Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [12]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-11741 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Rhodopsin Monoclonal Antibody (RET-P1)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- MA5-11741 targets Rhodopsin in immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry (paraffin) and Western blot applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, and rat samples. The MA5-11741 immunogen is membrane preparation from adult rat retina.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- RET-P1
- Vial size
- 500 μL
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references A Splicing Mutation in Slc4a5 Results in Retinal Detachment and Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction.
Rai1 frees mice from the repression of active wake behaviors by light.
Retinal Pigment Epithelium Atrophy 1 (rpea1): A New Mouse Model With Retinal Detachment Caused by a Disruption of Protein Kinase C, θ.
Effect of purified murine NGF on isolated photoreceptors of a rodent developing retinitis pigmentosa.
Proliferation of the ciliary epithelium with retinal neuronal and photoreceptor cell differentiation in human eyes with retinal detachment and proliferative vitreoretinopathy.
Identification and functional analysis of the vision-specific BBS3 (ARL6) long isoform.
Characterization of a canine model of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa due to a PDE6A mutation.
A Critical role for Bim in retinal ganglion cell death.
Retinal incorporation and differentiation of neural precursors derived from human embryonic stem cells.
Conversion of mammalian Müller glial cells into a neuronal lineage by in vitro aggregate-culture.
Late development of vitelliform lesions and flecks in a patient with best disease: clinicopathologic correlation.
Detailed histopathologic characterization of the retinopathy, globe enlarged (rge) chick phenotype.
Collin GB, Shi L, Yu M, Akturk N, Charette JR, Hyde LF, Weatherly SM, Pera MF, Naggert JK, Peachey NS, Nishina PM, Krebs MP
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Feb 17;23(4)
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Feb 17;23(4)
Rai1 frees mice from the repression of active wake behaviors by light.
Diessler S, Kostic C, Arsenijevic Y, Kawasaki A, Franken P
eLife 2017 May 26;6
eLife 2017 May 26;6
Retinal Pigment Epithelium Atrophy 1 (rpea1): A New Mouse Model With Retinal Detachment Caused by a Disruption of Protein Kinase C, θ.
Ji X, Liu Y, Hurd R, Wang J, Fitzmaurice B, Nishina PM, Chang B
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2016 Mar;57(3):877-88
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2016 Mar;57(3):877-88
Effect of purified murine NGF on isolated photoreceptors of a rodent developing retinitis pigmentosa.
Rocco ML, Balzamino BO, Petrocchi Passeri P, Micera A, Aloe L
PloS one 2015;10(4):e0124810
PloS one 2015;10(4):e0124810
Proliferation of the ciliary epithelium with retinal neuronal and photoreceptor cell differentiation in human eyes with retinal detachment and proliferative vitreoretinopathy.
Ducournau Y, Boscher C, Adelman RA, Guillaubey C, Schmidt-Morand D, Mosnier JF, Ducournau D
Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 2012 Mar;250(3):409-23
Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 2012 Mar;250(3):409-23
Identification and functional analysis of the vision-specific BBS3 (ARL6) long isoform.
Pretorius PR, Baye LM, Nishimura DY, Searby CC, Bugge K, Yang B, Mullins RF, Stone EM, Sheffield VC, Slusarski DC
PLoS genetics 2010 Mar 19;6(3):e1000884
PLoS genetics 2010 Mar 19;6(3):e1000884
Characterization of a canine model of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa due to a PDE6A mutation.
Tuntivanich N, Pittler SJ, Fischer AJ, Omar G, Kiupel M, Weber A, Yao S, Steibel JP, Khan NW, Petersen-Jones SM
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2009 Feb;50(2):801-13
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2009 Feb;50(2):801-13
A Critical role for Bim in retinal ganglion cell death.
McKernan DP, Cotter TG
Journal of neurochemistry 2007 Aug;102(3):922-30
Journal of neurochemistry 2007 Aug;102(3):922-30
Retinal incorporation and differentiation of neural precursors derived from human embryonic stem cells.
Banin E, Obolensky A, Idelson M, Hemo I, Reinhardtz E, Pikarsky E, Ben-Hur T, Reubinoff B
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2006 Feb;24(2):246-57
Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 2006 Feb;24(2):246-57
Conversion of mammalian Müller glial cells into a neuronal lineage by in vitro aggregate-culture.
Kubota A, Nishida K, Nakashima K, Tano Y
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2006 Dec 15;351(2):514-20
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2006 Dec 15;351(2):514-20
Late development of vitelliform lesions and flecks in a patient with best disease: clinicopathologic correlation.
Mullins RF, Oh KT, Heffron E, Hageman GS, Stone EM
Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) 2005 Nov;123(11):1588-94
Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) 2005 Nov;123(11):1588-94
Detailed histopathologic characterization of the retinopathy, globe enlarged (rge) chick phenotype.
Montiani-Ferreira F, Fischer A, Cernuda-Cernuda R, Kiupel M, DeGrip WJ, Sherry D, Cho SS, Shaw GC, Evans MG, Hocking PM, Petersen-Jones SM
Molecular vision 2005 Jan 13;11:11-27
Molecular vision 2005 Jan 13;11:11-27
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
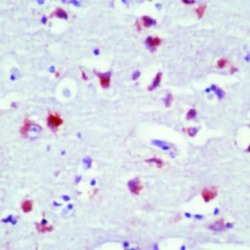
- Experimental details
- Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human brain stained with Rhodopsin antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and AEC chromogen. Note cytoplasmic staining of neurons.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
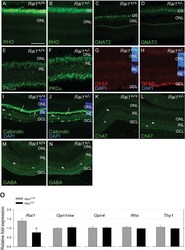
- Experimental details
- Figure 9. Retinal protein and gene expression levels were normal in Rai1 +/- mice. Immunostaining for Rhodopsin protein ( A, B ), the cone protein GNAT2 ( C, D ), the bipolar protein PKCa ( E, F ), the Muller cell protein GFAP ( G, H ), and Calbindin ( I, J ), ChAT ( K, L ), and GABA ( M, N ) markers did not differ between Rai1 +/- ( B, D, F, H, J, L, N ) and Rai1 +/+ mice ( A, C, E, G, I, K, M ). As expected, rhodopsin was mainly localized in outer-segments of rods ( A, B ) and GNAT2 in cone cells ( C, D ). PKCa labeled whole ON bipolar cells with both dendrite and synapse structure ( E, F ). GFAP expression was restricted to the foot of Muller cells not extending to their cell bodies that show no activation in these retinal cells ( G, H ). Calbindin was expressed in horizontal cells (arrows) and some amacrine cells (arrowhead) as well as in ganglion cells located in the GCL ( I, J ). Three strata of connections (star) were well labeled by calbindin in both genotypes in the layer connecting the INL and GCL layers. Both ChAT ( K, L ) and GABA ( M, N ) labeled subpopulations of amacrine cells (arrowheads) and different strata of connections (star) in a pattern similar for Rai1 +/- ( L, N ) and Rai1 +/+ ( K, M ) mice. White horizontal bars represents 50 um in A, B, E, F, G, and H and 100 um in C, D, and I through M. OS: outer-segments; ONL: outer-nuclear layer; INL: inner-nuclear layer; GCL: ganglion cell layer; RHO: rhodopsin in green; GNAT2: G-protein subunit alpha transducin
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
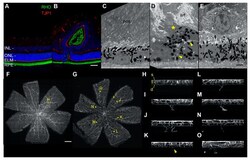
- Experimental details
- Fluorescence and electron microscopy analysis of control and tvrm77 mice at 1 month of age. ( A , B ) Fluorescence microscopy of ( A ) B6 (n = 4) and ( B ) tvrm77 (n = 5) mice with antibodies against rhodopsin (RHO) and ELM protein TJP1. Scale bar in B , 50 um, applies to ( A , B ). ( C - E ) TEM of B6 (n = 4) and tvrm77 (n = 5) posterior eyecups. Representative TEM of B6 samples ( C ) reveals normal apposition of photoreceptor outer segments (pos) with RPE cells. Nuclei, n. In tvrm77 eyecups ( D , E ), subretinal fluid (srf) and debris (asterisk) accumulate above a region of RPE perturbation. A cell boundary (yellow arrowheads) can be seen separating the primary RPE layer from a displaced RPE cell or cellular process. In ( E ), a nucleated cell, likely an immune cell, lies at the retina-RPE interface. Scale bar in I, 2 um, applies to ( C , D ) . ( F , G ) Maximum intensity projections of retinal flatmounts (n = 6) of B6 ( F ) or tvrm77 ( G ) mice stained with isolectin B4. Yellow dots indicate regions selected for orthogonal display in panels ( H - O ). Scale bar in ( F ), 0.5 mm, applies to ( G ). ( H ) Orthogonal maximum intensity projection of a 0.3 mm square region of interest in panel ( F ). Normal superficial (s), intermediate (i), and deep (d) vascular beds appear in B6 retinas. ( I - O ) Projections of all detected neovascular lesions from the tvrm77 retina in G are shown. The vessels appear to originate from the deep vascular bed and migrate toward the outer retina.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry