PA5-20237
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: TNFRSF14
ATAR, CD270, HVEA, HVEM, LIGHTR, TR2
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-20237 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- TNFRSF14 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- A suggested positive control is mouse thymus tissue lysate. PA5-20237 can be used with blocking peptide PEP-0356.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 3 months. For long term storage store at -20°C
Submitted references Interaction between DNMT3B and MYH11 via hypermethylation regulates gastric cancer progression.
Wang J, Xu P, Hao Y, Yu T, Liu L, Song Y, Li Y
BMC cancer 2021 Aug 12;21(1):914
BMC cancer 2021 Aug 12;21(1):914
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
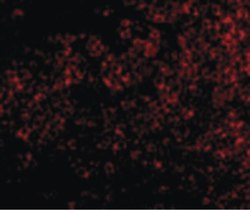
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of mouse thymus cells using a TNFRSF14 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-20237) at a 10 µg/mL dilution.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
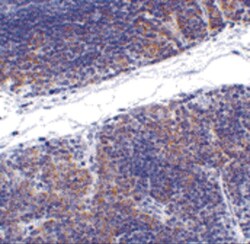
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry of TNFRSF14 in mouse thymus tissue with TNFRSF14 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-20237) at 1 µg/mL.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
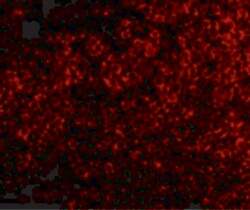
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence of TNFRSF14 in Mouse Thymus tissue with TNFRSF14 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-20237) at 10 µg/mL.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
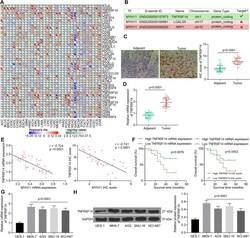
- Fig. 3 TNFRSF14 expression correlates with MYH11 expression in GC. A , factors with significant correlation with MYH11 expression in cancers; B , the possible interacting relation between MYH11 and TNFRSF14; C , immunohistochemical detection of TNFRSF14 expression in tumor tissues and their adjacent tissues; D , TNFRSF14 expression in tumor tissues and their adjacent tissues by RT-qPCR; E , correlation between TNFRSF14 expression and MYH11 expression in tumor tissues analyzed by Pearson's correlation analysis (r = -0.7240, p < 0.001); F , five-year survival analysis of patients with different TNFRSF14 expression analyzed using Log-rank test; G , TNFRSF14 mRNA expression in GES-1 cells and GC cells by RT-qPCR; H , TNFRSF14 protein expression in GES-1 cells and GC cells by western blot. Each assay was performed at least three times. Statistical significance was analyzed by paired t test (panels C and D) or one-way ANOVA (panels G and H) and Tukey's multiple range tests
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
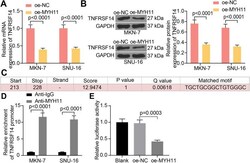
- Fig. 4 MYH11 interacts with TNFRSF14 by direct binding in GC cells. A , TNFRSF14 expression in GC cells in response to oe-MYH11 or oe-NC by RT-qPCR; B , TNFRSF14 expression in GC cells in response to oe-MYH11 or oe-NC by western blot; C , the binding sites between MYH11 and TNFRSF14 promoter; D , the enrichment ability of MYH11 on TNFRSF14 promoter examined by ChIP-qPCR; E , the transcriptional activity of TNFRSF14 promoter detected by a luciferase report assay. Each assay was performed at least three times. Statistical significance was analyzed by one-way (panel E) or two-way ANOVA (panels A, B and D) and Tukey's multiple range tests
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
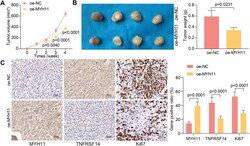
- Fig. 8 MYH11 overexpression impedes tumor growth in GC. GC cells transfected with oe-MYH11 or oe-NC were delivered into nude mice ( n = 4). A , tumor growth rate; B , weight of harvested xenograft tumors; C , immunohistochemical detection of MYH11, TNFRSF14, and Ki67 expression in xenograft tumors. Statistical significance was analyzed by unpaired t test (panel B) or two-way ANOVA (panels A and C) and Tukey's multiple range tests
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry