Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [6]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [7]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-32173 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- ZPK Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- Recommended positive controls: Neuro 2A, C8D30, NIH-3T3, Raw264.7, C2C12, Mouse brain, mouse embryonic stem cell, rat brain. Store product as a concentrated solution. Centrifuge briefly prior to opening the vial.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.93 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references FK506-binding protein-like and FK506-binding protein 8 regulate dual leucine zipper kinase degradation and neuronal responses to axon injury.
PDK1 is a negative regulator of axon regeneration.
Coupled Control of Distal Axon Integrity and Somal Responses to Axonal Damage by the Palmitoyl Acyltransferase ZDHHC17.
Dual Leucine Zipper Kinase Is Constitutively Active in the Adult Mouse Brain and Has Both Stress-Induced and Homeostatic Functions.
Neuronal hyperexcitability is a DLK-dependent trigger of herpes simplex virus reactivation that can be induced by IL-1.
Neuronal Stress Pathway Mediating a Histone Methyl/Phospho Switch Is Required for Herpes Simplex Virus Reactivation.
Lee B, Oh Y, Cho E, DiAntonio A, Cavalli V, Shin JE, Choi HW, Cho Y
The Journal of biological chemistry 2022 Mar;298(3):101647
The Journal of biological chemistry 2022 Mar;298(3):101647
PDK1 is a negative regulator of axon regeneration.
Kim H, Lee J, Cho Y
Molecular brain 2021 Feb 12;14(1):31
Molecular brain 2021 Feb 12;14(1):31
Coupled Control of Distal Axon Integrity and Somal Responses to Axonal Damage by the Palmitoyl Acyltransferase ZDHHC17.
Niu J, Sanders SS, Jeong HK, Holland SM, Sun Y, Collura KM, Hernandez LM, Huang H, Hayden MR, Smith GM, Hu Y, Jin Y, Thomas GM
Cell reports 2020 Nov 17;33(7):108365
Cell reports 2020 Nov 17;33(7):108365
Dual Leucine Zipper Kinase Is Constitutively Active in the Adult Mouse Brain and Has Both Stress-Induced and Homeostatic Functions.
Goodwani S, Fernandez C, Acton PJ, Buggia-Prevot V, McReynolds ML, Ma J, Hu CH, Hamby ME, Jiang Y, Le K, Soth MJ, Jones P, Ray WJ
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jul 9;21(14)
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Jul 9;21(14)
Neuronal hyperexcitability is a DLK-dependent trigger of herpes simplex virus reactivation that can be induced by IL-1.
Cuddy SR, Schinlever AR, Dochnal S, Seegren PV, Suzich J, Kundu P, Downs TK, Farah M, Desai BN, Boutell C, Cliffe AR
eLife 2020 Dec 22;9
eLife 2020 Dec 22;9
Neuronal Stress Pathway Mediating a Histone Methyl/Phospho Switch Is Required for Herpes Simplex Virus Reactivation.
Cliffe AR, Arbuckle JH, Vogel JL, Geden MJ, Rothbart SB, Cusack CL, Strahl BD, Kristie TM, Deshmukh M
Cell host & microbe 2015 Dec 9;18(6):649-58
Cell host & microbe 2015 Dec 9;18(6):649-58
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
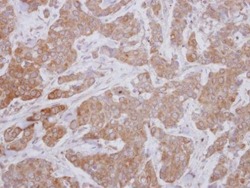
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer, using MAP3K12 (Product # PA5-32173) antibody at 1:250 dilution.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
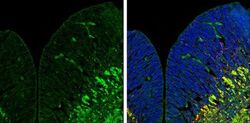
- Immunohistochemistry (Frozen) analysis of ZPK was performed in frozen sectioned E13.5 Rat brain tissue using ZPK Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-32173) at a dilution of 1:250 (Green). Red: beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1, a mature neuron marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1 antibody diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
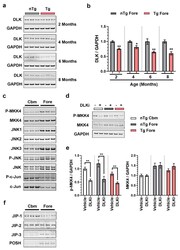
- Figure 4 DLK is constitutively active in all the brain regions of adult mouse brain but has brain region specific scaffolding proteins. ( a ) Representative immunoblots of DLK from the homogenates obtained from nTg and Tg forebrain of 2, 4, 6, and 8 months old female mice. ( b ) Quantification of the immunoblots of DLK/GAPDH from the nTg and Tg forebrain homogenates from 2, 4, 6, and 8 months old female mice, plotted as mean fold change relative to nTg group of respective age cohort. Unpaired t -test. + p < 0.05, ++ p < 0.01, n = 6. ( c ) Immunoblots showing differential expression of DLK signaling components: p-MKK4, MKK4, JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, p-JNK, JNK, p-c-Jun, and c-Jun from cerebellum (Cbm) and forebrain (Fore) from 3-4 months old male WT mice. ( d ) Representative immunoblots of p-MKK4 and MKK4 in homogenates from nTg cerebellum (nTg Cbm), nTg forebrain (nTg Fore), and Tg forebrain (Tg Fore) of 7-8 months old female mice treated with 50 mg/kg of DLKi or vehicle QD for 7 days. ( e ) Quantification of the immunoblots of p-MKK4/GAPDH and MKK4/GAPDH from homogenates obtained from nTg cerebellum, nTg forebrain, and Tg forebrain of mice treated with vehicle or DLKi, plotted as mean fold change relative to vehicle group in the respective brain region. Unpaired t -test. ** p < 0.01, n = 6. ( f ) Immunoblots showing differential expression of DLK scaffolding proteins: JIP1, JIP2, JIP3, and POSH from cerebellum (Cbm) and forebrain (Fore) from 3-4 months old male WT mice.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
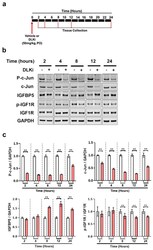
- Figure 9 Acute pharmacological inhibition of DLK is sufficient to upregulate IGFBP5 in uninjured mouse cerebellum. ( a ) Schematic representation of study timeline; 3-4 months old male WT mice were treated with a single oral dose of 50 mg/kg of DLKi or vehicle QD. The study was terminated approximately 2, 4, 8, 12, or 24 h after single dose. ( b ) Representative immunoblots of p-c-Jun, c-Jun, IGFBP5, p-IGF1R, and IGF1R from cerebellar homogenates of WT mice treated with a single dose of vehicle or DLKi for either 2, 4, 8, 12, or 24 h. ( c ) Quantification of the immunoblots of p-c-Jun/GAPDH, c-Jun/GAPDH, IGFBP5/GAPDH, and p-IGF1R/IGF1R from cerebellar homogenates of WT mice treated with single dose of vehicle or DLKi for either 2, 4, 8, 12, or 24 h, plotted as mean fold change relative to vehicle group at respective time-point. Unpaired t -test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, n = 5.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
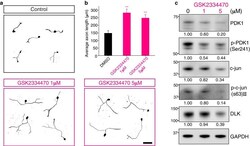
- Fig. 4 GSK2334470, a chemical inhibitor of PDK1, promotes axon regeneration in vitro. a In vitro axon regeneration assays. Mouse embryonic DRG neurons were re-plated in GSK2334470 (1 muM or 5 muM as indicated) or a vehicle (control) containing culture medium, fixed, and immunostained with TUJ1 antibody. Scale bar, 100 mum. b Average length of the regenerating axons from ( a ) (Mean +- S.E.M. ; n = 151, 156, and 161 cells for each condition; ** p < 0.01 from a t -test). c Western blot analysis of protein lysates from control (0, vehicle only) or GSK2334470-treated embryonic DRG neuron cultures. Numbers indicate the relative intensities
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
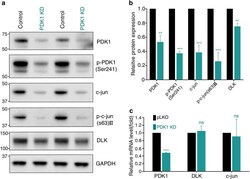
- Fig. 6 PDK1 knockdown leads to downregulation of the DLK/c-jun pathway. a Western blot analysis of protein lysates from control or PDK1-knockdown embryonic DRG neurons. b Relative intensity of ( a ) (Mean +- S.E.M. ; n = 4 for each condition; *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01 from a t -test). c Relative mRNA levels measured using quantitative RT-PCR from cultured embryonic DRG neurons (Mean +- S.D. ; n = 6; *** p < 0.001 from a t -test)
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
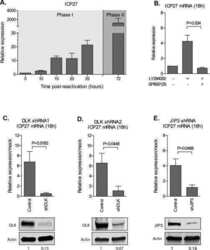
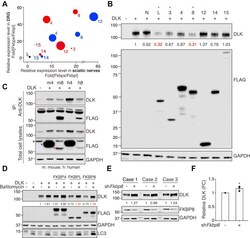
- Figure 3 FKBPL and FKBP8 induced lysosome-dependent DLK degradation. A , comparative analysis of relative expression levels in mouse L4,5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) tissues, sciatic nerve tissues, and cultured embryonic DRG neurons (, , , ). Red and blue circles indicate Illumina short-read sequencing and Oxford Nanopore direct RNA long-read sequencing, respectively. Circle sizes indicate relative levels of microarray data from cultured embryonic DRG neurons. B , Western blot analysis for the expression of DLK with FKBPs (N; vector, L; FKBPL, 3; FKBP3, 4; FKBP4, 8; FKBP8, 12; FKBP12, 14; FKBP14, 15; FKBP15). The number indicates normalized relative intensity. Dual leucine zipper kinase and FLAG-epitope-tagged FKBP protein family members were expressed in HEK293T cells and subjected to SDS-PAGE. C , Western blot analysis for the immunoprecipitation of DLK with mouse (m) and human (h) FKBP4/8 that was overexpressed in HEK293T cells. Empty arrowhead , non-specific band; blue arrowhead , FKBP4; red arrowhead , FKBP8. D , Western blot analysis for the expression of DLK and FKBPL/4/8 expressed in HEK293T cells with or without bafilomycin A1 treatment. The numbers indicate the normalized relative intensity. E , Western blot analysis of DLK protein levels under Fkbp8 knockdown (sh Fkbp8 ) by lentiviral delivery in primary cultured embryonic DRG neurons. The numbers indicate the normalized relative intensity. F , statistical analysis of ( E ) (FC, fold change; n = 3 for each cond
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
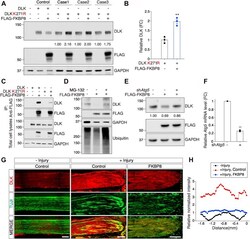
- Figure 5 FKBP8 mediates ubiquitin-dependent DLK degradation. A , Western blot analysis for the expression of DLK, its K271R mutant, and FKBP8 in HEK293T cells. The numbers indicate the normalized relative intensity. B , statistical analysis of (A) (n = 3 for each condition; ** p < 0.01 by t test; mean +- S.E.M.). C , Western blot analysis for the immunoprecipitation assays of FKBP8 with DLK and the K271R mutant. Dual leucine zipper kinase, DLK K271R, and FLAG-epitope-tagged FKBP8 were expressed in HEK293T cells. The protein lysates were immunoprecipitated using an anti-FLAG antibody followed by SDS-PAGE analysis. D , Western blot analysis for validating DLK levels by the expression of FKBP8 with or without MG-132 treatment in primary cultured embryonic DRG neurons. Embryonic DRG neurons were incubated with or without 10 muM MG-132 treatment for 6 h and lysed for Western blot analysis. E , primary cultured embryonic DRG neurons were infected by lentivirus of FLAG-FKBP8 with or without Atg5 -shRNA at DIV2 and lysed for Western blot analysis. F , relative expression of Atg5 mRNA analyzed via RT-qPCR (FC, fold change; n = 3; mean +- SEM; ** p < 0.01 by t test). G , sciatic nerves from AAV-control- or AAV-FKBP8-injected mice were ligated and dissected at 24 h after injury. Longitudinal sections were immunostained with the anti-DLK antibody and TUJI antibody. Yellow dotted arrows indicate the injury site. The scale bar represents 200 mum. H , relative normalized intensity of DLK wa
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry