Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [11]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [7]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 48-1200 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Doublecortin Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.25 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Krüppel-like factor 7 attenuates hippocampal neuronal injury after traumatic brain injury.
High-fat diet increases gliosis and immediate early gene expression in APOE3 mice, but not APOE4 mice.
Bio-electrosprayed human neural stem cells are viable and maintain their differentiation potential.
Fluoxetine effects on behavior and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in female C57BL/6J mice across the estrous cycle.
Increased Expression of Y-Encoded Demethylases During Differentiation of Human Male Neural Stem Cells.
Social instability is an effective chronic stress paradigm for both male and female mice.
Spontaneous Differentiation of Human Neural Stem Cells on Nanodiamonds.
3D Culture Method for Alzheimer's Disease Modeling Reveals Interleukin-4 Rescues Aβ42-Induced Loss of Human Neural Stem Cell Plasticity.
Dynamic microtubule association of Doublecortin X (DCX) is regulated by its C-terminus.
Use of induced pluripotent stem cell derived neurons engineered to express BDNF for modulation of stressor related pathology.
Interaction between nonviral reprogrammed fibroblast stem cells and trophic factors for brain repair.
Li WY, Fu XM, Wang ZD, Li ZG, Ma D, Sun P, Liu GB, Zhu XF, Wang Y
Neural regeneration research 2022 Mar;17(3):661-672
Neural regeneration research 2022 Mar;17(3):661-672
High-fat diet increases gliosis and immediate early gene expression in APOE3 mice, but not APOE4 mice.
Jones NS, Watson KQ, Rebeck GW
Journal of neuroinflammation 2021 Sep 18;18(1):214
Journal of neuroinflammation 2021 Sep 18;18(1):214
Bio-electrosprayed human neural stem cells are viable and maintain their differentiation potential.
Helenes González C, Jayasinghe SN, Ferretti P
F1000Research 2020;9:267
F1000Research 2020;9:267
Fluoxetine effects on behavior and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in female C57BL/6J mice across the estrous cycle.
Yohn CN, Shifman S, Garino A, Diethorn E, Bokka L, Ashamalla SA, Samuels BA
Psychopharmacology 2020 May;237(5):1281-1290
Psychopharmacology 2020 May;237(5):1281-1290
Increased Expression of Y-Encoded Demethylases During Differentiation of Human Male Neural Stem Cells.
Pottmeier P, Doszyn O, Peuckert C, Jazin E
Stem cells and development 2020 Dec 1;29(23):1497-1509
Stem cells and development 2020 Dec 1;29(23):1497-1509
Social instability is an effective chronic stress paradigm for both male and female mice.
Yohn CN, Ashamalla SA, Bokka L, Gergues MM, Garino A, Samuels BA
Neuropharmacology 2019 Dec 1;160:107780
Neuropharmacology 2019 Dec 1;160:107780
Spontaneous Differentiation of Human Neural Stem Cells on Nanodiamonds.
Taylor AC, González CH, Ferretti P, Jackman RB
Advanced biosystems 2019 Apr;3(4):e1800299
Advanced biosystems 2019 Apr;3(4):e1800299
3D Culture Method for Alzheimer's Disease Modeling Reveals Interleukin-4 Rescues Aβ42-Induced Loss of Human Neural Stem Cell Plasticity.
Papadimitriou C, Celikkaya H, Cosacak MI, Mashkaryan V, Bray L, Bhattarai P, Brandt K, Hollak H, Chen X, He S, Antos CL, Lin W, Thomas AK, Dahl A, Kurth T, Friedrichs J, Zhang Y, Freudenberg U, Werner C, Kizil C
Developmental cell 2018 Jul 2;46(1):85-101.e8
Developmental cell 2018 Jul 2;46(1):85-101.e8
Dynamic microtubule association of Doublecortin X (DCX) is regulated by its C-terminus.
Moslehi M, Ng DCH, Bogoyevitch MA
Scientific reports 2017 Jul 12;7(1):5245
Scientific reports 2017 Jul 12;7(1):5245
Use of induced pluripotent stem cell derived neurons engineered to express BDNF for modulation of stressor related pathology.
Liu G, Rustom N, Litteljohn D, Bobyn J, Rudyk C, Anisman H, Hayley S
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2014;8:316
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2014;8:316
Interaction between nonviral reprogrammed fibroblast stem cells and trophic factors for brain repair.
Liu G, Anisman H, Bobyn J, Hayley S
Molecular neurobiology 2014 Oct;50(2):673-84
Molecular neurobiology 2014 Oct;50(2):673-84
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
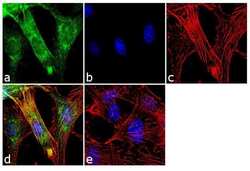
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Doublecortin was performed using 70% confluent log phase U-87MG cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Doublecortin/DCX Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # 48-1200) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
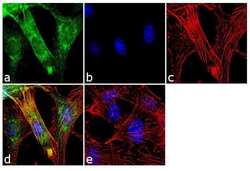
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Doublecortin was performed using 70% confluent log phase U-87MG cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Doublecortin/DCX Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # 48-1200) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
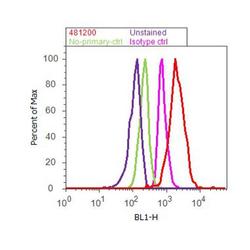
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Doublecortin was done on SH-SY5Y cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with Doublecortin Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (481200, red histogram) or with rabbit isotype control (pink histogram) at 3-5 ug/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Goat Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody (A11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
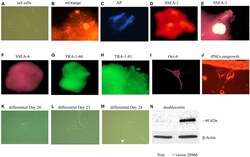
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 3 In vitro iPSCs and neural progenitor cells produced from adult mouse fibroblasts (see Materials and Methods). The panels show that control (absence of the 20866 vector) tail cells still retain their original shape on Day 47 after culturing (A) . The presence of the mOrange marker suggests that the fibroblasts have successfully integrated the 20866 plasmid (B) . The iPSCs were further characterized by an alkaline phosphatase live stain (C) , as well as staining of the three cell-surface stage-specific embryonic antigens: SSEA-1 to -4 (D-F) , TRA-1-60 (G) , TRA-1-81 (H) , and Oct-4 (I) . By Day 18, iPSCs began displaying projections (J) and further differentiation was clearly evident by Days 20, 23, and 28 (K-M) , respectively. By the later time point (M) , the cells had morphology consistent with that of neural progenitor cells and displayed a robust induction of the immature neuronal marker, doublecortin (N) .
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
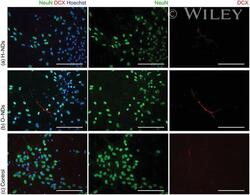
- Experimental details
- Fluorescently stained images of neurons, which have been differentiated from hNSCs after a) 25 DIV and b) NeuN (green), DCX (red) and Hoechst (blue). All scale bars 100 um.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
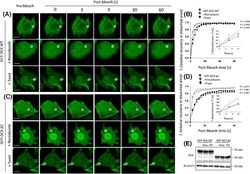
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 FRAP analysis reveals that GFP-DCX dynamics can be influenced by agents that alter MT stability. COS-1 cells were transfected to express ( A ) GFP-DCX WT or ( C ) GFP-DCX DeltaC. Cells were exposed to nocodazole (20 uM, 2 h) to depolymerise MTs or to taxol (10 uM, 1 h) to stabilize MT polymers. A small ROI (indicated by white rectangle in each cell image) was photobleached in ( A ) and ( C ) and the fluorescence recovery was subsequently monitored post-bleach at 3 s intervals for 60 s. Plots of the recovery of fluorescence in the small area of bleach for ( B ) DCX WT and ( D ) DCX DeltaC constructs before and after nocodazole or taxol treatments are shown. Regression values for the accuracy of each curve fit are indicated. The insets represent the initial recovery of fluorescence in the photobleached area for first three time-points (0-6 s of post-bleach) with the line of best fit used for the calculation of the initial recovery rates. ( E ) Equivalent expression of the GFP-DCX constructs was detected in the presence and absence of nocodazole or taxol by immunoblotting for DCX (upper panel), with equivalent protein loading detected by immunoblotting for total alpha-tubulin (lower panel). Scale bars represent 10 um. See Fig. 4 for quantitative pooled data.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
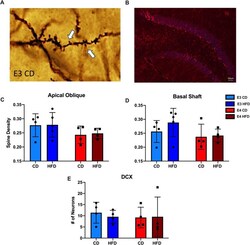
- Experimental details
- Fig. 7 HFD does not alter neurogenesis or spine density in APOE 3 and APOE 4 mice. A Image of spines quantified from Golgi staining. B Image of DCX positive cells. C - D Quantification of spine density on the Apical Oblique and Basal Shaft. E Quantification of DCX positive cells
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
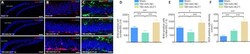
- Experimental details
- Figure 10 KLF7 increases neural proliferation following TBI. (A-C) Immunofluorescence staining of BrdU (proliferating neurons, red, stained by Alexa 555), DCX (newly generated neurons, red, stained by Alexa 555), and GFAP (astrocytes, green, stained by fluorescein isothiocyanate) with nuclear staining (DAPI; blue) in the ipsilateral hippocampus dentate gyrus (DG) in the three groups at 3 and 7 days following TBI. Compared with the TBI + AAV-NC group, BrdU-positive cells increased in the TBI + AAV-KLF7 group at 3 and 7 days following TBI. DCX-positive cells exhibited a similar pattern of change under the different treatment conditions. Scale bars: 100 mum in A, 200 mum in B and C. (D, E) Quantification of the number of BrdU-positive cells in the DG at 3 (D) and 7 (E) days following TBI. (F) Quantification of the density of DCX-positive cells at 3 days following TBI. Data are expressed as the mean +- SD ( n = 4). * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc test). AAV: Adeno-associated virus; BrdU: 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine; DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DCX: doublecortin; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; KLF7: Kruppel-like factor 7; NC: negative control; TBI: traumatic brain injury.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
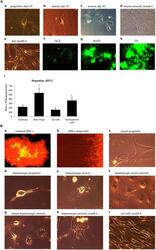
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 5 (A) Immature neuronal cells that were cultured in a Dopaminergic Neuronal Progenitor Medium began to show morphological signs of neuronal maturity between Day 29-50 (a,b,c) and after 6 months these cells displayed further signs of mature network formation (d). Importantly, control tail cells that were not subject to the reprogramming procedures kept their original shape at 6 months (e). As well, during this time, expression of the early immature neuronal cell marker, DCX, was greatly diminished (f), together with increased expression of the mature general neuronal cell marker, microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP2), (g), and specific dopaminergic neuronal marker, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), (h) was evident. Further confirmation that the reprogrammed neurons were mature dopaminergic neurons was obtained using HPLC (i); wherein tail cells that were re-programmed (Tail-Dopamine cells) displayed significantly increased dopamine levels, compared to non-reprogrammed controls (Tail cells). Furthermore, dopamine levels in non-reprogrammed controls were, as expected, quite low (Tail tissue), whereas freshly dissected adult midbrain tissue had the expected highest concentration of dopamine (Brain tissue). * p < 0.05, relative to control tails. (B) Shows the time course for dopaminergic neuron derivation. The adult mouse (aged 2 months) fibroblasts were reprogrammed by vector 20866 with c-Myc, Klf4, Oct4, and Sox2 genes and an mOrange marker was used to detect gene expression a
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
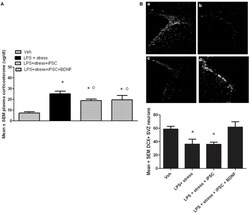
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 4 As shown in the bar graph on the left (A) , the single icv LPS infusion (2 mug) plus a 3-week twice-daily different stressor challenge (LPS + stress) increased plasma corticosterone, relative to vehicle treatment (Veh). Icv infusion of either the iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells alone (LPS + stress + iPSC) or in combination with the cDNA BDNF (LPS + stress + iPSC + BDNF) attenuated the plasma corticosterone rise induced by the LPS + stress treatment. The photomicrograph on the right (B) displays doublecortin (DCX) immunoreactivity in the subventricular zone (SVZ) in response to vehicle (a), LPS + stressor exposure (b), LPS + stressor exposure + iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells (c), or LPS + stressor exposure + iPSC-derived neural progenitors + BDNF cDNA (d). As quantified in the bottom bar graph, the LPS + stressor exposure alone or in combination with the iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells significantly reduced the number of DCX+ cells within the SVZ ( p < 0.05). However, infusion of the iPSC derived neural progenitor cells that were transfected with cDNA BDNF completely prevented this DCX reduction. * p < 0.05 relative to Veh treatment, o p < 0.05 relative to LPS + stress treatment.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation