Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [26]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunoprecipitation [1]
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA3-017 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- HSF1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- PA3-017 detects heat shock factor 1 (HSF-1) from human, mouse and rat tissues and cells. PA3-017 has been successfully used in Western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, ELISA, and gel super shift protocols. By Western blot, this antibody detects an ~83 kDa protein representing HSF-1 from NIH-3T3 cell lysate. The PA3-017 immunogen is recombinant human HSF-1 protein expressed in E. coli.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- Conc. Not Determined
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Basic Limonoid modulates Chaperone-mediated Proteostasis and dissolve Tau fibrils.
Targeted production of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria to overcome cancer drug resistance.
Response of small heat shock proteins in diabetic rat retina.
Heat shock protein accumulation and heat shock transcription factor activation in rat skeletal muscle during compensatory hypertrophy.
A comparison of Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta interactions with cochaperones and substrates.
Heat shock factor 2 (HSF2) contributes to inducible expression of hsp genes through interplay with HSF1.
Cadmium-responsive element of the human heme oxygenase-1 gene mediates heat shock factor 1-dependent transcriptional activation.
Castration inhibits exercise-induced accumulation of Hsp70 in male rodent hearts.
Phase I trial of 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in patients with advanced cancer.
Estrogen, heat shock proteins, and NFkappaB in human vascular endothelium.
Developmentally dictated expression of heat shock factors: exclusive expression of HSF4 in the postnatal lens and its specific interaction with alphaB-crystallin heat shock promoter.
Enhancement of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated gene expression by constitutively active heat shock factor 1.
Exercise improves postischemic cardiac function in males but not females: consequences of a novel sex-specific heat shock protein 70 response.
Interspecific- and acclimation-induced variation in levels of heat-shock proteins 70 (hsp70) and 90 (hsp90) and heat-shock transcription factor-1 (HSF1) in congeneric marine snails (genus Tegula): implications for regulation of hsp gene expression.
Estrogen attenuates postexercise HSP70 expression in skeletal muscle.
Transcriptional activation domains of human heat shock factor 1 recruit human SWI/SNF.
The myocardial heat shock response following sodium salicylate treatment.
Activation of HSF and selective increase in heat-shock proteins by acute dexamethasone treatment.
Activation of HSF and selective increase in heat-shock proteins by acute dexamethasone treatment.
Higher induction of heat shock protein 72 by heat stress in cisplatin-resistant than in cisplatin-sensitive cancer cells.
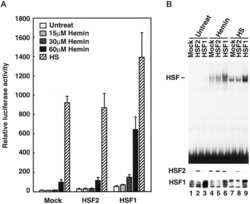
Heat shock factor 1 mediates hemin-induced hsp70 gene transcription in K562 erythroleukemia cells.
Heat shock transcription factor 1 binds selectively in vitro to Ku protein and the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase.
Diminished heat shock response in the aged myocardium.
Human heat shock factors 1 and 2 are differentially activated and can synergistically induce hsp70 gene transcription.
Arachidonate is a potent modulator of human heat shock gene transcription.
Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper.
Gorantla NV, Das R, Chidambaram H, Dubey T, Mulani FA, Thulasiram HV, Chinnathambi S
Scientific reports 2020 Mar 4;10(1):4023
Scientific reports 2020 Mar 4;10(1):4023
Targeted production of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria to overcome cancer drug resistance.
Wang H, Gao Z, Liu X, Agarwal P, Zhao S, Conroy DW, Ji G, Yu J, Jaroniec CP, Liu Z, Lu X, Li X, He X
Nature communications 2018 Feb 8;9(1):562
Nature communications 2018 Feb 8;9(1):562
Response of small heat shock proteins in diabetic rat retina.
Reddy VS, Raghu G, Reddy SS, Pasupulati AK, Suryanarayana P, Reddy GB
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2013 Nov 19;54(12):7674-82
Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 2013 Nov 19;54(12):7674-82
Heat shock protein accumulation and heat shock transcription factor activation in rat skeletal muscle during compensatory hypertrophy.
Locke M
Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 2008 Mar;192(3):403-11
Acta physiologica (Oxford, England) 2008 Mar;192(3):403-11
A comparison of Hsp90alpha and Hsp90beta interactions with cochaperones and substrates.
Taherian A, Krone PH, Ovsenek N
Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 2008 Feb;86(1):37-45
Biochemistry and cell biology = Biochimie et biologie cellulaire 2008 Feb;86(1):37-45
Heat shock factor 2 (HSF2) contributes to inducible expression of hsp genes through interplay with HSF1.
Ostling P, Björk JK, Roos-Mattjus P, Mezger V, Sistonen L
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7077-86
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Mar 9;282(10):7077-86
Cadmium-responsive element of the human heme oxygenase-1 gene mediates heat shock factor 1-dependent transcriptional activation.
Koizumi S, Gong P, Suzuki K, Murata M
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Mar 23;282(12):8715-23
The Journal of biological chemistry 2007 Mar 23;282(12):8715-23
Castration inhibits exercise-induced accumulation of Hsp70 in male rodent hearts.
Milne KJ, Thorp DB, Melling CW, Noble EG
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2006 Apr;290(4):H1610-6
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2006 Apr;290(4):H1610-6
Phase I trial of 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in patients with advanced cancer.
Goetz MP, Toft D, Reid J, Ames M, Stensgard B, Safgren S, Adjei AA, Sloan J, Atherton P, Vasile V, Salazaar S, Adjei A, Croghan G, Erlichman C
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2005 Feb 20;23(6):1078-87
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2005 Feb 20;23(6):1078-87
Estrogen, heat shock proteins, and NFkappaB in human vascular endothelium.
Hamilton KL, Mbai FN, Gupta S, Knowlton AA
Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2004 Sep;24(9):1628-33
Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2004 Sep;24(9):1628-33
Developmentally dictated expression of heat shock factors: exclusive expression of HSF4 in the postnatal lens and its specific interaction with alphaB-crystallin heat shock promoter.
Somasundaram T, Bhat SP
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Oct 22;279(43):44497-503
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Oct 22;279(43):44497-503
Enhancement of glucocorticoid receptor-mediated gene expression by constitutively active heat shock factor 1.
Jones TJ, Li D, Wolf IM, Wadekar SA, Periyasamy S, Sánchez ER
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Mar;18(3):509-20
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2004 Mar;18(3):509-20
Exercise improves postischemic cardiac function in males but not females: consequences of a novel sex-specific heat shock protein 70 response.
Paroo Z, Haist JV, Karmazyn M, Noble EG
Circulation research 2002 May 3;90(8):911-7
Circulation research 2002 May 3;90(8):911-7
Interspecific- and acclimation-induced variation in levels of heat-shock proteins 70 (hsp70) and 90 (hsp90) and heat-shock transcription factor-1 (HSF1) in congeneric marine snails (genus Tegula): implications for regulation of hsp gene expression.
Tomanek L, Somero GN
The Journal of experimental biology 2002 Mar;205(Pt 5):677-85
The Journal of experimental biology 2002 Mar;205(Pt 5):677-85
Estrogen attenuates postexercise HSP70 expression in skeletal muscle.
Paroo Z, Dipchand ES, Noble EG
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2002 Feb;282(2):C245-51
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2002 Feb;282(2):C245-51
Transcriptional activation domains of human heat shock factor 1 recruit human SWI/SNF.
Sullivan EK, Weirich CS, Guyon JR, Sif S, Kingston RE
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Sep;21(17):5826-37
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Sep;21(17):5826-37
The myocardial heat shock response following sodium salicylate treatment.
Locke M, Atance J
Cell stress & chaperones 2000 Oct;5(4):359-68
Cell stress & chaperones 2000 Oct;5(4):359-68
Activation of HSF and selective increase in heat-shock proteins by acute dexamethasone treatment.
Sun L, Chang J, Kirchhoff SR, Knowlton AA
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2000 Apr;278(4):H1091-7
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2000 Apr;278(4):H1091-7
Activation of HSF and selective increase in heat-shock proteins by acute dexamethasone treatment.
Sun L, Chang J, Kirchhoff SR, Knowlton AA
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2000 Apr;278(4):H1091-7
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2000 Apr;278(4):H1091-7
Higher induction of heat shock protein 72 by heat stress in cisplatin-resistant than in cisplatin-sensitive cancer cells.
Abe T, Gotoh S, Higashi K
Biochimica et biophysica acta 1999 Apr 14;1445(1):123-33
Biochimica et biophysica acta 1999 Apr 14;1445(1):123-33
Heat shock factor 1 mediates hemin-induced hsp70 gene transcription in K562 erythroleukemia cells.
Yoshima T, Yura T, Yanagi H
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Sep 25;273(39):25466-71
The Journal of biological chemistry 1998 Sep 25;273(39):25466-71
Heat shock transcription factor 1 binds selectively in vitro to Ku protein and the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase.
Huang J, Nueda A, Yoo S, Dynan WS
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Oct 10;272(41):26009-16
The Journal of biological chemistry 1997 Oct 10;272(41):26009-16
Diminished heat shock response in the aged myocardium.
Locke M, Tanguay RM
Cell stress & chaperones 1996 Dec;1(4):251-60
Cell stress & chaperones 1996 Dec;1(4):251-60
Human heat shock factors 1 and 2 are differentially activated and can synergistically induce hsp70 gene transcription.
Sistonen L, Sarge KD, Morimoto RI
Molecular and cellular biology 1994 Mar;14(3):2087-99
Molecular and cellular biology 1994 Mar;14(3):2087-99
Arachidonate is a potent modulator of human heat shock gene transcription.
Jurivich DA, Sistonen L, Sarge KD, Morimoto RI
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2280-4
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2280-4
Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper.
Rabindran SK, Haroun RI, Clos J, Wisniewski J, Wu C
Science (New York, N.Y.) 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230-4
Science (New York, N.Y.) 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230-4
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
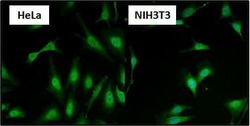
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) (green) in HeLa and NIH3T3 cells. Formalin fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 1% Blocker BSA (Product # 37525) for 15 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017), at a dilution of 1:50 for at least 1 hour at room temperature, washed with PBS, and incubated with DyLight 488 goat-anti rabbit IgG secondary antibody (Product # 35552) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ArrayScan at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
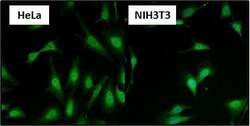
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) (green) in HeLa and NIH3T3 cells. Formalin fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 1% Blocker BSA (Product # 37525) for 15 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017), at a dilution of 1:50 for at least 1 hour at room temperature, washed with PBS, and incubated with DyLight 488 goat-anti rabbit IgG secondary antibody (Product # 35552) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ArrayScan at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
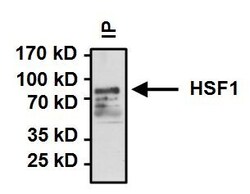
- Experimental details
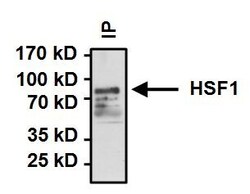
- Immunoprecipitation of Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF 1) was performed on HeLa cells. Antigen:antibody complexes were formed by incubating 500µg whole cell lysate with 2µl of HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017) overnight on a rocking platform at 4°C. Immune complexes were captured on 50µl Protein A/G Plus Agarose (Product # 20423), washed extensively, and eluted with 5X Lane Marker Reducing Sample Buffer (Product # 39000). Samples were resolved on a 4-20% Tris-HCl polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blocked with 5% BSA/TBST for at least 1 hour. The membrane was probed with a HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017) at a dilution of 1:1000 overnight rotating at 4°C, washed in TBST, and probed with Clean Blot IP Detection Reagent-HRP (Product # 21232) at a dilution of 1:1000 for at least one hour. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using SuperSignal West Dura (Product # 34075).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Immunoprecipitation of Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF 1) was performed on HeLa cells. Antigen:antibody complexes were formed by incubating 500µg whole cell lysate with 2µl of HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017) overnight on a rocking platform at 4°C. Immune complexes were captured on 50µl Protein A/G Plus Agarose (Product # 20423), washed extensively, and eluted with 5X Lane Marker Reducing Sample Buffer (Product # 39000). Samples were resolved on a 4-20% Tris-HCl polyacrylamide gel, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and blocked with 5% BSA/TBST for at least 1 hour. The membrane was probed with a HSF1 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA3-017) at a dilution of 1:1000 overnight rotating at 4°C, washed in TBST, and probed with Clean Blot IP Detection Reagent-HRP (Product # 21232) at a dilution of 1:1000 for at least one hour. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using SuperSignal West Dura (Product # 34075).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
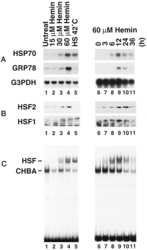
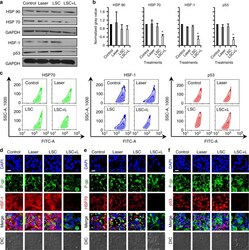
- Fig. 8 Possible mechanisms of the LSC + L treatment in sensitizing the drug-resistant cells to cancer therapy. a Qualitative western blot data of heat shock protein 90 and 70 (HSP90 and HSP70), heat shock factor-1 (HSF-1), and mutant p53 proteins, showing decreased expression of HSP70, HSF-1, and mutant p53 after the treatment of LSC nanoparticles and NIR laser irradiation (LSC + L). b Quantitative data of the western blot results, showing the decreased expression of HSP70, HSF-1, and mutant p53 in the NCI/RES-ADR cells with the LSC + L treatment is statistically significant. Error bars represent s.d. ( n = 3). * p < 0.05 (Kruskal-Wallis H-test). c Flow cytometry analysis showing decreased expression of HSP70, HSF-1, and mutant p53 in NCI/RES-ADR cells treated with LSC nanoparticles and NIR laser irradiation. d Confocal images of HSF-1 showing the HSF-1 distributes in both nuclei and cytoplasm. e Confocal images of HSF70 showing the HSF70 mainly distributes in cytoplasm. f Confocal images of mutant p53 show the mutant p53 mainly distributes in nuclei. The distribution of P-gp is similar to that shown in Fig. 4a . No treatment (laser or nanoparticle) was conducted on the cells in the control group. The cells were permeabilized for the flow cytometry and confocal analyses. The NIR laser irradiation was at 1 W cm -2 for 1 min. The concentration of LSC nanoparticles used for the LSC or LSC + L groups was 0.2 mg ml -1 . Scale bars: 20 mum
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry