Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA039281 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA039281, RRID:AB_10795583
- Product name
- Anti-DIS3
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human DIS3, Gene description: DIS3 exosome endoribonuclease and 3'-5' exoribonuclease, Alternative Gene Names: dis3p, EXOSC11, KIAA1008, RRP44, Validated applications: IHC, ICC, WB, Uniprot ID: Q9Y2L1, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.3 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references The MTR4/hnRNPK complex surveils aberrant polyadenylated RNAs with multiple exons
Macrophage development and activation involve coordinated intron retention in key inflammatory regulators
A Functional Link between Nuclear RNA Decay and Transcriptional Control Mediated by the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2
Multiple myeloma-associated hDIS3 mutations cause perturbations in cellular RNA metabolism and suggest hDIS3 PIN domain as a potential drug target
Taniue K, Sugawara A, Zeng C, Han H, Gao X, Shimoura Y, Ozeki A, Onoguchi-Mizutani R, Seki M, Suzuki Y, Hamada M, Akimitsu N
Nature Communications 2024;15(1)
Nature Communications 2024;15(1)
Macrophage development and activation involve coordinated intron retention in key inflammatory regulators
Wong J, Rasko J, Hayashi R, Larance M, Schmitz U, Roediger B, Clark S, Nair S, Wong A, Kwok C, Halstead J, Lee Q, Song R, Pinello N, Green I
Nucleic Acids Research 2020;48(12):6513-6529
Nucleic Acids Research 2020;48(12):6513-6529
A Functional Link between Nuclear RNA Decay and Transcriptional Control Mediated by the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2
Garland W, Comet I, Wu M, Radzisheuskaya A, Rib L, Vitting-Seerup K, Lloret-Llinares M, Sandelin A, Helin K, Jensen T
Cell Reports 2019;29(7):1800-1811.e6
Cell Reports 2019;29(7):1800-1811.e6
Multiple myeloma-associated hDIS3 mutations cause perturbations in cellular RNA metabolism and suggest hDIS3 PIN domain as a potential drug target
Tomecki R, Drazkowska K, Kucinski I, Stodus K, Szczesny R, Gruchota J, Owczarek E, Kalisiak K, Dziembowski A
Nucleic Acids Research 2013;42(2):1270-1290
Nucleic Acids Research 2013;42(2):1270-1290
No comments: Submit comment
Enhanced validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Genetic validation
- Main image
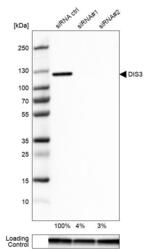
- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis in U-87MG ATCC cells transfected with control siRNA, target specific siRNA probe #1 and #2, using Anti-DIS3 antibody. Remaining relative intensity is presented. Loading control: Anti-GAPDH.
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
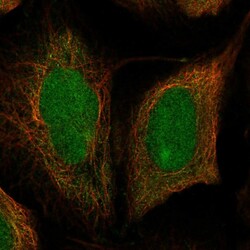
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line U-2 OS shows localization to nucleus & cytosol.
- Sample type
- Human
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry