Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [3]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA013180 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA013180, RRID:AB_1854383
- Product name
- Anti-NETO2
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human NETO2, Gene description: neuropilin (NRP) and tolloid (TLL)-like 2, Alternative Gene Names: FLJ10430, NEOT2, Validated applications: IHC, ICC, Uniprot ID: Q8NC67, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.1 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references Glioma-derived LRIG3 interacts with NETO2 in tumor-associated macrophages to modulate microenvironment and suppress tumor growth
Phosphorylation of the kainate receptor (KAR) auxiliary subunit Neto2 at serine 409 regulates synaptic targeting of the KAR subunit GluK1
Synaptic Targeting and Functional Modulation of GluK1 Kainate Receptors by the Auxiliary Neuropilin and Tolloid-Like (NETO) Proteins
Li Y, Wang W, Hou X, Huang W, Zhang P, He Y, Wang B, Duan Q, Mao F, Guo D
Cell Death & Disease 2023;14(1)
Cell Death & Disease 2023;14(1)
Phosphorylation of the kainate receptor (KAR) auxiliary subunit Neto2 at serine 409 regulates synaptic targeting of the KAR subunit GluK1
Lomash R, Sheng N, Li Y, Nicoll R, Roche K
Journal of Biological Chemistry 2017;292(37):15369-15377
Journal of Biological Chemistry 2017;292(37):15369-15377
Synaptic Targeting and Functional Modulation of GluK1 Kainate Receptors by the Auxiliary Neuropilin and Tolloid-Like (NETO) Proteins
Copits B, Robbins J, Frausto S, Swanson G
The Journal of Neuroscience 2011;31(20):7334-7340
The Journal of Neuroscience 2011;31(20):7334-7340
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
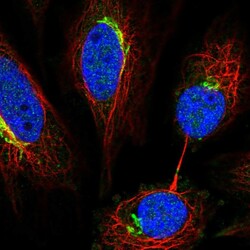
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line SiHa shows localization to the Golgi apparatus.
- Sample type
- Human
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry