Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [3]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA022001 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA022001, RRID:AB_2297599
- Product name
- Anti-MFSD11
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human MFSD11, Gene description: major facilitator superfamily domain containing 11, Alternative Gene Names: FLJ20226, FLJ22196, Validated applications: ICC, WB, Uniprot ID: O43934, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.1 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references Characteristics of 29 novel atypical solute carriers of major facilitator superfamily type: evolutionary conservation, predicted structure and neuronal co-expression
The Putative SLC Transporters Mfsd5 and Mfsd11 Are Abundantly Expressed in the Mouse Brain and Have a Potential Role in Energy Homeostasis
Immunofluorescence and fluorescent-protein tagging show high correlation for protein localization in mammalian cells
Perland E, Bagchi S, Klaesson A, Fredriksson R
Open Biology 2017;7(9)
Open Biology 2017;7(9)
The Putative SLC Transporters Mfsd5 and Mfsd11 Are Abundantly Expressed in the Mouse Brain and Have a Potential Role in Energy Homeostasis
Allodi S, Perland E, Lekholm E, Eriksson M, Bagchi S, Arapi V, Fredriksson R
PLOS ONE 2016;11(6):e0156912
PLOS ONE 2016;11(6):e0156912
Immunofluorescence and fluorescent-protein tagging show high correlation for protein localization in mammalian cells
Stadler C, Rexhepaj E, Singan V, Murphy R, Pepperkok R, Uhlén M, Simpson J, Lundberg E
Nature Methods 2013;10(4):315-323
Nature Methods 2013;10(4):315-323
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
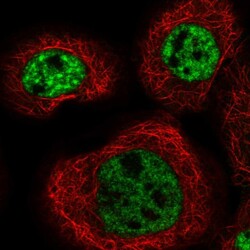
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line A-431 shows localization to nuclear speckles.
- Sample type
- Human
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry