Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [12]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [4]
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA1-924 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- KCNMB1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- PA1-924 detects large conductance, calcium-activated potassium channel beta (Maxi K+ Beta) from human, mouse, and rat samples. PA1-924 has been successfully used in western blot and immunofluorescence. By western blot, this antibody detects an ~28kDa protein representing Maxi K+ beta from mouse myometrial smooth muscle cell extracts. The molecular weight detected varies due to glycosylation, multimerization and binding to actin. Immunizing peptide corresponds to amino acid residues 90-103 from human Maxi K+ beta. This sequence is completely conserved across many species. PA1-924 immunizing peptide (Cat. # PEP-119) is available for use in neutralization and control experiments.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Different Effects of Hypertension and Age on the Function of Large Conductance Calcium- and Voltage-Activated Potassium Channels in Human Mesentery Artery Smooth Muscle Cells.
Western blot analysis of BK channel β1-subunit expression should be interpreted cautiously when using commercially available antibodies.
Reduced vascular smooth muscle BK channel current underlies heart failure-induced vasoconstriction in mice.
Function of BKCa channels is reduced in human vascular smooth muscle cells from Han Chinese patients with hypertension.
Shear stress-induced volume decrease in C11-MDCK cells by BK-alpha/beta4.
Exercise training attenuates ageing-induced BKCa channel downregulation in rat coronary arteries.
Impaired function of coronary BK(Ca) channels in metabolic syndrome.
Interleukin-4 activates large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium (BKCa) channels in human airway smooth muscle cells.
Altered expression of BK channel beta1 subunit in vascular tissues from spontaneously hypertensive rats.
BK-{beta}1 subunit: immunolocalization in the mammalian connecting tubule and its role in the kaliuretic response to volume expansion.
Somatic localization of a specific large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel subtype controls compartmentalized ethanol sensitivity in the nucleus accumbens.
Downregulation of the BK channel beta1 subunit in genetic hypertension.
Cheng J, Mao L, Wen J, Li PY, Wang N, Tan XQ, Zhang XD, Zeng XR, Xu L, Xia XM, Xia D, He K, Su S, Yao H, Yang Y
Journal of the American Heart Association 2016 Sep 14;5(9)
Journal of the American Heart Association 2016 Sep 14;5(9)
Western blot analysis of BK channel β1-subunit expression should be interpreted cautiously when using commercially available antibodies.
Bhattarai Y, Fernandes R, Kadrofske MM, Lockwood LR, Galligan JJ, Xu H
Physiological reports 2014 Oct 1;2(10)
Physiological reports 2014 Oct 1;2(10)
Reduced vascular smooth muscle BK channel current underlies heart failure-induced vasoconstriction in mice.
Wan E, Kushner JS, Zakharov S, Nui XW, Chudasama N, Kelly C, Waase M, Doshi D, Liu G, Iwata S, Shiomi T, Katchman A, D'Armiento J, Homma S, Marx SO
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2013 May;27(5):1859-67
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2013 May;27(5):1859-67
Function of BKCa channels is reduced in human vascular smooth muscle cells from Han Chinese patients with hypertension.
Yang Y, Li PY, Cheng J, Mao L, Wen J, Tan XQ, Liu ZF, Zeng XR
Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979) 2013 Feb;61(2):519-25
Hypertension (Dallas, Tex. : 1979) 2013 Feb;61(2):519-25
Shear stress-induced volume decrease in C11-MDCK cells by BK-alpha/beta4.
Holtzclaw JD, Liu L, Grimm PR, Sansom SC
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2010 Sep;299(3):F507-16
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2010 Sep;299(3):F507-16
Exercise training attenuates ageing-induced BKCa channel downregulation in rat coronary arteries.
Albarwani S, Al-Siyabi S, Baomar H, Hassan MO
Experimental physiology 2010 Jun;95(6):746-55
Experimental physiology 2010 Jun;95(6):746-55
Impaired function of coronary BK(Ca) channels in metabolic syndrome.
Borbouse L, Dick GM, Asano S, Bender SB, Dincer UD, Payne GA, Neeb ZP, Bratz IN, Sturek M, Tune JD
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2009 Nov;297(5):H1629-37
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2009 Nov;297(5):H1629-37
Interleukin-4 activates large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium (BKCa) channels in human airway smooth muscle cells.
Martin G, O'Connell RJ, Pietrzykowski AZ, Treistman SN, Ethier MF, Madison JM
Experimental physiology 2008 Jul;93(7):908-18
Experimental physiology 2008 Jul;93(7):908-18
Altered expression of BK channel beta1 subunit in vascular tissues from spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Chang T, Wu L, Wang R
American journal of hypertension 2006 Jul;19(7):678-85
American journal of hypertension 2006 Jul;19(7):678-85
BK-{beta}1 subunit: immunolocalization in the mammalian connecting tubule and its role in the kaliuretic response to volume expansion.
Pluznick JL, Wei P, Grimm PR, Sansom SC
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2005 Apr;288(4):F846-54
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2005 Apr;288(4):F846-54
Somatic localization of a specific large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel subtype controls compartmentalized ethanol sensitivity in the nucleus accumbens.
Martin G, Puig S, Pietrzykowski A, Zadek P, Emery P, Treistman S
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2004 Jul 21;24(29):6563-72
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2004 Jul 21;24(29):6563-72
Downregulation of the BK channel beta1 subunit in genetic hypertension.
Amberg GC, Santana LF
Circulation research 2003 Nov 14;93(10):965-71
Circulation research 2003 Nov 14;93(10):965-71
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
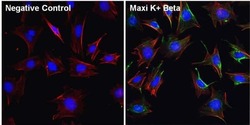
- Experimental details
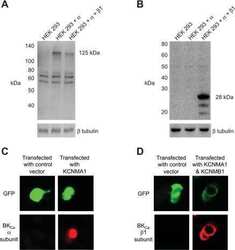
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Maxi K+ Beta (green) in Movas cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a Maxi K+ Beta polyclonal antibody (Product # PA1-924) at a dilution of 1:100 in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). F-actin (red) was stained by Dylight 554 Phalloidin (Product # 21834) and Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Instrument at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
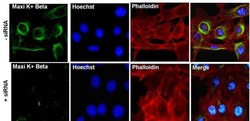
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Maxi K+ Beta (green) in Movas cells transfected with (+) and without (-) Maxi K+ Beta siRNA. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a p38 polyclonal antibody (Product # AHO1202) at a dilution of 1:100 in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). F-actin (red) was stained by Dylight 554 Phalloidin (Product # 21834) and Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific EVOS FL Instrument at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
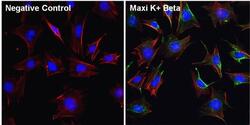
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Maxi K+ Beta (green) in Movas cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a Maxi K+ Beta polyclonal antibody (Product # PA1-924) at a dilution of 1:100 in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). F-actin (red) was stained by Dylight 554 Phalloidin (Product # 21834) and Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ToxInsight Instrument at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
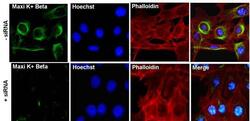
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Maxi K+ Beta (green) in Movas cells transfected with (+) and without (-) Maxi K+ Beta siRNA. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 minutes, and blocked with 3% BSA in PBS (Product # 37525) for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a p38 polyclonal antibody (Product # AHO1202) at a dilution of 1:100 in staining buffer for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). F-actin (red) was stained by Dylight 554 Phalloidin (Product # 21834) and Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific EVOS FL Instrument at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
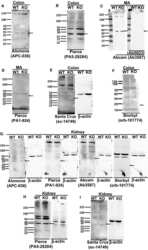
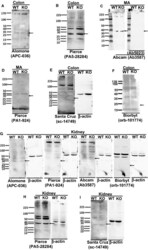
- Figure 1. Representative western blot obtained using anti-BK beta 1-subunit antibodies in MA, colonic, or kidney tissues from WT and BK beta 1-KO mice, (A) Alomone Labs (APC-036), (B) Pierce (PA5-28284), and (C) Abcam (Ab3587) antibodies detected a protein band at ~28 kDa or ~38 kDa in colons or MA from both mice. The bands in Abcam sets were diminished after preincubation of the primary antibody with the competing peptide. (D) Pierce (PA1-924), (E) Santa Cruz (sc-14749), and (F) Biorbyt (orb-101774) antibodies did not detect any band at ~28 kDa or ~21 kDa in MA or colons from WT mice. (G) Alomone Labs (APC-036), Pierce (PA1-924), Abcam (Ab3587), and Biorbyt (Orb-101774) antibodies did not detect protein band at ~28 kDa, ~38 kDa, or ~21 kDa in kidneys from WT mice. (H) Pierce (PA5-28284) and (I) Santa Cruz (sc-14749) antibodies detected the protein band at ~28 kDa in kidneys from both mice. beta -actin was reblotted on each membrane after anti-BK beta 1-subunit antibody was stripped. All representative blot images from kidney are in the tissue from same WT or BK beta 1-KO mouse, and blotted with primary anti-BK beta 1-subunit antibody at 1:200. Arrows indicate the manufacturer's recommended molecular weight of BK beta 1-subunit protein.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
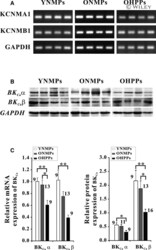
- Messenger RNA s and proteins of KCNMA 1 and KCNMB 1 in human mesenteric cells. A, Images from relative quantification in reverse transcripitioin polymerase chain reaction. B, Protein expression of BK C a subunits alpha and beta1 with Western blot analysis. C, Mean values of mRNA and protein expression of KCNMA 1 and KCNMB 1 in human mesenteric cells from YNMPs , ONMPs , and OHPPs (* P
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry