Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [15]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA024629 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA024629, RRID:AB_1668927
- Product name
- Anti-KLF17
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human KLF17, Gene description: Kruppel-like factor 17, Alternative Gene Names: FLJ40160, Zfp393, ZNF393, Validated applications: IHC, WB, Uniprot ID: Q5JT82, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references The emergence of human gastrulation upon in vitro attachment.
Human early syncytiotrophoblasts are highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection
BRD9-containing non-canonical BAF complex maintains somatic cell transcriptome and acts as a barrier to human reprogramming
Genome-wide screening identifies Polycomb repressive complex 1.3 as an essential regulator of human naïve pluripotent cell reprogramming.
Human naive epiblast cells possess unrestricted lineage potential
Principles of signaling pathway modulation for enhancing human naive pluripotency induction.
The pluripotent stem cell-specific transcript ESRG is dispensable for human pluripotency.
Naive stem cell blastocyst model captures human embryo lineage segregation.
Temporal activation of LRH‐1 and RAR‐γ in human pluripotent stem cells induces a functional naïve‐like state
Wnt Inhibition Facilitates RNA-Mediated Reprogramming of Human Somatic Cells to Naive Pluripotency.
TFAP2C regulates transcription in human naive pluripotency by opening enhancers
Reduced MEK inhibition preserves genomic stability in naive human embryonic stem cells
Comprehensive Cell Surface Protein Profiling Identifies Specific Markers of Human Naive and Primed Pluripotent States.
Tankyrase inhibition promotes a stable human naïve pluripotent state with improved functionality
Defining the three cell lineages of the human blastocyst by single-cell RNA-seq
De Santis R, Rice E, Croft G, Yang M, Rosado-Olivieri EA, Brivanlou AH
Stem cell reports 2024 Jan 9;19(1):41-53
Stem cell reports 2024 Jan 9;19(1):41-53
Human early syncytiotrophoblasts are highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection
Ruan D, Ye Z, Yuan S, Li Z, Zhang W, Ong C, Tang K, Ka Ki Tam T, Guo J, Xuan Y, Huang Y, Zhang Q, Lee C, Lu L, Chiu P, Yeung W, Liu F, Jin D, Liu P
Cell Reports Medicine 2022;3(12):100849
Cell Reports Medicine 2022;3(12):100849
BRD9-containing non-canonical BAF complex maintains somatic cell transcriptome and acts as a barrier to human reprogramming
Sevinç K, Sevinç G, Cavga A, Philpott M, Kelekçi S, Can H, Cribbs A, Yıldız A, Yılmaz A, Ayar E, Arabacı D, Dunford J, Ata D, Sigua L, Qi J, Oppermann U, Onder T
Stem Cell Reports 2022;17(12):2629-2642
Stem Cell Reports 2022;17(12):2629-2642
Genome-wide screening identifies Polycomb repressive complex 1.3 as an essential regulator of human naïve pluripotent cell reprogramming.
Collier AJ, Bendall A, Fabian C, Malcolm AA, Tilgner K, Semprich CI, Wojdyla K, Nisi PS, Kishore K, Roamio Franklin VN, Mirshekar-Syahkal B, D'Santos C, Plath K, Yusa K, Rugg-Gunn PJ
Science advances 2022 Mar 25;8(12):eabk0013
Science advances 2022 Mar 25;8(12):eabk0013
Human naive epiblast cells possess unrestricted lineage potential
Guo G, Stirparo G, Strawbridge S, Spindlow D, Yang J, Clarke J, Dattani A, Yanagida A, Li M, Myers S, Özel B, Nichols J, Smith A
Cell Stem Cell 2021;28(6):1040-1056.e6
Cell Stem Cell 2021;28(6):1040-1056.e6
Principles of signaling pathway modulation for enhancing human naive pluripotency induction.
Bayerl J, Ayyash M, Shani T, Manor YS, Gafni O, Massarwa R, Kalma Y, Aguilera-Castrejon A, Zerbib M, Amir H, Sheban D, Geula S, Mor N, Weinberger L, Naveh Tassa S, Krupalnik V, Oldak B, Livnat N, Tarazi S, Tawil S, Wildschutz E, Ashouokhi S, Lasman L, Rotter V, Hanna S, Ben-Yosef D, Novershtern N, Viukov S, Hanna JH
Cell stem cell 2021 Sep 2;28(9):1549-1565.e12
Cell stem cell 2021 Sep 2;28(9):1549-1565.e12
The pluripotent stem cell-specific transcript ESRG is dispensable for human pluripotency.
Takahashi K, Nakamura M, Okubo C, Kliesmete Z, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Watanabe A, Ueda M, Takashima Y, Hellmann I, Yamanaka S
PLoS genetics 2021 May;17(5):e1009587
PLoS genetics 2021 May;17(5):e1009587
Naive stem cell blastocyst model captures human embryo lineage segregation.
Yanagida A, Spindlow D, Nichols J, Dattani A, Smith A, Guo G
Cell stem cell 2021 Jun 3;28(6):1016-1022.e4
Cell stem cell 2021 Jun 3;28(6):1016-1022.e4
Temporal activation of LRH‐1 and RAR‐γ in human pluripotent stem cells induces a functional naïve‐like state
Taei A, Kiani T, Taghizadeh Z, Moradi S, Samadian A, Mollamohammadi S, Sharifi‐Zarchi A, Guenther S, Akhlaghpour A, Asgari Abibeiglou B, Najar‐Asl M, Karamzadeh R, Khalooghi K, Braun T, Hassani S, Baharvand H
EMBO reports 2020;21(10)
EMBO reports 2020;21(10)
Wnt Inhibition Facilitates RNA-Mediated Reprogramming of Human Somatic Cells to Naive Pluripotency.
Bredenkamp N, Yang J, Clarke J, Stirparo GG, von Meyenn F, Dietmann S, Baker D, Drummond R, Ren Y, Li D, Wu C, Rostovskaya M, Eminli-Meissner S, Smith A, Guo G
Stem cell reports 2019 Dec 10;13(6):1083-1098
Stem cell reports 2019 Dec 10;13(6):1083-1098
TFAP2C regulates transcription in human naive pluripotency by opening enhancers
Pastor W, Liu W, Chen D, Ho J, Kim R, Hunt T, Lukianchikov A, Liu X, Polo J, Jacobsen S, Clark A
Nature Cell Biology 2018;20(5):553-564
Nature Cell Biology 2018;20(5):553-564
Reduced MEK inhibition preserves genomic stability in naive human embryonic stem cells
Di Stefano B, Ueda M, Sabri S, Brumbaugh J, Huebner A, Sahakyan A, Clement K, Clowers K, Erickson A, Shioda K, Gygi S, Gu H, Shioda T, Meissner A, Takashima Y, Plath K, Hochedlinger K
Nature Methods 2018;15(9):732-740
Nature Methods 2018;15(9):732-740
Comprehensive Cell Surface Protein Profiling Identifies Specific Markers of Human Naive and Primed Pluripotent States.
Collier AJ, Panula SP, Schell JP, Chovanec P, Plaza Reyes A, Petropoulos S, Corcoran AE, Walker R, Douagi I, Lanner F, Rugg-Gunn PJ
Cell stem cell 2017 Jun 1;20(6):874-890.e7
Cell stem cell 2017 Jun 1;20(6):874-890.e7
Tankyrase inhibition promotes a stable human naïve pluripotent state with improved functionality
Zimmerlin L, Park T, Huo J, Verma K, Pather S, Talbot C, Agarwal J, Steppan D, Zhang Y, Considine M, Guo H, Zhong X, Gutierrez C, Cope L, Canto-Soler M, Friedman A, Baylin S, Zambidis E
Development 2016;143(23):4368-4380
Development 2016;143(23):4368-4380
Defining the three cell lineages of the human blastocyst by single-cell RNA-seq
Blakeley P, Fogarty N, del Valle I, Wamaitha S, Hu T, Elder K, Snell P, Christie L, Robson P, Niakan K
Development 2015
Development 2015
No comments: Submit comment
Enhanced validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Recombinant expression validation
- Main image
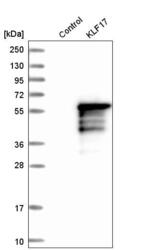
- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis in control (vector only transfected HEK293T lysate) and KLF17 over-expression lysate (Co-expressed with a C-terminal myc-DDK tag (~3.1 kDa) in mammalian HEK293T cells, LY406601).
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Orthogonal validation
- Main image
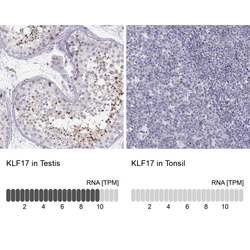
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis in human testis and tonsil tissues using HPA024629 antibody. Corresponding KLF17 RNA-seq data are presented for the same tissues.
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry