison KA, Owens-Grillo JK, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 May 31;271(22):12833-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 May 31;271(22):12833-9
Reconstitution of the steroid receptor.hsp90 heterocomplex assembly system of rabbit reticulocyte lysate.
Dittmar KD, Hutchison KA, Owens-Grillo JK, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 May 31;271(22):12833-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 May 31;271(22):12833-9
Dexamethasone responsiveness of a major glucocorticoid-inducible CYP3A gene is mediated by elements unrelated to a glucocorticoid receptor binding motif.
Huss JM, Wang SI, Astrom A, McQuiddy P, Kasper CB
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996 May 14;93(10):4666-70
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1996 May 14;93(10):4666-70
The tetratricopeptide repeat domain of protein phosphatase 5 mediates binding to glucocorticoid receptor heterocomplexes and acts as a dominant negative mutant.
Chen MS, Silverstein AM, Pratt WB, Chinkers M
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 Dec 13;271(50):32315-20
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 Dec 13;271(50):32315-20
Use of the thiol-specific derivatizing agent N-iodoacetyl-3-[125I]iodotyrosine to demonstrate conformational differences between the unbound and hsp90-bound glucocorticoid receptor hormone binding domain.
Stancato LF, Silverstein AM, Gitler C, Groner B, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 Apr 12;271(15):8831-6
The Journal of biological chemistry 1996 Apr 12;271(15):8831-6
The cyclosporin A-binding immunophilin CyP-40 and the FK506-binding immunophilin hsp56 bind to a common site on hsp90 and exist in independent cytosolic heterocomplexes with the untransformed glucocorticoid receptor.
Owens-Grillo JK, Hoffmann K, Hutchison KA, Yem AW, Deibel MR Jr, Handschumacher RE, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20479-84
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20479-84
The cyclosporin A-binding immunophilin CyP-40 and the FK506-binding immunophilin hsp56 bind to a common site on hsp90 and exist in independent cytosolic heterocomplexes with the untransformed glucocorticoid receptor.
Owens-Grillo JK, Hoffmann K, Hutchison KA, Yem AW, Deibel MR Jr, Handschumacher RE, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20479-84
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20479-84
Zinc ions antagonize the inhibitory effect of aurothiomalate on glucocorticoid receptor function at physiological concentrations.
Tanaka H, Makino Y, Dahlman-Wright K, Gustafsson JA, Okamoto K, Makino I, Wright KD [corrected to Dahlman-Wright K]
Molecular pharmacology 1995 Nov;48(5):938-45
Molecular pharmacology 1995 Nov;48(5):938-45
Cyclosporin A potentiates the dexamethasone-induced mouse mammary tumor virus-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity in LMCAT cells: a possible role for different heat shock protein-binding immunophilins in glucocorticosteroid receptor-mediated gene expression.
Renoir JM, Mercier-Bodard C, Hoffmann K, Le Bihan S, Ning YM, Sanchez ER, Handschumacher RE, Baulieu EE
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1995 May 23;92(11):4977-81
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1995 May 23;92(11):4977-81
Effect of stress on cochlear glucocorticoid protein: acoustic stress.
Rarey KE, Gerhardt KJ, Curtis LM, ten Cate WJ
Hearing research 1995 Feb;82(2):135-8
Hearing research 1995 Feb;82(2):135-8
Effect of stress on cochlear glucocorticoid protein. II. Restraint.
Curtis LM, Rarey KE
Hearing research 1995 Dec;92(1-2):120-5
Hearing research 1995 Dec;92(1-2):120-5
The 23-kDa acidic protein in reticulocyte lysate is the weakly bound component of the hsp foldosome that is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a functional heterocomplex with hsp90.
Hutchison KA, Stancato LF, Owens-Grillo JK, Johnson JL, Krishna P, Toft DO, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18841-7
The Journal of biological chemistry 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18841-7
BCL-2 expression and mitochondrial activity in leukemic cells with different sensitivity to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis.
Smets LA, Van den Berg J, Acton D, Top B, Van Rooij H, Verwijs-Janssen M
Blood 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1613-9
Blood 1994 Sep 1;84(5):1613-9
High levels of non-activated receptors in glucocorticoid-sensitive S49wt mouse lymphoma cells incubated with dexamethasone.
van den Berg JD, Smets LA, Hutchison KA, van Rooij H, van den Elshout MM
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 1994 Oct;51(1-2):33-40
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology 1994 Oct;51(1-2):33-40
Conservation of Hsp90 macromolecular complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Chang HC, Lindquist S
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24983-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24983-8
Metal oxyanion stabilization of the rat glucocorticoid receptor is independent of thiols.
Modarress KJ, Cavanaugh AH, Chakraborti PK, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25621-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25621-8
All of the factors required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a functional heterocomplex with heat shock protein 90 are preassociated in a self-sufficient protein folding structure, a "foldosome".
Hutchison KA, Dittmar KD, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Nov 11;269(45):27894-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Nov 11;269(45):27894-9
Absence of intramolecular disulfides in the structure and function of native rat glucocorticoid receptors.
Opoku J, Simons SS Jr
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Jan 7;269(1):503-10
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Jan 7;269(1):503-10
Proof that hsp70 is required for assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor into a heterocomplex with hsp90.
Hutchison KA, Dittmar KD, Czar MJ, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5043-9
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5043-9
A functional glucocorticoid-responsive unit composed of two overlapping inactive receptor-binding sites: evidence for formation of a receptor tetramer.
Garlatti M, Daheshia M, Slater E, Bouguet J, Hanoune J, Beato M, Barouki R
Molecular and cellular biology 1994 Dec;14(12):8007-17
Molecular and cellular biology 1994 Dec;14(12):8007-17
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptors interact with insulin degrading enzyme.
Kupfer SR, Wilson EM, French FS
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20622-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20622-8
Characterization of the protein-protein interactions determining the heat shock protein (hsp90.hsp70.hsp56) heterocomplex.
Czar MJ, Owens-Grillo JK, Dittmar KD, Hutchison KA, Zacharek AM, Leach KL, Deibel MR Jr, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11155-61
The Journal of biological chemistry 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11155-61
Raf exists in a native heterocomplex with hsp90 and p50 that can be reconstituted in a cell-free system.
Stancato LF, Chow YH, Hutchison KA, Perdew GH, Jove R, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21711-6
The Journal of biological chemistry 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21711-6
Inhibition of mouse GATA-1 function by the glucocorticoid receptor: possible mechanism of steroid inhibition of erythroleukemia cell differentiation.
Chang TJ, Scher BM, Waxman S, Scher W
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1993 Apr;7(4):528-42
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1993 Apr;7(4):528-42
Comparison of the 90-kilodalton heat shock protein interaction with in vitro translated glucocorticoid and estrogen receptors.
Schlatter LK, Howard KJ, Parker MG, Distelhorst CW
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1992 Jan;6(1):132-40
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1992 Jan;6(1):132-40
Reconstitution of the multiprotein complex of pp60src, hsp90, and p50 in a cell-free system.
Hutchison KA, Brott BK, De Leon JH, Perdew GH, Jove R, Pratt WB
The Journal of biological chemistry 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2902-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2902-8
Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors.
Yoshinaga SK, Peterson CL, Herskowitz I, Yamamoto KR
Science (New York, N.Y.) 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598-604
Science (New York, N.Y.) 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598-604
Direct stoichiometric evidence that the untransformed Mr 300,000, 9S, glucocorticoid receptor is a core unit derived from a larger heteromeric complex.
Bresnick EH, Dalman FC, Pratt WB
Biochemistry 1990 Jan 16;29(2):520-7
Biochemistry 1990 Jan 16;29(2):520-7
Phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptor-associated and free forms of the approximately 90-kDa heat shock protein before and after receptor activation.
Ortí E, Mendel DB, Munck A
The Journal of biological chemistry 1989 Jan 5;264(1):231-7
The Journal of biological chemistry 1989 Jan 5;264(1):231-7
The glucocorticoid antagonist 17 alpha-methyltestosterone binds to the 10 S glucocorticoid receptor and blocks agonist-mediated dissociation of the 10 S oligomer to the 4 S deoxyribonucleic acid-binding subunit.
Raaka BM, Finnerty M, Samuels HH
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1989 Feb;3(2):332-41
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1989 Feb;3(2):332-41
Kinetic pulse-chase labeling study of the glucocorticoid receptor in mouse lymphoma cells. Effect of glucocorticoid and antiglucocorticoid hormones on intracellular receptor half-life.
Distelhorst CW, Howard KJ
The Journal of biological chemistry 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13080-5
The Journal of biological chemistry 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13080-5
Relationship between glucocorticoid receptor steroid-binding capacity and association of the Mr 90,000 heat shock protein with the unliganded receptor.
Bresnick EH, Sanchez ER, Pratt WB
Journal of steroid biochemistry 1988;30(1-6):267-9
Journal of steroid biochemistry 1988;30(1-6):267-9
Isolation of ribonucleic acid from the unactivated rat liver glucocorticoid receptor.
Unger AL, Uppaluri R, Ahern S, Colby JL, Tymoczko JL
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1988 Oct;2(10):952-8
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 1988 Oct;2(10):952-8
Immunocytochemical localization of glucocorticoid receptors in cells, cytoplasts, and nucleoplasts.
LaFond RE, Kennedy SW, Harrison RW, Villee CA
Experimental cell research 1988 Mar;175(1):52-62
Experimental cell research 1988 Mar;175(1):52-62
Evidence for intracellular association of the glucocorticoid receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein.
Howard KJ, Distelhorst CW
The Journal of biological chemistry 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3474-81
The Journal of biological chemistry 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3474-81
Analysis of the disruptive action of an epididymal protease and the stabilizing influence of molybdate on nondenatured and denatured glucocorticoid receptor.
Hendry WJ 3rd, Danzo BJ, Harrison RW 3rd
Endocrinology 1987 Feb;120(2):629-39
Endocrinology 1987 Feb;120(2):629-39
Immunochemical comparison of mutant glucocorticoid receptors and wild type receptor fragments produced by neutrophil elastase and chymotrypsin.
Rehmus EH, Howard KJ, Janiga KE, Distelhorst CW
Journal of steroid biochemistry 1987 Aug;28(2):167-77
Journal of steroid biochemistry 1987 Aug;28(2):167-77
Characterization of a monoclonal antibody to the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor.
Gametchu B, Harrison RW
Endocrinology 1984 Jan;114(1):274-9
Endocrinology 1984 Jan;114(1):274-9
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
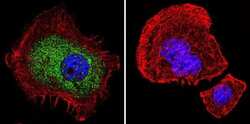
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in A549 Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
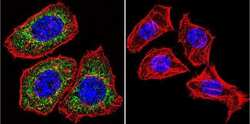
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in Hela Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
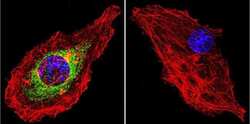
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in U251 Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
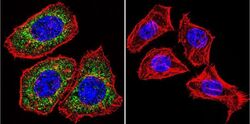
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in Hela Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
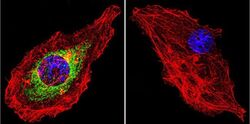
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in U251 Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
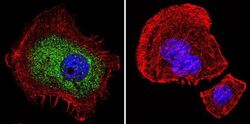
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor using Glucocorticoid Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (BuGR2) (Product # MA1-510) shows staining in A549 Cells. Glucocorticoid Receptor (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing Glucocorticoid Receptor (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4 °C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552 for GAR, Product # 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
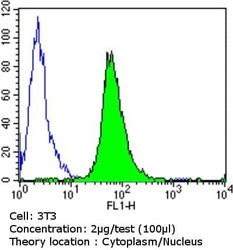
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor in NIH/3T3 cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were penetrated by dropping the supernatant, adding 90% methanol and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Follwing penetration, cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Glucocorticoid Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 2 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
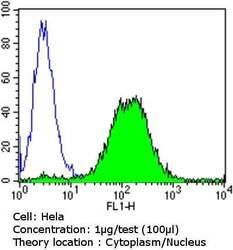
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor in Hela cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were penetrated by dropping the supernatant, adding 90% methanol and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Follwing penetration, cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Glucocorticoid Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
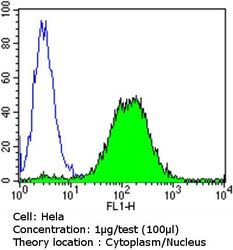
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor in Hela cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were penetrated by dropping the supernatant, adding 90% methanol and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Follwing penetration, cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Glucocorticoid Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
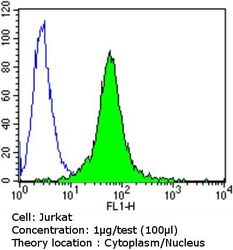
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor in Jurkat cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were penetrated by dropping the supernatant, adding 90% methanol and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Follwing penetration, cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Glucocorticoid Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
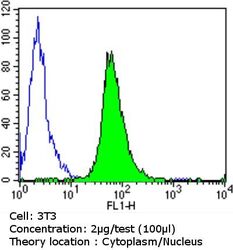
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor in NIH/3T3 cells compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were penetrated by dropping the supernatant, adding 90% methanol and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Follwing penetration, cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a Glucocorticoid Receptor monoclonal antibody (Product # MA1-510) at a dilution of 2 µg/test for 60 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
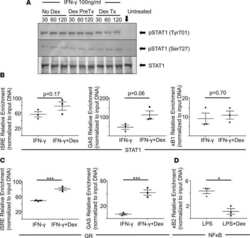
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
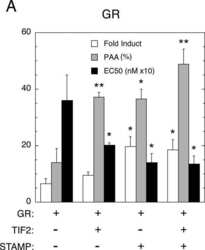
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
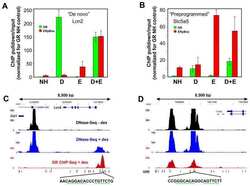
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
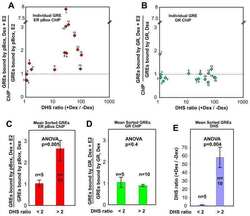
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure 2 GR and MR labeling in the rat amygdala. (A & E) GR-ir neurons are distributed throughout the amygdala predominately labeling the nucleus. (B & F) MR-ir (MA1-620) neurons are distributed throughout the amygdala but immunoreactivity is not as dense as GR-ir. Large proximal dendrites showed immunoreactivity (F inset). (C & G) MR-ir (rMR1-18 1D5) neurons are distributed in amygdala nuclei and cell membrane but do not appear as densely labeled in perikaryon (G inset). (D & H) Control section shows little immunoreactivity of cells in amygdala or surrounding nuclei. Scale bars = 200 um for A-D, 10 um for D-G and 5 um for F & G insets. Amygdala nuclei subdivisions B = basal, Ce = central, Lad = lateral (dorsal division), Lvl = lateral (ventral-lateral), Lvm = lateral (ventral-medial).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
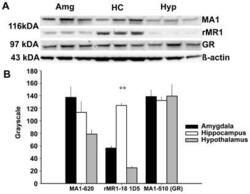
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 Immunoblots of MR and GR in amygdala (Amg), hippocampal (HC) and hypothalamic (Hyp) nuclei. As indicated by the representative immunoblots standardized to beta-Actin (A) there was a significant difference in relative density of MR between brain nuclei (B). GR was equally distributed in all brain regions. (** denotes p's
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
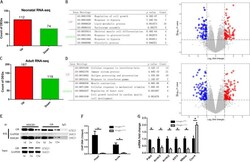
- Experimental details
- Fig. 5 Global gene expression profile in neonatal and 12-week-old control and HMGB1 ^CM hearts. a Total number of genes differentially expressed in the hearts of neonatal HMGB1 ^CM compared to their control littermates. b Volcano plots and biological process most significantly associated with the dysregulated genes in the neonatal knockout hearts as determined by DAVID. c Total number of genes differentially expressed in the hearts of 12-week-old HMGB1 ^CM mice compared to their control littermates. d Volcano plots and biological process most significantly associated with the dysregulated genes in the adult knockout hearts as determined by DAVID. e The physical interaction of HMGB1 and glucocorticoid receptor was analysed by immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis. f The effect of HMGB1 knockout on the recruitment of GR onto the Fkbp5 and Klf15 promoters was assessed by ChIP assays using an anti-GR antibody and neonatal hearts. Amounts of ChIP DNA were measured with quantitative PCR. n = 6/group. g qRT-PCR results of the GR downstream genes in neonatal hearts of the two groups, n = 6/group. * p < 0.05 versus control, t -test, mean +- SEM.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
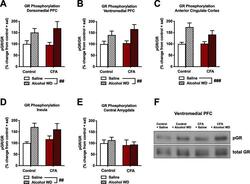
- Experimental details
- Fig. 5 The interaction of chronic inflammatory pain and binge alcohol withdrawal on glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation. Binge alcohol exposure and withdrawal increased GR phosphorylation (Ser232 in both control and CFA-treated animals in the (A) dorsomedial PFC, (B) ventromedial PFC, (C) anterior cingulate cortex, and (D) insula (##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 main effect of group). (E) In the CeA, there was no effect of CFA treatment or acute alcohol WD on GR Ser232 phosphorylation. (F) Representative Western blots of pGR and total GR in the ventromedial PFC. Data were analyzed using 2-way RM ANOVA and Sidak''s multiple comparisons test (B) or 2-way ANOVA and Tukey''s post hoc tests (C-G). Data are represented as mean +- SEM. Saline control + saline, solid white (n = 9); Saline control + acute alcohol WD, white striped (n = 11); CFA + saline, solid red (n = 9); CFA + acute alcohol WD, red striped (n = 9). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
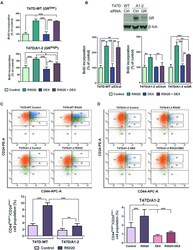
- Experimental details
- Figure 1. GR interferes with progestin-induced cell proliferation and dedifferentiation. ( A and B ) Cell proliferation was evaluated by using ELISA BrdU colorimetric assay (Roche) in T47D-WT (GR low ) and T47D/A1-2 (GR high ) growing cells incubated with R5020 10 nM, DEX 10 nM or both hormones. (A) Cells were harvested at 14 h (upper panel) or 18 h (lower panel) after hormone treatment. (B) Previous to hormone treatment, cells were transfected with control (Ctrol) or GR siRNAs. GR expression was analyzed by western blotting using a specific GR antibody (upper panel). Values are expressed as percentage of increased proliferation relative to untreated cells (Control). Means +- S.D. from five independent experiments are shown. ***, P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
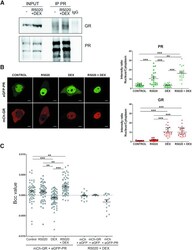
- Experimental details
- Figure 5. PR and GR can be part of the same complex. ( A ) Nuclear extracts from T47D/A1-2 cells treated or not with R5020 10 nM and DEX 10 nM for 1 h were immunoprecipitated with alpha-PR specific antibody. Rabbit IgG was used as a negative control (IgG). The immunoprecipitates (IP) and inputs lysates were analyzed by western blotting with alpha-GR or alpha-PR as indicated. Blots correspond to one representative from three independent experiments. ( B and C ) T47D-WT cells transiently expressing mCherry-GR and GFP-PR were treated with R5020 10 nM and/or DEX 10 nM for 1 h and imaged by confocal microscopy. (B) Subcellular distribution of mCherry-GR and GFP-PR in each condition. Representative cells are shown (Scale bar: 7 mum) (left panel). Fluorescence intensity ratios between nucleus and cytoplasm for each receptor in the indicated conditions are shown (right panels). ***, P
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn