Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Other assay [9]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 33-8900 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- IQGAP1 Monoclonal Antibody (AF1)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant protein fragment
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- AF1
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Purpuric drug eruptions induced by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors are associated with IQGAP1-mediated increase in vascular permeability.
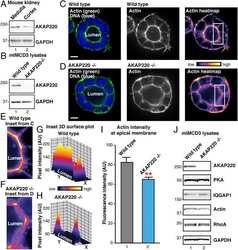
AKAP220 manages apical actin networks that coordinate aquaporin-2 location and renal water reabsorption.
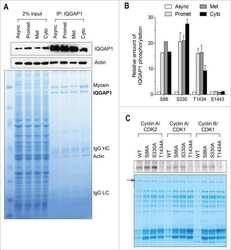
IQGAP1 is associated with nuclear envelope reformation and completion of abscission.
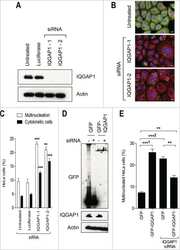
Patient Mutation Directed shRNA Screen Uncovers Novel Bladder Tumor Growth Suppressors.
IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven tumors.
Sheen YS, Lin MH, Tzeng WC, Chu CY
The Journal of pathology 2020 Apr;250(4):452-463
The Journal of pathology 2020 Apr;250(4):452-463
AKAP220 manages apical actin networks that coordinate aquaporin-2 location and renal water reabsorption.
Whiting JL, Ogier L, Forbush KA, Bucko P, Gopalan J, Seternes OM, Langeberg LK, Scott JD
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Jul 26;113(30):E4328-37
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2016 Jul 26;113(30):E4328-37
IQGAP1 is associated with nuclear envelope reformation and completion of abscission.
Lian AT, Hains PG, Sarcevic B, Robinson PJ, Chircop M
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2015;14(13):2058-74
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2015;14(13):2058-74
Patient Mutation Directed shRNA Screen Uncovers Novel Bladder Tumor Growth Suppressors.
Hensel J, Duex JE, Owens C, Dancik GM, Edwards MG, Frierson HF, Theodorescu D
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2015 Sep;13(9):1306-15
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2015 Sep;13(9):1306-15
IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven tumors.
Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J, Zarnegar B, Sage J, Khavari PA
Nature medicine 2013 May;19(5):626-630
Nature medicine 2013 May;19(5):626-630
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
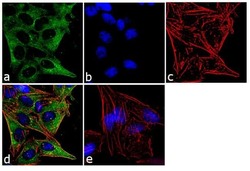
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of IQGAP1 Monoclonal Antibody was performed using 70% confluent log phase HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with IQGAP1 (AF1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 33-8900) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA, incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
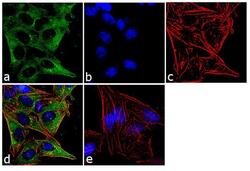
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of IQGAP1 Monoclonal Antibody was performed using 70% confluent log phase HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with IQGAP1 (AF1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 33-8900) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA, incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
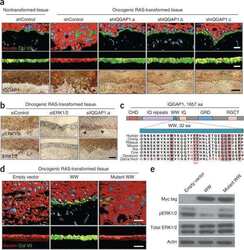
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
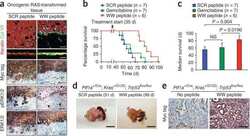
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
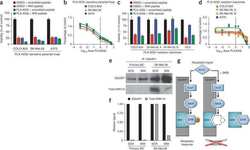
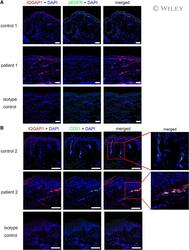
- IQGAP1 is expressed and co-localized in CD-31-positive vascular endothelial cells in the lesional skin of purpuric eruptions. (A) Three-color immunofluorescence images were obtained for IQGAP1 (red), pEGFR (green), and nuclei (blue) in lesional skin and normal skin from healthy controls. The administration of erlotinib resulted in reduced pEGFR and increased IQGAP1 expression of the basal keratinocytes and vessels in the upper dermis. Images were acquired using confocal microscopy (10x objective). (B) Three-color immunofluorescence images were obtained for IQGAP1 (red), CD31 (green), and nuclei (blue) in lesional skin and normal skin from healthy controls. Double-positive cells are yellow in merged images. IQGAP1-positive cells were co-localized with the CD31-positive cells in the superficial dermis from the patient treated with erlotinib. The regions in red boxes are shown magnified (right). All cells were negative using an isotype control. The images were acquired by confocal microscopy using a 20x objective (bar = 100 mum).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
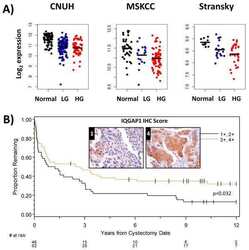
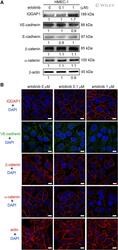
- Expression of IQGAP1, VE-cadherin/catenin complexes, and actin during erlotinib treatment in HMEC-1s. HMEC-1s were treated with erlotinib with indicated concentrations for 72 h. (A) Erlotinib treatment increased IQGAP1 expression but did not change VE-cadherin, E-cadherin, beta-catenin, or alpha-catenin protein expression significantly. (B) Increased IQGAP1 fluorescence at the cell borders and perinucleus area was detected after erlotinib treatment. The erlotinib-treated HMEC-1s revealed a punctate alpha-catenin fluorescence in the areas of cell-cell contacts compared with control cells. Erlotinib treatment did not affect the distribution of VE-cadherin, beta-catenin, and actin filament in HMEC-1s. The images were acquired by confocal microscopy using a 100x objective (bar = 10 mum).
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry