Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [2]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 702069 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Apelin Receptor Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (5H5L9)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- This antibody is predicted to react with Monkey, Rabbit, Horse and Dog Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies are produced using in vitro expression systems. The expression systems are developed by cloning in the specific antibody DNA sequences from immunoreactive rabbits. Then, individual clones are screened to select the best candidates for production. The advantages of using recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies include: better specificity and sensitivity, lot-to-lot consistency, animal origin-free formulations, and broader immunoreactivity to diverse targets due to larger rabbit immune repertoire.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 5H5L9
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references The Apelin-Apelin Receptor Axis Triggers Cholangiocyte Proliferation and Liver Fibrosis During Mouse Models of Cholestasis.
Spatiotemporal extracellular matrix modeling for in situ cell niche studies.
Chen L, Zhou T, White T, O'Brien A, Chakraborty S, Liangpunsakul S, Yang Z, Kennedy L, Saxena R, Wu C, Meng F, Huang Q, Francis H, Alpini G, Glaser S
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2021 Jun;73(6):2411-2428
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2021 Jun;73(6):2411-2428
Spatiotemporal extracellular matrix modeling for in situ cell niche studies.
Olesen K, Rodin S, Mak WC, Felldin U, Österholm C, Tilevik A, Grinnemo KH
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2021 Dec;39(12):1751-1765
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2021 Dec;39(12):1751-1765
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
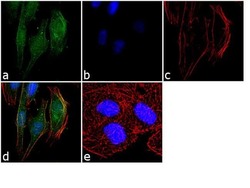
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence was performed on fixed and permeabilized HeLa cells for detection of endogenous APLNR using Anti-APLNR Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 702069, 2 µg/mL) and labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034, 1:2000). Panel a) shows representative cells that were stained for detection and localization of APLNR protein (green), Panel b) is stained for nuclei (blue) using SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). Panel c) represents cytoskeletal F-actin staining using Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d) is a composite image of Panels a, b and c clearly demonstrating membrane localization of APLNR. Panel e) represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
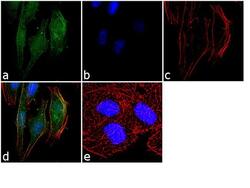
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence was performed on fixed and permeabilized HeLa cells for detection of endogenous APLNR using Anti-APLNR Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 702069, 2 µg/mL) and labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034, 1:2000). Panel a) shows representative cells that were stained for detection and localization of APLNR protein (green), Panel b) is stained for nuclei (blue) using SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). Panel c) represents cytoskeletal F-actin staining using Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d) is a composite image of Panels a, b and c clearly demonstrating membrane localization of APLNR. Panel e) represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
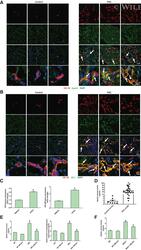
- Experimental details
- 1 FIG. APJ-mediated APLN expression is increased in cholangiocytes during cholestasis. (A) Immunofluorescence of APLN (costained with CK-19) in liver sections from patients with PSC (n = 7). Upper three panels, original magnification, x40; scale bar, 50 mum. Lower panel, original magnification, x40 zoom5; scale bar, 10 mum (red CK-19, green APLN, blue 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI]). (B) Immunofluorescence of APJ (costained with CK-19) in liver sections from patients with PSC (n = 7). Upper three panels, original magnification, x40; scale bar, 50 mum. Lower panel, original magnification, x40 zoom5; scale bar, 10 mum (red CK-19, green APJ, blue DAPI). (C) The mRNA expression of APLN and APLNR in cholangiocytes from patients with PSC (hPSCL; mean +- SD, n = 3), * P < 0.05 versus HIBEpiCs. (D) APLN levels in serum of patients with PSC (mean +- SD, n = 26), * P < 0.05 versus control. (E) APLN levels in BDL mouse serum and cholangiocyte supernatant (mean +- SD, n = 3), * P < 0.05 versus WT, # P < 0.05 versus BDL. (F) APLN levels in Mdr2 -/- mouse serum (mean +- SD, n = 3), * P < 0.05 versus WT, # P < 0.05 versus Mdr2 -/- .
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry