Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- ELISA [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-18667 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- DGAT2 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- This antibody is predicted to react with canine, mouse and rat based on sequence homology. This antibody is tested in Peptide ELISA: antibody detection limit dilution 128,000.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Goat
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Novel role of xanthine oxidase-dependent H(2)O(2) production in 12/15-lipoxygenase-mediated de novo lipogenesis, triglyceride biosynthesis and weight gain.
Govatati S, Pichavaram P, Mani AM, Kumar R, Sharma D, Dienel A, Meena S, Puchowicz MA, Park EA, Rao GN
Redox biology 2021 Nov;47:102163
Redox biology 2021 Nov;47:102163
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
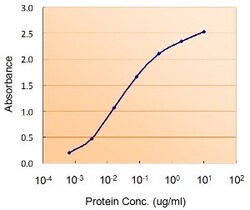
- Experimental details
- ELISA of DGAT2 using two DGAT2 antibodies. The reporter antibody (Product # PA5-18667) was used at a concentration of 0.5 µg/ml and the reporter antibody was used at a concentration of 2.5 µg/ml.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
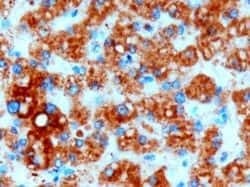
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry (PFA fixed) analysis of DGAT2 using DGAT2 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-18667) (3 µg/mL) in staining of paraffin embedded Human Liver. Microwaved antigen retrieval with Tris/EDTA buffer pH9, HRP-staining.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
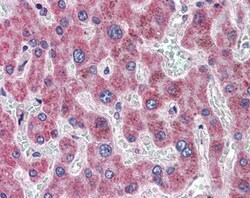
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of DGAT2 in human liver. Samples were incubated with DGAT2 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-18667) using a dilution of 3.75 µg/mL. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue after heat-induced antigen retrieval.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
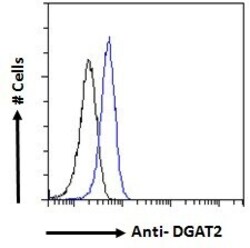
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometric analysis of DGAT2 in HeLa cells using a polyclonal antibody (Product #PA5-18667). HeLa cells (blue line) were paraformaldehyde fixed and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton. The primary antibody was incubated for one hour (10 µg/mL) followed by an Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody (1 µg/mL). IgG control: Unimmunized goat IgG (black line) followed by an Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
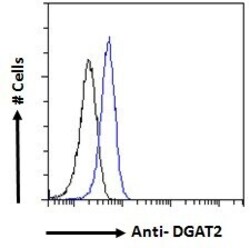
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometric analysis of DGAT2 in HeLa cells using a polyclonal antibody (Product #PA5-18667). HeLa cells (blue line) were paraformaldehyde fixed and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton. The primary antibody was incubated for one hour (10 µg/mL) followed by an Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody (1 µg/mL). IgG control: Unimmunized goat IgG (black line) followed by an Alexa Fluor 488 secondary antibody.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
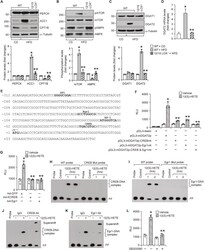
- Experimental details
- Fig. 2 12/15-LOX deficiency prevents HFD-induced DGAT2 expression and 12/15-LOX dependent HFD-induced DGAT2 expression requires CREB and Egr1 : A-C, Epididymal WAT extracts of CD-fed WT and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. D, Relative mRNA expression levels of DGAT2 in WAT of CD-fed WT and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice. E, TRANSFAC analysis of mouse DGAT2 proximal promoter sequence encompassing from -312 nt to +92 nt for the identification of potential transcriptional factor binding sites. F, The effect of site-directed mutagenesis of CREB binding site at -12 nt and Egr1 binding site at -117 nt in pGL3-mDGAT2p construct on 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM)-induced luciferase activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. G, 3T3-L1 adipocytes that were infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-KCREB or Ad-Egr1 were transfected with pGL3-mDGAT2p construct, treated with and without 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) for 1 h, and luciferase activity was measured. H and I, Time course effect of 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) on protein and mDGAT2 promoter DNA binding activity by EMSA using CREB binding element at -12 nt (H), and Egr1 binding element at -117 nt (I) as biotin labeled probes. J and K, Supershift EMSA analysis of nuclear extracts of control and 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM)-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes for CREB and Egr1 using CREB-binding element at -12 nt (J), and Egr1-binding element at -117 nt (K) as biotin labeled probes. L,
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
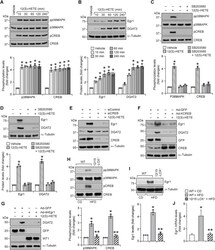
- Experimental details
- Fig. 3 p38MAPK-CREB-Egr1 signaling is required for 12(S)-HETE induced DGAT2 expression : A and B, 3T3-L1 adipocytes were growth-arrested, treated with and without 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) for indicated time periods and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. C and D, Growth-arrested 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with and without 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) in the presence or absence of SB203580 (10 muM) for 10 min (C) or 1 h (D) and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. E-G, 3T3-L1 adipocytes that were transfected with siControl or siCREB (100 nmoles) (E), or infected with Ad-GFP or Ad-KCREB or Ad-Egr1 (40 moi) (F and G), and growth-arrested were treated with and without 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) for 1 h and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting. The efficacy of siCREB was shown by its effect on CREB levels and over-expression of the vectors for GFP, KCREB and dn-Egr1 was shown by probing for their expression levels. H and I, White adipose tissue extracts of CD-fed WT and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. J, Relative mRNA expression levels of Egr1 in WAT of CD-fed WT and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice. *, p < 0.05 versus vehicle or WT mice on CD; **, p < 0.05 WT mice on HFD. WT1, Wilmer tumor
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
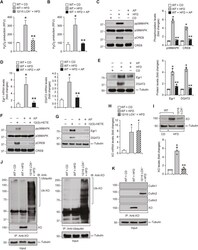
- Experimental details
- Fig. 4 XO-dependent H 2 O 2 production is required for 12/15-LOX-induced p38MAPK-CREB-Egr1-mediated DGAT2 expression : A, H 2 O 2 production in WAT of CD-fed WT and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice was measured using Amplex Red. B, WAT from WT mice fed with CD or HFD in combination with and without Allopurinol (125 mg/L of drinking water) for 12 wks were analyzed for H 2 O 2 production using Amplex Red. C-E, WAT in panel B were analyzed by western blotting (C and E) and qRT-PCR (D) for protein levels and relative mRNA levels, respectively, of the indicated molecules. F and G, Growth-arrested 3T3-L1 adipocytes were treated with and without 12(S)-HETE (0.5 muM) in the presence or absence of Allopurinol (50 muM) for 10 min (F) or 1 h (G) and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. H and I, WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice were fed with CD or HFD for 12 wks, and mRNA and protein levels of XO were measured by qRT-PCR (H) and Western blot analysis (I). J and K, WAT extracts containing equal amounts of protein from each regimen were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. *, p < 0.05 versus WT mice on CD; **, p < 0.05 versus WT mice on HFD. Fig. 4
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
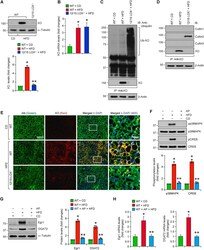
- Experimental details
- Fig. 7 12/15-LOX deficiency leads to HFD-induced XO ubiquitination and degradation and Allopurinol mimics 12/15-LOX deficiency by inhibiting HFD-induced XO-mediated p38MAPK-CREB-Egr1 activation and DGAT2 expression in the liver : A and B, WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice were fed with CD or HFD for 12 wks, and protein (A) and mRNA (B) levels of XO in the liver tissue were measured by western blotting and qRT-PCR, respectively. C and D, Liver extracts containing equal amounts of protein from each regimen were immunoprecipitated with anti-XO antibody and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins using their specific antibodies. The blots were reprobed for XO. The same tissue extracts were also analyzed by western blotting for beta-actin. E, Liver sections of CD-fed WT mice and 12 wks of HFD-fed WT and 12/15-LOX -/- mice were coimmunostained for Albumin and XO. The selected areas in the 3rd column are shown in the 4th column at 40X magnification. F, WT mice were fed with CD or HFD in combination with and without Allopurinol (125 mg/L of drinking water) for 12 wks, and phosphorylation of p38MAPK and CREB were analyzed by western blotting in the liver and the blots were normalized for their total levels. G and H, The protein and RNA from the liver tissue of the mice in panel F were analyzed for Egr1 and DGAT2 protein and mRNA levels by western blotting (G) and qRT-PCR (H), respectively. *, p < 0.05 versus WT mice on CD; **, p < 0.05 versus WT mice o
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn ELISA
ELISA