Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [5]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-24495 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- POC1B Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 400 μL
- Concentration
- 2 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references The human sperm basal body is a complex centrosome important for embryo preimplantation development.
WDR90 is a centriolar microtubule wall protein important for centriole architecture integrity.
PPP1R35 is a novel centrosomal protein that regulates centriole length in concert with the microcephaly protein RTTN.
Human microcephaly protein RTTN interacts with STIL and is required to build full-length centrioles.
CEP295 interacts with microtubules and is required for centriole elongation.
Amargant F, Pujol A, Ferrer-Vaquer A, Durban M, Martínez M, Vassena R, Vernos I
Molecular human reproduction 2021 Nov 2;27(11)
Molecular human reproduction 2021 Nov 2;27(11)
WDR90 is a centriolar microtubule wall protein important for centriole architecture integrity.
Steib E, Laporte MH, Gambarotto D, Olieric N, Zheng C, Borgers S, Olieric V, Le Guennec M, Koll F, Tassin AM, Steinmetz MO, Guichard P, Hamel V
eLife 2020 Sep 18;9
eLife 2020 Sep 18;9
PPP1R35 is a novel centrosomal protein that regulates centriole length in concert with the microcephaly protein RTTN.
Sydor AM, Coyaud E, Rovelli C, Laurent E, Liu H, Raught B, Mennella V
eLife 2018 Aug 31;7
eLife 2018 Aug 31;7
Human microcephaly protein RTTN interacts with STIL and is required to build full-length centrioles.
Chen HY, Wu CT, Tang CC, Lin YN, Wang WJ, Tang TK
Nature communications 2017 Aug 15;8(1):247
Nature communications 2017 Aug 15;8(1):247
CEP295 interacts with microtubules and is required for centriole elongation.
Chang CW, Hsu WB, Tsai JJ, Tang CJ, Tang TK
Journal of cell science 2016 Jul 1;129(13):2501-13
Journal of cell science 2016 Jul 1;129(13):2501-13
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
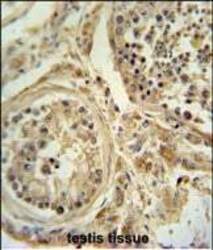
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of POC1B in formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human testis tissue. Samples were incubated with POC1B polyclonal antibody (Product # PA5-24495) followed by peroxidase conjugation of the secondary antibody and DAB staining. This data demonstrates the use of this antibody for immunohistochemistry. Clinical relevance has not been evaluated.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
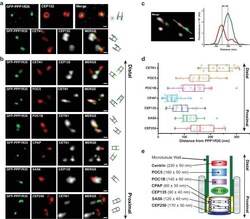
- Experimental details
- Figure 2. PPP1R35 localizes to the proximal end of the centriolar lumen above the cartwheel. ( a,b ) 3D structured illumination microscopy (3DSIM) micrographs of U2OS cells expressing GFP-PPP1R35 (treated with digitonin to remove the cytoplasmic PPP1R35 population) and co-stained with CEP152 ( a ) and various other markers ( b ) labeling the distal (POC5, POC1B, CETN1) and proximal (SAS6, CEP135, CPAP, CEP250) regions of the centriole. The cartoon depiction of the centriole is alongside the images to assist in orienting the 3DSIM micrographs. Scale bars, 250 nm. ( c ) By measuring the distances between the fluorescence maxima of PPP1R35 and various centriolar markers on the same z-plane, the distance between GFP-PPP1R35 and the corresponding marker was determined. The fluorescence intensity along the line drawn in the micrograph (green, GFP-PPP1R35; red, POC5; white, CETN1) is plotted as a function of the distance along the line. The grey lines are centered at the fluorescence maxima and the distance between these lines corresponds to the distance between GFP-PPP1R35 and the corresponding marker (POC5 in this example). ( d ) By combining the analysis of the micrographs with these measurements, the position of PPP1R35 was mapped on to the centriole and the distances are shown in a Tukey box and whiskers plot, with the whiskers representing datum within an interquartile range of 1.5 and the band in the box as the mean. ( e ) A cartoon depiction of the localization of PPP1
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
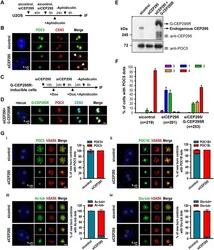
- Experimental details
- Fig. 3. The G2 centrioles in CEP295-depleted cells fail to recruit POC5 or POC1B and do not show post-translational modification of centriolar microtubules. (A,B) U2OS cells were treated with sicontrol or siCEP295 as shown in (A) and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy (B). Arrows in B indicate inhibited targeting of POC5 to nascent centrioles. (C-F) Rescue experiment. G-CEP295R-inducible cells were treated as described in (C) and analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy (D) or immunoblot analysis (E). (F) Histograms illustrating the percentages of cells exhibiting POC5 signals. Error bars represent the mean+-s.e.m. from four independent experiments. The total number n as indicated. (G) PLK4-myc-inducible cells were treated with siCEP295 as described in Fig. 1 C, analyzed by immunofluorescence staining with antibodies against: (i) POC5 and hSAS6; (ii) POC1B and hSAS6; (iii) hSAS6 and Ac-tub, and (iv) hSAS6 and Glu-tub, and expression in new-born centrioles quantified. Error bars represent the mean+-s.e.m. n =3 independent experiments each scoring 100 cells. Scale bars: 0.5 mum in the enlarged figures.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
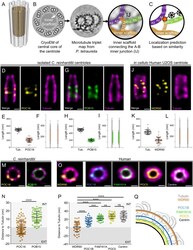
- Experimental details
- Figure 1. POC16/WDR90 is a conserved central core microtubule wall component. ( A ) 3D representation of a centriole highlighting the centriolar microtubule wall in light grey and the inner scaffold in yellow. ( B ) Cryo-EM image of the central core of Paramecium tetraurelia centrioles from which a microtubule triplet map has been generated (). Schematic representation of the inner junction (IJ) between A- and B-microtubules connecting the inner scaffold. ( C ) Schematic localization of POC16/WDR90 proteins within the IJ based on its similarity to FAP20. Purple: A-microtubule, green: B microtubule, yellow/gold: inner scaffold and stem, orange: DUF667 domain positioned at the IJ. ( D ) Isolated U-ExM expanded Chlamydomonas centriole stained for POC16 (yellow) and tubulin (magenta), lateral view. Scale bar: 100 nm. ( E ) Respective lengths of tubulin and POC16 based on D. Average +/- SD: Tubulin: 495 nm +/- 33, POC16: 204 nm +/- 53, n = 46 centrioles from three independent experiments. ( F ) POC16 length coverage and positioning: 41% +/- 11, n = 46 centrioles from three independent experiments. ( G ) Expanded isolated Chlamydomonas centriole stained for POB15 (green) and tubulin (magenta), lateral view. Scale bar: 100 nm. ( H ) Respective length of tubulin and POB15 based on G. Average +/- SD: tubulin = 497 nm +/- 33, POB15 = 200 nm +/- 30, n = 39 centrioles from three independent experiments. ( I ) POB15 length coverage and positioning: 40% +/- 6, n = 39 centrioles from three
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
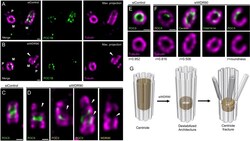
- Figure 5. WDR90 is important for centriole architecture integrity (see also Figure 5-figure supplement 1 , Videos 1 and 2 ). ( A, B ) Expanded centrioles from S-phase U2OS cells treated with control ( A ) or wdr90 siRNA ( B ), stained for tubulin (magenta) and POC1B (green). White arrowhead: broken microtubule wall of the mature centriole. P: procentriole, M: mature centriole. Scale bars: 100 nm. ( C, D ) Expanded centrioles from U2OS cells treated with control ( C ) or wdr90 siRNA ( D ), stained for tubulin (magenta) and POC5 (green) or WDR90 (yellow), displaying microtubule wall fractures (white arrowheads), lateral view. Scale bars: 100 nm. ( E, F ) Top views of expanded centrioles from U2OS cells treated with control ( E ) or wdr90 siRNA ( F ) stained as specified above. Note the loss of roundness of centrioles treated with wdr90 siRNA. Scale bars: 100 nm. ( G ) Model of WDR90 function holding microtubule triplets in the central core region of centrioles. Figure 5-figure supplement 1. WDR90 depletion leads to severe centriolar structure defects. ( A ) Quantification of the orientation of mother centrioles in control cells following the appendages marker CEP164. N = 215 centrioles from three independent experiments. ( B, C ) Percentage of normal and defective top viewed centrioles depleted for WDR90. Centrioles were considered as defective when the roundness of the centriole was lost. N = 356 centrioles from nine independent experiments. Average +/- SD: Top view depleted:
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
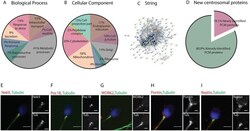
- Figure 3. Classification of the human sperm tail proteins. ( A ) Gene Ontology of the 3406 proteins based on their biological process. ( B ) Gene ontology of the same 3406 proteins based on their subcellular localization. ( C ) String network of the 251 identified centrosomal proteins. ( D ) Comparison of the pericentriolar material (PCM) proteins only identified in this work (19.1%--pink fraction) to all the previously published human sperm proteomic data (green fraction). ( E-I ) Antibodies against five of the centrosomal proteins identified in our proteomic analysis and co-stained with tubulin to visualize the centrioles. Nek9 (E), Poc1B (F) and WDR62 (G) co-localize with the proximal and distal centriole. Pontin (H) and Reptin (I) have a diffuse localization around the basal body. Scale: 3 mum, insets: 1 mum. N = 2 different sperm samples.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry