Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [13]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [8]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 33-9400 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- SRSF3 Monoclonal Antibody (1H4G7)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Reactivity
- Human, Xenopus
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 1H4G7
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Therapeutic manipulation of IKBKAP mis-splicing with a small molecule to cure familial dysautonomia.
Splicing Enhancers at Intron-Exon Borders Participate in Acceptor Splice Sites Recognition.
Anti-tumor efficacy of a novel CLK inhibitor via targeting RNA splicing and MYC-dependent vulnerability.
Balanced splicing at the Tat-specific HIV-1 3'ss A3 is critical for HIV-1 replication.
Digoxin suppresses HIV-1 replication by altering viral RNA processing.
Serine arginine splicing factor 3 is involved in enhanced splicing of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA in response to nutrients and hormones in liver.
The cardiotonic steroid digitoxin regulates alternative splicing through depletion of the splicing factors SRSF3 and TRA2B.
Engineering DYRK1A overdosage yields Down syndrome-characteristic cortical splicing aberrations.
Changes in brain MicroRNAs contribute to cholinergic stress reactions.
RNA splicing capability of live neuronal dendrites.
RNA folding affects the recruitment of SR proteins by mouse and human polypurinic enhancer elements in the fibronectin EDA exon.
RNA folding affects the recruitment of SR proteins by mouse and human polypurinic enhancer elements in the fibronectin EDA exon.
Cyclin L is an RS domain protein involved in pre-mRNA splicing.
Ajiro M, Awaya T, Kim YJ, Iida K, Denawa M, Tanaka N, Kurosawa R, Matsushima S, Shibata S, Sakamoto T, Studer L, Krainer AR, Hagiwara M
Nature communications 2021 Jul 23;12(1):4507
Nature communications 2021 Jul 23;12(1):4507
Splicing Enhancers at Intron-Exon Borders Participate in Acceptor Splice Sites Recognition.
Kováčová T, Souček P, Hujová P, Freiberger T, Grodecká L
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Sep 8;21(18)
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Sep 8;21(18)
Anti-tumor efficacy of a novel CLK inhibitor via targeting RNA splicing and MYC-dependent vulnerability.
Iwai K, Yaguchi M, Nishimura K, Yamamoto Y, Tamura T, Nakata D, Dairiki R, Kawakita Y, Mizojiri R, Ito Y, Asano M, Maezaki H, Nakayama Y, Kaishima M, Hayashi K, Teratani M, Miyakawa S, Iwatani M, Miyamoto M, Klein MG, Lane W, Snell G, Tjhen R, He X, Pulukuri S, Nomura T
EMBO molecular medicine 2018 Jun;10(6)
EMBO molecular medicine 2018 Jun;10(6)
Balanced splicing at the Tat-specific HIV-1 3'ss A3 is critical for HIV-1 replication.
Erkelenz S, Hillebrand F, Widera M, Theiss S, Fayyaz A, Degrandi D, Pfeffer K, Schaal H
Retrovirology 2015 Mar 28;12:29
Retrovirology 2015 Mar 28;12:29
Digoxin suppresses HIV-1 replication by altering viral RNA processing.
Wong RW, Balachandran A, Ostrowski MA, Cochrane A
PLoS pathogens 2013 Mar;9(3):e1003241
PLoS pathogens 2013 Mar;9(3):e1003241
Serine arginine splicing factor 3 is involved in enhanced splicing of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA in response to nutrients and hormones in liver.
Walsh CM, Suchanek AL, Cyphert TJ, Kohan AB, Szeszel-Fedorowicz W, Salati LM
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Jan 25;288(4):2816-28
The Journal of biological chemistry 2013 Jan 25;288(4):2816-28
The cardiotonic steroid digitoxin regulates alternative splicing through depletion of the splicing factors SRSF3 and TRA2B.
Anderson ES, Lin CH, Xiao X, Stoilov P, Burge CB, Black DL
RNA (New York, N.Y.) 2012 May;18(5):1041-9
RNA (New York, N.Y.) 2012 May;18(5):1041-9
Engineering DYRK1A overdosage yields Down syndrome-characteristic cortical splicing aberrations.
Toiber D, Azkona G, Ben-Ari S, Torán N, Soreq H, Dierssen M
Neurobiology of disease 2010 Oct;40(1):348-59
Neurobiology of disease 2010 Oct;40(1):348-59
Changes in brain MicroRNAs contribute to cholinergic stress reactions.
Meerson A, Cacheaux L, Goosens KA, Sapolsky RM, Soreq H, Kaufer D
Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN 2010 Jan;40(1-2):47-55
Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN 2010 Jan;40(1-2):47-55
RNA splicing capability of live neuronal dendrites.
Glanzer J, Miyashiro KY, Sul JY, Barrett L, Belt B, Haydon P, Eberwine J
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Nov 15;102(46):16859-64
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Nov 15;102(46):16859-64
RNA folding affects the recruitment of SR proteins by mouse and human polypurinic enhancer elements in the fibronectin EDA exon.
Buratti E, Muro AF, Giombi M, Gherbassi D, Iaconcig A, Baralle FE
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Feb;24(3):1387-400
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Feb;24(3):1387-400
RNA folding affects the recruitment of SR proteins by mouse and human polypurinic enhancer elements in the fibronectin EDA exon.
Buratti E, Muro AF, Giombi M, Gherbassi D, Iaconcig A, Baralle FE
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Feb;24(3):1387-400
Molecular and cellular biology 2004 Feb;24(3):1387-400
Cyclin L is an RS domain protein involved in pre-mRNA splicing.
Dickinson LA, Edgar AJ, Ehley J, Gottesfeld JM
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Jul 12;277(28):25465-73
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Jul 12;277(28):25465-73
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
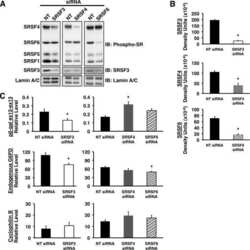
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
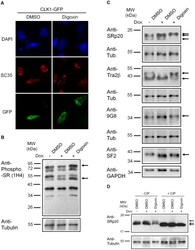
- Experimental details
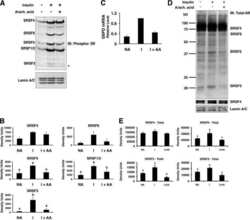
- Figure 6 Digoxin alters the activity of SR protein kinases and induces modification of a subset of SR proteins. (A) To assess the effect of digoxin on CLK kinase function, HeLa rtTA-HIV-Delta Mls cells were transfected with vectors expressing GFP-tagged CLK1. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were treated with DMSO or 100 nM digoxin. After 24 h of treatment, cells were fixed, stained for SC35/SRSF2 nuclear speckles (Texas Red), and nuclei stained with DAPI. Images are representative of the localization patterns observed from >=5 independent experiments. Magnification 630x. (B, C, D) Western blot analysis of the effect of digoxin treatment on SR proteins. Lysates were harvested from HeLa rtTA-HIV-Delta Mls cells treated with 100 nM digoxin or DMSO and were induced with Dox (+) or left uninduced (-) as described in Fig. 1 . Immunoblots were probed by specific antibody for (B) phospho-SR proteins (1H4) or (C) SRp20, Tra2beta1, 9G8, or SF2/ASF (SF2). (D) Cell lysates from above were dephosphorylated by treatment with (+) and without (-) calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), then immunoblotted with a SRp20-specific antibody. Arrows on the right indicate the protein specie(s) detected and their modified/unmodified isoform(s). Anti-tubulin (Anti-Tub.) blots for each experiment served as an internal loading control for the relative amount of protein lysate per lane. Immunoblots are representative of >=4 independent trials.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
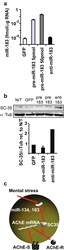
- Experimental details
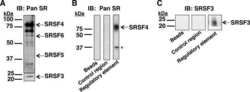
- Figure 2 miR-183 regulates the splicing factor SC35. a QRT-PCR for miR-183 in CHO cells transfected with pre-miR-183 or anti-miR-183 (Ambion) and GFP-transfected controls. Bars : SD; t test p < 10 -5 for both concentrations of pre-miR-183 compared to GFP control. b Scan and quantification of immunoblot for SC35 in cells in a with alpha-tubulin used for normalization. c Suggested interplay of alternative splicing and miRs (exemplified by miR-134, miR-183, and their target, the splicing factor SC35) contributes to the complexity of stress responses in the brain, including regulation of the alternative splicing choice between the major ""synaptic"" AChE transcript AChE-S and the normally minor stress-induced variant AChE-R
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
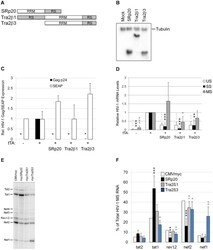
- Experimental details
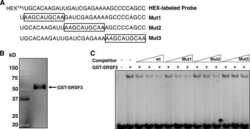
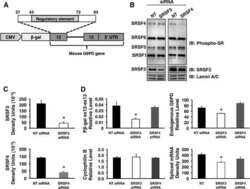
- Figure 7 Overexpression of SRp20, Tra2beta1, or Tra2beta3 suppress HIV-1 expression. (A) Diagram of SRp20, Tra2beta1, and Tra2beta3 protein domain structure. (B) Cells were transfected with the vectors CMVmyc (mock), CMVmyc SRp20 (SRp20), CMVmyc Tra2beta1 (Tra2beta1), or CMVmyc Tra2beta3 (Tra2beta3). Forty-eight hours post-transfection, cells were harvested, lysed in RIPA buffer, and proteins analyzed by western blot with anti-myc antibody followed by anti-tubulin (Tubulin) antibody to indicate loading. (C) HeLa rtTA-HIV-Delta Mls cells were transfected with (+) (or without, -) CMVtTApA (tTA) to activate the endogenous HIV-1 provirus along with CMV PLAP and either CMVmyc, CMVmyc SRp20, CMVmyc Tra2beta1, or CMVmyc Tra2beta3. Forty-eight hours post transfection, cell media was harvested and assayed by p24 CA ELISA for expression of HIV-1 Gag (black) and production of SEAP (white). Results are averaged from 6 independent assays, error bars are SEM, and asterisks indicate values deemed significant from CMVmyc (+tTA) as detailed in "" Materials & Methods "". (D) In parallel, total RNA was extracted from transfected cells and the abundance of individual viral RNA (unspliced, US; singly spliced, SS; multiply spliced, MS) were determined by qRT-PCR. Shown are results averaged from 6 independent assays, error bars are SEM, and asterisks indicate significance as noted above. (E, F) MS HIV-1 RNAs from transfected cells were amplified by RT-PCR as described in Fig. 4 . Amplicons were fra
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Other assay
Other assay