MA1-80734
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: GZMB
CCPI, CGL-1, CGL1, CSP-B, CSPB, CTLA1, CTSGL1, HLP, SECT
 Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [63]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Other assay [7]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA1-80734 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Granzyme B Monoclonal Antibody (GB11)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- Membrane permeabilization is required for flow cytometry applications. For FACS analysis, use 10 µL of the suggested working dilution to label 1x10^6 cells in 100 µL. Mouse anti Granzyme B antibody, clone GB11 recognizes the serine protease Granzyme B, which is important in the induction of apoptosis in target cells by cytolytic lymphocytes (CTLs).
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- GB11
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Lymph node CXCR5+ NK cells associate with control of chronic SHIV infection.
Selection of tumor‑resistant variants following sustained natural killer cell‑mediated immune stress.
TIGIT limits immune pathology during viral infections.
Comprehensive Analysis of the Immune and Stromal Compartments of the CNS in EAE Mice Reveal Pathways by Which Chloroquine Suppresses Neuroinflammation.
Protection of Batf3-deficient mice from experimental cerebral malaria correlates with impaired cytotoxic T-cell responses and immune regulation.
Human γδ T-cell receptor repertoire is shaped by influenza viruses, age and tissue compartmentalisation.
CD56 expression in breast cancer induces sensitivity to natural killer-mediated cytotoxicity by enhancing the formation of cytotoxic immunological synapse.
TLR2 Stimulation Increases Cellular Metabolism in CD8(+) T Cells and Thereby Enhances CD8(+) T Cell Activation, Function, and Antiviral Activity.
Multiplexed imaging of immune cells in staged multiple sclerosis lesions by mass cytometry.
Long-term outcomes of a phase I study of agonist CD40 antibody and CTLA-4 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma.
Mass cytometry reveals innate lymphoid cell differentiation pathways in the human fetal intestine.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ inhibition promotes antitumor responses but antagonizes checkpoint inhibitors.
Canonical TGF-β Signaling Pathway Represses Human NK Cell Metabolism.
Human CD40 ligand-expressing type 3 innate lymphoid cells induce IL-10-producing immature transitional regulatory B cells.
Early IL-6 signalling promotes IL-27 dependent maturation of regulatory T cells in the lungs and resolution of viral immunopathology.
Low-dose interleukin-2 promotes STAT-5 phosphorylation, T(reg) survival and CTLA-4-dependent function in autoimmune liver diseases.
Systems-guided forward genetic screen reveals a critical role of the replication stress response protein ETAA1 in T cell clonal expansion.
Perturbed CD8(+) T cell TIGIT/CD226/PVR axis despite early initiation of antiretroviral treatment in HIV infected individuals.
NKG2C/E Marks the Unique Cytotoxic CD4 T Cell Subset, ThCTL, Generated by Influenza Infection.
Type 1 interferon licenses naïve CD8 T cells to mediate anti-viral cytotoxicity.
Graded Foxo1 activity in Treg cells differentiates tumour immunity from spontaneous autoimmunity.
Nonapoptotic and extracellular activity of granzyme B mediates resistance to regulatory T cell (Treg) suppression by HLA-DR-CD25hiCD127lo Tregs in multiple sclerosis and in response to IL-6.
Activated regulatory T cells suppress effector NK cell responses by an IL-2-mediated mechanism during an acute retroviral infection.
Therapeutic antiviral T cells noncytopathically clear persistently infected microglia after conversion into antigen-presenting cells.
The Interferon-Stimulated Gene Ifi27l2a Restricts West Nile Virus Infection and Pathogenesis in a Cell-Type- and Region-Specific Manner.
Immunological Outcome in Haploidentical-HSC Transplanted Patients Treated with IL-10-Anergized Donor T Cells.
Out-of-sequence signal 3 as a mechanism for virus-induced immune suppression of CD8 T cell responses.
Midline 1 directs lytic granule exocytosis and cytotoxicity of mouse killer T cells.
Immunomodulatory action of SGI-110, a hypomethylating agent, in acute myeloid leukemia cells and xenografts.
GPR18 is required for a normal CD8αα intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte compartment.
Rapid proliferation and differentiation impairs the development of memory CD8+ T cells in early life.
The phenotype and activation status of regulatory T cells during Friend retrovirus infection.
Role of NK cells in host defense against pulmonary type A Francisella tularensis infection.
CD4+ T cells develop antiretroviral cytotoxic activity in the absence of regulatory T cells and CD8+ T cells.
FoxO1 controls effector-to-memory transition and maintenance of functional CD8 T cell memory.
Arf-like GTPase Arl8b regulates lytic granule polarization and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
IL-7 and IL-15 do not synergize during CD8 T cell recall response against an obligate intracellular parasite.
TGF-β signaling to T cells inhibits autoimmunity during lymphopenia-driven proliferation.
Chronic HIV infection affects the expression of the 2 transcription factors required for CD8 T-cell differentiation into cytolytic effectors.
An optimized SIV DNA vaccine can serve as a boost for Ad5 and provide partial protection from a high-dose SIVmac251 challenge.
Cutting edge: tumor-targeting antibodies enhance NKG2D-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity by stabilizing NK cell-tumor cell interactions.
Primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection limits replication but not lung inflammation upon homologous rechallenge.
DOCK8 deficiency impairs CD8 T cell survival and function in humans and mice.
Virus-specific CD8+ T cells upregulate programmed death-1 expression during acute friend retrovirus infection but are highly cytotoxic and control virus replication.
A CD8α(-) subpopulation of macaque circulatory natural killer cells can mediate both antibody-dependent and antibody-independent cytotoxic activities.
The magnitude of the T cell response to a clinically significant dose of influenza virus is regulated by TRAIL.
Early induction of polyfunctional simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific T lymphocytes and rapid disappearance of SIV from lymph nodes of sooty mangabeys during primary infection.
Immune infiltration of spontaneous mouse astrocytomas is dominated by immunosuppressive cells from early stages of tumor development.
Perforin activates clathrin- and dynamin-dependent endocytosis, which is required for plasma membrane repair and delivery of granzyme B for granzyme-mediated apoptosis.
IFN-alpha beta and self-MHC divert CD8 T cells into a distinct differentiation pathway characterized by rapid acquisition of effector functions.
IL-2 and antigen dose differentially regulate perforin- and FasL-mediated cytolytic activity in antigen specific CD4+ T cells.
Tc17, a unique subset of CD8 T cells that can protect against lethal influenza challenge.
IL-15 trans-presentation promotes human NK cell development and differentiation in vivo.
A phase I/II study of a MUC1 peptide pulsed autologous dendritic cell vaccine as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected pancreatic and biliary tumors.
CD8 T cells utilize TRAIL to control influenza virus infection.
IL-21 is produced by NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and cytokine production.
IL-21 is produced by NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and cytokine production.
Brain microenvironment promotes the final functional maturation of tumor-specific effector CD8+ T cells.
CTLA-4 ablation and interleukin-12 driven differentiation synergistically augment cardiac pathogenicity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Gammaherpesvirus persistence alters key CD8 T-cell memory characteristics and enhances antiviral protection.
The CD8+ T cell population elicited by recombinant adenovirus displays a novel partially exhausted phenotype associated with prolonged antigen presentation that nonetheless provides long-term immunity.
T-bet concomitantly controls migration, survival, and effector functions during the development of Valpha14i NKT cells.
Central memory self/tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells confer superior antitumor immunity compared with effector memory T cells.
Rahman SA, Billingsley JM, Sharma AA, Styles TM, Govindaraj S, Shanmugasundaram U, Babu H, Riberio SP, Ali SA, Tharp GK, Ibegbu C, Waggoner SN, Johnson RP, Sekaly RP, Villinger F, Bosinger SE, Amara RR, Velu V
JCI insight 2022 Apr 22;7(8)
JCI insight 2022 Apr 22;7(8)
Selection of tumor‑resistant variants following sustained natural killer cell‑mediated immune stress.
Carré T, Thiery J, Janji B, Terry S, Gros G, Meurice G, Kieda C, Olive D, Chouaib S
Oncology reports 2021 Feb;45(2):582-594
Oncology reports 2021 Feb;45(2):582-594
TIGIT limits immune pathology during viral infections.
Schorer M, Rakebrandt N, Lambert K, Hunziker A, Pallmer K, Oxenius A, Kipar A, Stertz S, Joller N
Nature communications 2020 Mar 9;11(1):1288
Nature communications 2020 Mar 9;11(1):1288
Comprehensive Analysis of the Immune and Stromal Compartments of the CNS in EAE Mice Reveal Pathways by Which Chloroquine Suppresses Neuroinflammation.
Thome R, Boehm A, Ishikawa LLW, Casella G, Munhoz J, Ciric B, Zhang GX, Rostami A
Brain sciences 2020 Jun 5;10(6)
Brain sciences 2020 Jun 5;10(6)
Protection of Batf3-deficient mice from experimental cerebral malaria correlates with impaired cytotoxic T-cell responses and immune regulation.
Kuehlwein JM, Borsche M, Korir PJ, Risch F, Mueller AK, Hübner MP, Hildner K, Hoerauf A, Dunay IR, Schumak B
Immunology 2020 Feb;159(2):193-204
Immunology 2020 Feb;159(2):193-204
Human γδ T-cell receptor repertoire is shaped by influenza viruses, age and tissue compartmentalisation.
Sant S, Jenkins MR, Dash P, Watson KA, Wang Z, Pizzolla A, Koutsakos M, Nguyen TH, Lappas M, Crowe J, Loudovaris T, Mannering SI, Westall GP, Kotsimbos TC, Cheng AC, Wakim L, Doherty PC, Thomas PG, Loh L, Kedzierska K
Clinical & translational immunology 2019;8(9):e1079
Clinical & translational immunology 2019;8(9):e1079
CD56 expression in breast cancer induces sensitivity to natural killer-mediated cytotoxicity by enhancing the formation of cytotoxic immunological synapse.
Taouk G, Hussein O, Zekak M, Abouelghar A, Al-Sarraj Y, Abdelalim EM, Karam M
Scientific reports 2019 Jun 19;9(1):8756
Scientific reports 2019 Jun 19;9(1):8756
TLR2 Stimulation Increases Cellular Metabolism in CD8(+) T Cells and Thereby Enhances CD8(+) T Cell Activation, Function, and Antiviral Activity.
Zhang E, Ma Z, Li Q, Yan H, Liu J, Wu W, Guo J, Zhang X, Kirschning CJ, Xu H, Lang PA, Yang D, Dittmer U, Yan H, Lu M
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2019 Dec 1;203(11):2872-2886
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2019 Dec 1;203(11):2872-2886
Multiplexed imaging of immune cells in staged multiple sclerosis lesions by mass cytometry.
Ramaglia V, Sheikh-Mohamed S, Legg K, Park C, Rojas OL, Zandee S, Fu F, Ornatsky O, Swanson EC, Pitt D, Prat A, McKee TD, Gommerman JL
eLife 2019 Aug 1;8
eLife 2019 Aug 1;8
Long-term outcomes of a phase I study of agonist CD40 antibody and CTLA-4 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma.
Bajor DL, Mick R, Riese MJ, Huang AC, Sullivan B, Richman LP, Torigian DA, George SM, Stelekati E, Chen F, Melenhorst JJ, Lacey SF, Xu X, Wherry EJ, Gangadhar TC, Amaravadi RK, Schuchter LM, Vonderheide RH
Oncoimmunology 2018;7(10):e1468956
Oncoimmunology 2018;7(10):e1468956
Mass cytometry reveals innate lymphoid cell differentiation pathways in the human fetal intestine.
Li N, van Unen V, Höllt T, Thompson A, van Bergen J, Pezzotti N, Eisemann E, Vilanova A, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Lelieveldt BPF, Koning F
The Journal of experimental medicine 2018 May 7;215(5):1383-1396
The Journal of experimental medicine 2018 May 7;215(5):1383-1396
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ inhibition promotes antitumor responses but antagonizes checkpoint inhibitors.
Lim EL, Cugliandolo FM, Rosner DR, Gyori D, Roychoudhuri R, Okkenhaug K
JCI insight 2018 Jun 7;3(11)
JCI insight 2018 Jun 7;3(11)
Canonical TGF-β Signaling Pathway Represses Human NK Cell Metabolism.
Zaiatz-Bittencourt V, Finlay DK, Gardiner CM
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2018 Jun 15;200(12):3934-3941
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2018 Jun 15;200(12):3934-3941
Human CD40 ligand-expressing type 3 innate lymphoid cells induce IL-10-producing immature transitional regulatory B cells.
Komlósi ZI, Kovács N, van de Veen W, Kirsch AI, Fahrner HB, Wawrzyniak M, Rebane A, Stanic B, Palomares O, Rückert B, Menz G, Akdis M, Losonczy G, Akdis CA
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2018 Jul;142(1):178-194.e11
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2018 Jul;142(1):178-194.e11
Early IL-6 signalling promotes IL-27 dependent maturation of regulatory T cells in the lungs and resolution of viral immunopathology.
Pyle CJ, Uwadiae FI, Swieboda DP, Harker JA
PLoS pathogens 2017 Sep;13(9):e1006640
PLoS pathogens 2017 Sep;13(9):e1006640
Low-dose interleukin-2 promotes STAT-5 phosphorylation, T(reg) survival and CTLA-4-dependent function in autoimmune liver diseases.
Jeffery HC, Jeffery LE, Lutz P, Corrigan M, Webb GJ, Hirschfield GM, Adams DH, Oo YH
Clinical and experimental immunology 2017 Jun;188(3):394-411
Clinical and experimental immunology 2017 Jun;188(3):394-411
Systems-guided forward genetic screen reveals a critical role of the replication stress response protein ETAA1 in T cell clonal expansion.
Miosge LA, Sontani Y, Chuah A, Horikawa K, Russell TA, Mei Y, Wagle MV, Howard DR, Enders A, Tscharke DC, Goodnow CC, Parish IA
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2017 Jun 27;114(26):E5216-E5225
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2017 Jun 27;114(26):E5216-E5225
Perturbed CD8(+) T cell TIGIT/CD226/PVR axis despite early initiation of antiretroviral treatment in HIV infected individuals.
Tauriainen J, Scharf L, Frederiksen J, Naji A, Ljunggren HG, Sönnerborg A, Lund O, Reyes-Terán G, Hecht FM, Deeks SG, Betts MR, Buggert M, Karlsson AC
Scientific reports 2017 Jan 13;7:40354
Scientific reports 2017 Jan 13;7:40354
NKG2C/E Marks the Unique Cytotoxic CD4 T Cell Subset, ThCTL, Generated by Influenza Infection.
Marshall NB, Vong AM, Devarajan P, Brauner MD, Kuang Y, Nayar R, Schutten EA, Castonguay CH, Berg LJ, Nutt SL, Swain SL
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2017 Feb 1;198(3):1142-1155
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2017 Feb 1;198(3):1142-1155
Type 1 interferon licenses naïve CD8 T cells to mediate anti-viral cytotoxicity.
Urban SL, Berg LJ, Welsh RM
Virology 2016 Jun;493:52-9
Virology 2016 Jun;493:52-9
Graded Foxo1 activity in Treg cells differentiates tumour immunity from spontaneous autoimmunity.
Luo CT, Liao W, Dadi S, Toure A, Li MO
Nature 2016 Jan 28;529(7587):532-6
Nature 2016 Jan 28;529(7587):532-6
Nonapoptotic and extracellular activity of granzyme B mediates resistance to regulatory T cell (Treg) suppression by HLA-DR-CD25hiCD127lo Tregs in multiple sclerosis and in response to IL-6.
Bhela S, Kempsell C, Manohar M, Dominguez-Villar M, Griffin R, Bhatt P, Kivisakk-Webb P, Fuhlbrigge R, Kupper T, Weiner H, Baecher-Allan C
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2015 Mar 1;194(5):2180-9
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2015 Mar 1;194(5):2180-9
Activated regulatory T cells suppress effector NK cell responses by an IL-2-mediated mechanism during an acute retroviral infection.
Littwitz-Salomon E, Akhmetzyanova I, Vallet C, Francois S, Dittmer U, Gibbert K
Retrovirology 2015 Jul 30;12:66
Retrovirology 2015 Jul 30;12:66
Therapeutic antiviral T cells noncytopathically clear persistently infected microglia after conversion into antigen-presenting cells.
Herz J, Johnson KR, McGavern DB
The Journal of experimental medicine 2015 Jul 27;212(8):1153-69
The Journal of experimental medicine 2015 Jul 27;212(8):1153-69
The Interferon-Stimulated Gene Ifi27l2a Restricts West Nile Virus Infection and Pathogenesis in a Cell-Type- and Region-Specific Manner.
Lucas TM, Richner JM, Diamond MS
Journal of virology 2015 Dec 23;90(5):2600-15
Journal of virology 2015 Dec 23;90(5):2600-15
Immunological Outcome in Haploidentical-HSC Transplanted Patients Treated with IL-10-Anergized Donor T Cells.
Bacchetta R, Lucarelli B, Sartirana C, Gregori S, Lupo Stanghellini MT, Miqueu P, Tomiuk S, Hernandez-Fuentes M, Gianolini ME, Greco R, Bernardi M, Zappone E, Rossini S, Janssen U, Ambrosi A, Salomoni M, Peccatori J, Ciceri F, Roncarolo MG
Frontiers in immunology 2014;5:16
Frontiers in immunology 2014;5:16
Out-of-sequence signal 3 as a mechanism for virus-induced immune suppression of CD8 T cell responses.
Urban SL, Welsh RM
PLoS pathogens 2014 Sep;10(9):e1004357
PLoS pathogens 2014 Sep;10(9):e1004357
Midline 1 directs lytic granule exocytosis and cytotoxicity of mouse killer T cells.
Boding L, Hansen AK, Meroni G, Johansen BB, Braunstein TH, Bonefeld CM, Kongsbak M, Jensen BA, Woetmann A, Thomsen AR, Odum N, von Essen MR, Geisler C
European journal of immunology 2014 Oct;44(10):3109-18
European journal of immunology 2014 Oct;44(10):3109-18
Immunomodulatory action of SGI-110, a hypomethylating agent, in acute myeloid leukemia cells and xenografts.
Srivastava P, Paluch BE, Matsuzaki J, James SR, Collamat-Lai G, Karbach J, Nemeth MJ, Taverna P, Karpf AR, Griffiths EA
Leukemia research 2014 Nov;38(11):1332-41
Leukemia research 2014 Nov;38(11):1332-41
GPR18 is required for a normal CD8αα intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte compartment.
Wang X, Sumida H, Cyster JG
The Journal of experimental medicine 2014 Nov 17;211(12):2351-9
The Journal of experimental medicine 2014 Nov 17;211(12):2351-9
Rapid proliferation and differentiation impairs the development of memory CD8+ T cells in early life.
Smith NL, Wissink E, Wang J, Pinello JF, Davenport MP, Grimson A, Rudd BD
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2014 Jul 1;193(1):177-84
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2014 Jul 1;193(1):177-84
The phenotype and activation status of regulatory T cells during Friend retrovirus infection.
Joedicke JJ, Dietze KK, Zelinskyy G, Dittmer U
Virologica Sinica 2014 Feb;29(1):48-60
Virologica Sinica 2014 Feb;29(1):48-60
Role of NK cells in host defense against pulmonary type A Francisella tularensis infection.
Schmitt DM, O'Dee DM, Brown MJ, Horzempa J, Russo BC, Morel PA, Nau GJ
Microbes and infection 2013 Mar;15(3):201-11
Microbes and infection 2013 Mar;15(3):201-11
CD4+ T cells develop antiretroviral cytotoxic activity in the absence of regulatory T cells and CD8+ T cells.
Manzke N, Akhmetzyanova I, Hasenkrug KJ, Trilling M, Zelinskyy G, Dittmer U
Journal of virology 2013 Jun;87(11):6306-13
Journal of virology 2013 Jun;87(11):6306-13
FoxO1 controls effector-to-memory transition and maintenance of functional CD8 T cell memory.
Tejera MM, Kim EH, Sullivan JA, Plisch EH, Suresh M
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2013 Jul 1;191(1):187-99
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2013 Jul 1;191(1):187-99
Arf-like GTPase Arl8b regulates lytic granule polarization and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
Tuli A, Thiery J, James AM, Michelet X, Sharma M, Garg S, Sanborn KB, Orange JS, Lieberman J, Brenner MB
Molecular biology of the cell 2013 Dec;24(23):3721-35
Molecular biology of the cell 2013 Dec;24(23):3721-35
IL-7 and IL-15 do not synergize during CD8 T cell recall response against an obligate intracellular parasite.
Bhadra R, Khan IA
Microbes and infection 2012 Nov;14(13):1160-8
Microbes and infection 2012 Nov;14(13):1160-8
TGF-β signaling to T cells inhibits autoimmunity during lymphopenia-driven proliferation.
Zhang N, Bevan MJ
Nature immunology 2012 May 27;13(7):667-73
Nature immunology 2012 May 27;13(7):667-73
Chronic HIV infection affects the expression of the 2 transcription factors required for CD8 T-cell differentiation into cytolytic effectors.
Ribeiro-dos-Santos P, Turnbull EL, Monteiro M, Legrand A, Conrod K, Baalwa J, Pellegrino P, Shaw GM, Williams I, Borrow P, Rocha B
Blood 2012 May 24;119(21):4928-38
Blood 2012 May 24;119(21):4928-38
An optimized SIV DNA vaccine can serve as a boost for Ad5 and provide partial protection from a high-dose SIVmac251 challenge.
Hutnick NA, Myles DJ, Hirao L, Scott VL, Ferraro B, Khan AS, Lewis MG, Miller CJ, Bett AJ, Casimiro D, Sardesai NY, Kim JJ, Shiver J, Weiner DB
Vaccine 2012 May 2;30(21):3202-8
Vaccine 2012 May 2;30(21):3202-8
Cutting edge: tumor-targeting antibodies enhance NKG2D-mediated NK cell cytotoxicity by stabilizing NK cell-tumor cell interactions.
Deguine J, Breart B, Lemaître F, Bousso P
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2012 Dec 15;189(12):5493-7
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2012 Dec 15;189(12):5493-7
Primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection limits replication but not lung inflammation upon homologous rechallenge.
Clay C, Donart N, Fomukong N, Knight JB, Lei W, Price L, Hahn F, Van Westrienen J, Harrod KS
Journal of virology 2012 Apr;86(8):4234-44
Journal of virology 2012 Apr;86(8):4234-44
DOCK8 deficiency impairs CD8 T cell survival and function in humans and mice.
Randall KL, Chan SS, Ma CS, Fung I, Mei Y, Yabas M, Tan A, Arkwright PD, Al Suwairi W, Lugo Reyes SO, Yamazaki-Nakashimada MA, Garcia-Cruz Mde L, Smart JM, Picard C, Okada S, Jouanguy E, Casanova JL, Lambe T, Cornall RJ, Russell S, Oliaro J, Tangye SG, Bertram EM, Goodnow CC
The Journal of experimental medicine 2011 Oct 24;208(11):2305-20
The Journal of experimental medicine 2011 Oct 24;208(11):2305-20
Virus-specific CD8+ T cells upregulate programmed death-1 expression during acute friend retrovirus infection but are highly cytotoxic and control virus replication.
Zelinskyy G, Myers L, Dietze KK, Gibbert K, Roggendorf M, Liu J, Lu M, Kraft AR, Teichgräber V, Hasenkrug KJ, Dittmer U
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 Oct 1;187(7):3730-7
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 Oct 1;187(7):3730-7
A CD8α(-) subpopulation of macaque circulatory natural killer cells can mediate both antibody-dependent and antibody-independent cytotoxic activities.
Vargas-Inchaustegui DA, Demberg T, Robert-Guroff M
Immunology 2011 Nov;134(3):326-40
Immunology 2011 Nov;134(3):326-40
The magnitude of the T cell response to a clinically significant dose of influenza virus is regulated by TRAIL.
Brincks EL, Gurung P, Langlois RA, Hemann EA, Legge KL, Griffith TS
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 Nov 1;187(9):4581-8
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 Nov 1;187(9):4581-8
Early induction of polyfunctional simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific T lymphocytes and rapid disappearance of SIV from lymph nodes of sooty mangabeys during primary infection.
Meythaler M, Wang Z, Martinot A, Pryputniewicz S, Kasheta M, McClure HM, O'Neil SP, Kaur A
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 May 1;186(9):5151-61
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2011 May 1;186(9):5151-61
Immune infiltration of spontaneous mouse astrocytomas is dominated by immunosuppressive cells from early stages of tumor development.
Tran Thang NN, Derouazi M, Philippin G, Arcidiaco S, Di Berardino-Besson W, Masson F, Hoepner S, Riccadonna C, Burkhardt K, Guha A, Dietrich PY, Walker PR
Cancer research 2010 Jun 15;70(12):4829-39
Cancer research 2010 Jun 15;70(12):4829-39
Perforin activates clathrin- and dynamin-dependent endocytosis, which is required for plasma membrane repair and delivery of granzyme B for granzyme-mediated apoptosis.
Thiery J, Keefe D, Saffarian S, Martinvalet D, Walch M, Boucrot E, Kirchhausen T, Lieberman J
Blood 2010 Feb 25;115(8):1582-93
Blood 2010 Feb 25;115(8):1582-93
IFN-alpha beta and self-MHC divert CD8 T cells into a distinct differentiation pathway characterized by rapid acquisition of effector functions.
Marshall HD, Prince AL, Berg LJ, Welsh RM
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2010 Aug 1;185(3):1419-28
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2010 Aug 1;185(3):1419-28
IL-2 and antigen dose differentially regulate perforin- and FasL-mediated cytolytic activity in antigen specific CD4+ T cells.
Brown DM, Kamperschroer C, Dilzer AM, Roberts DM, Swain SL
Cellular immunology 2009;257(1-2):69-79
Cellular immunology 2009;257(1-2):69-79
Tc17, a unique subset of CD8 T cells that can protect against lethal influenza challenge.
Hamada H, Garcia-Hernandez Mde L, Reome JB, Misra SK, Strutt TM, McKinstry KK, Cooper AM, Swain SL, Dutton RW
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3469-81
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3469-81
IL-15 trans-presentation promotes human NK cell development and differentiation in vivo.
Huntington ND, Legrand N, Alves NL, Jaron B, Weijer K, Plet A, Corcuff E, Mortier E, Jacques Y, Spits H, Di Santo JP
The Journal of experimental medicine 2009 Jan 16;206(1):25-34
The Journal of experimental medicine 2009 Jan 16;206(1):25-34
A phase I/II study of a MUC1 peptide pulsed autologous dendritic cell vaccine as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected pancreatic and biliary tumors.
Lepisto AJ, Moser AJ, Zeh H, Lee K, Bartlett D, McKolanis JR, Geller BA, Schmotzer A, Potter DP, Whiteside T, Finn OJ, Ramanathan RK
Cancer therapy 2008;6(B):955-964
Cancer therapy 2008;6(B):955-964
CD8 T cells utilize TRAIL to control influenza virus infection.
Brincks EL, Katewa A, Kucaba TA, Griffith TS, Legge KL
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Oct 1;181(7):4918-25
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Oct 1;181(7):4918-25
IL-21 is produced by NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and cytokine production.
Coquet JM, Kyparissoudis K, Pellicci DG, Besra G, Berzins SP, Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2827-34
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2827-34
IL-21 is produced by NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and cytokine production.
Coquet JM, Kyparissoudis K, Pellicci DG, Besra G, Berzins SP, Smyth MJ, Godfrey DI
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2827-34
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2827-34
Brain microenvironment promotes the final functional maturation of tumor-specific effector CD8+ T cells.
Masson F, Calzascia T, Di Berardino-Besson W, de Tribolet N, Dietrich PY, Walker PR
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Jul 15;179(2):845-53
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2007 Jul 15;179(2):845-53
CTLA-4 ablation and interleukin-12 driven differentiation synergistically augment cardiac pathogenicity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Love VA, Grabie N, Duramad P, Stavrakis G, Sharpe A, Lichtman A
Circulation research 2007 Aug 3;101(3):248-57
Circulation research 2007 Aug 3;101(3):248-57
Gammaherpesvirus persistence alters key CD8 T-cell memory characteristics and enhances antiviral protection.
Obar JJ, Fuse S, Leung EK, Bellfy SC, Usherwood EJ
Journal of virology 2006 Sep;80(17):8303-15
Journal of virology 2006 Sep;80(17):8303-15
The CD8+ T cell population elicited by recombinant adenovirus displays a novel partially exhausted phenotype associated with prolonged antigen presentation that nonetheless provides long-term immunity.
Yang TC, Millar J, Groves T, Grinshtein N, Parsons R, Takenaka S, Wan Y, Bramson JL
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Jan 1;176(1):200-10
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Jan 1;176(1):200-10
T-bet concomitantly controls migration, survival, and effector functions during the development of Valpha14i NKT cells.
Matsuda JL, Zhang Q, Ndonye R, Richardson SK, Howell AR, Gapin L
Blood 2006 Apr 1;107(7):2797-805
Blood 2006 Apr 1;107(7):2797-805
Central memory self/tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells confer superior antitumor immunity compared with effector memory T cells.
Klebanoff CA, Gattinoni L, Torabi-Parizi P, Kerstann K, Cardones AR, Finkelstein SE, Palmer DC, Antony PA, Hwang ST, Rosenberg SA, Waldmann TA, Restifo NP
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Jul 5;102(27):9571-6
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Jul 5;102(27):9571-6
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
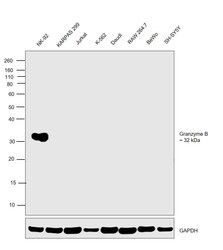
- Experimental details
- Western blot was performed using Anti-Granzyme B Monoclonal Antibody (GB11) (Product # MA1-80734) and a 32 kDa band corresponding to Granzyme B was observed only in NK-92 cells which is reported to be positive and not in any other cell lines. Whole cell extracts (30 µg lysate) of NK-92 (Lane 1), KARPAS 299 (Lane 2), Jurkat (Lane 3), K-562 (Lane 4), Daudi (Lane 5), RAW 264.7 (Lane 6), BeWo (Lane 7) and SH-SY5Y (Lane 8) were electrophoresed using NuPAGE™ 10% Bis-Tris Protein Gel (Product # NP0302BOX). Resolved proteins were then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Product # IB23001) by iBlot® 2 Dry Blotting System (Product # IB21001). The blot was probed with the primary antibody (1:1000 dilution) and detected by chemiluminescence with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, HRP (Product # A28177,1:4000 dilution) using the iBright FL 1000 (Product # A32752). Chemiluminescent detection was performed using SuperSignal™ West Dura Extended Duration Substrate (Product # 34076).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
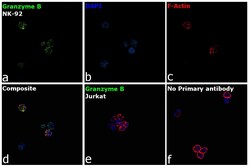
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Granzyme B was performed using 70% confluent log phase NK-92 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Granzyme B Monoclonal Antibody (GB11) (Product # MA1-80734) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32766), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b: Blue) were stained with ProLong™ Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # P36962). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained withRhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic granule localization. Panel e represents Jurkat cells having no expression of Granzyme B. Panel f represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
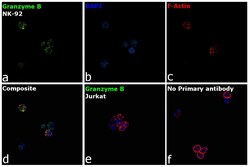
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Granzyme B was performed using 70% confluent log phase NK-92 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Granzyme B Monoclonal Antibody (GB11) (Product # MA1-80734) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32766), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b: Blue) were stained with ProLong™ Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # P36962). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained withRhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic granule localization. Panel e represents Jurkat cells having no expression of Granzyme B. Panel f represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
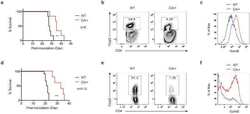
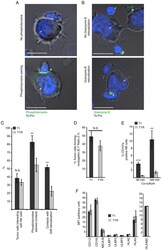
- Figure 3. The acquisition of resistance to NK cell-mediated lysis correlates with an effector/target interaction default. (A) Confocal microscopy staining of phosphotyrosine (arrowhead, accumulated at the contact zone) on co-harvested tumor (arrow) and NK cells. (B) Confocal microscopy staining of Granzyme B (arrowhead, relocalized at the contact zone) on co-harvested tumor (arrow) and NK cells. Scale bar, 10 um. (C) Statistical analysis of confocal microscopy evaluation of tumor and NK cell contacts, of the establishment of active immune synapses (by phosphotyrosine staining) and of Granzyme B relocalization toward the contact zone. At least 200 tumor cells in 10 different fields were counted for each three independent batches of T1 and each three independent batches of T1R cells. Data represent mean percentage +- standard deviation. (D) Flow cytometry evaluation of conjugate formation between NK cells and tumor cells. Data represent the means of three experiments for the three independent batches of T1 and the three independent batches of T1R cells +- standard deviation. (E) Flow cytometry evaluation of CD107a externalization on NK cell membrane in response to cocultured cells (T1R) in comparison to reference cells (T1). Data represent the means of the three independent batches of T1 and the three independent batches of T1R cells +- standard deviation. (F) Flow cytometry evaluation of main KIR, DNAM1 and NKG2D ligand expression on cocultured cells (T1R) in comparison to ref
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
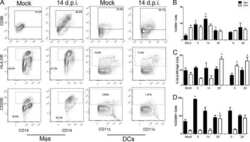
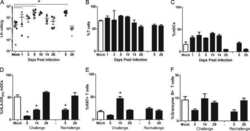
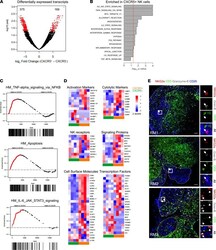
- Figure 3 CXCR5 + NK cells are transcriptionally distinct from CXCR5 - NK cells during chronic SHIV infection. ( A ) Purified NK cells from lymph nodes (LNs) at week 14 after infection were RNA sequenced, and volcano plots were analyzed for differentially expressed transcripts ( n = 4). ( B ) Normalized enrichment scores for upregulated gene sets in CXCR5 + NK cells are depicted. Dashed line indicates normalized enrichment score cutoff of greater than 135 with FDR of less than 0.2. ( C ) GSEA plots comparing CXCR5 + and CXCR5 - NK cells. ( D ) Global gene expression analysis showing gene expression profile for CXCR5 + and CXCR5 - NK cells. The color intensity for heatmaps represents Z score of differential expression by CXCR5 + versus CXCR5 - NK cells, calculated as described in Methods. ( E ) IHC images showing CD20 (blue), CD3 (green), NKG2A (red), and granzyme B (gray) staining of LN sections of SHIV-infected macaques. Scale bar: 50 mum. Arrow indicates NK cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
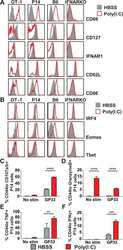
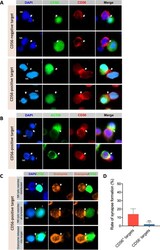
- Figure 4 CD56 expression at immunological synapse and association with granzyme B transfer from NK-92 into CD56-positive target cells. CD56-expressing (hTERT-HME1) and/or CD56-negative (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and/or SKBR3) target cells were labeled (panels A and C) or not (panel B) with CFSE and cocultured with NK-92 cells at 1:1 effector-to-target ratio for 2 hours. Cells were then transferred to poly-L-lysin-coated coverslips, fixed, permeabilized and stained as indicated for CD56 (panels A and B), actin (panel B), granzyme b (panel C) and nuclei (DAPI) (panels A, B and C) before analysis by fluorescent microscopy. Images is panel A are for MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 (CD56-negative targets) and hTERT-HME1 (CD56-positive target) and correspond to representative fields from two or three independent experiments. Images in panel C are for three different synapses observed after 2 hours in the same coculture of NK-92 and hTERT-HME1. ( D ) Graph presenting the mean rates of synapse formation +- SD obtained from six representative fields for CD56-positive target (hTERT-HME1) and nine representative fields for CD56-negative targets (three fields for each cell line MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 and SKBR3). ***p < 0.001.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn