PA5-22819
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: ERVW-1
envW, ERVWE1, HERV-7q, HERV-W, HERV-W-ENV, HERVW
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-22819 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- HERV Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references An Ancestral Retrovirus Envelope Protein Regulates Persistent Gammaherpesvirus Lifecycles.
Frey TR, Akinyemi IA, Burton EM, Bhaduri-McIntosh S, McIntosh MT
Frontiers in microbiology 2021;12:708404
Frontiers in microbiology 2021;12:708404
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
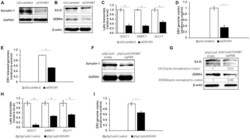
- FIGURE 2 Depletion of Syncytin-1 impairs EBV lytic activation. Akata cells were nucleofected with scrambled control or ERVW-1 specific siRNAs for 18 h and harvested for western blot analysis for Syncytin-1 (A) or treated with rabbit anti-human IgG to induce lytic activation and harvested at 24 h (B) , 36 h (C,D) , or 72 h (E) to analyze lytic readouts in each siRNA treatment group. Lytic proteins EA-D and ZEBRA were probed using western blot in B. Lytic transcript levels of representative genes of each EBV kinetic class were assayed using RT-qPCR in (C) . (D) EBV BamW qPCR was performed on DNA isolated from cell pellets. (E) EBV BamW qPCR was performed on DNase-treated, filtered cell culture medium. (F-I) Akata cells were nucleofected with pSpCas9 BB-2A-puro or pSpCas9 BB-2A-puro ERVW-1 guide RNA for 24 h prior to harvest for western blot analysis (F) or treated with rabbit anti-human IgG to induce lytic activation. Cells were harvested at 24 h (G) or 36 h (H,I) to analyze lytic readouts as in (B-D) , respectively. Data represent averages of three independent experiments; error bars, SEM; ** p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
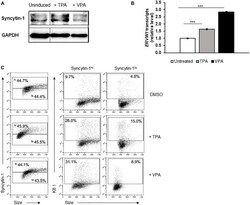
- FIGURE 4 Cells high in Syncytin-1 more readily support the KSHV lytic phase. The KSHV + PEL cell line BCBL-1 was exposed to TPA or VPA and harvested after 24 h (A,B) or 48 h (C) for immunoblotting (A) , RT-qPCR (B) , or flow cytometry (C) . In (C) , Syncytin-1 positive cells were sub-gated roughly equally into Syncytin-1 hi and Syncytin-1 lo sub-populations, which were then further examined for expression of the KSHV lytic K8.1 protein. Data represent averages of three independent experiments; error bars, SEM; *** p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
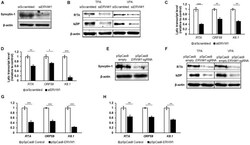
- FIGURE 5 Syncytin-1 supports the KSHV lytic cascade. BCBL-1 cells were nucleofected with scrambled control or ERVW-1 specific siRNAs for 18 h and harvested for western blot analysis for Syncytin-1 (A) or treated with TPA or VPA to induce lytic activation and harvested at 24 h (B) or 36 h (C,D) to analyze lytic readouts in each siRNA treatment group. Lytic proteins RTA and bZIP were probed using western blot in (B) . Lytic transcript levels of representative genes of each KSHV kinetic class were assayed using RT-qPCR after induction with TPA (C) or VPA (D) . (E-H) BCBL-1 cells were nucleofected with pSpCas9 BB-2A-puro or pSpCas9 BB-2A- puro ERVW-1 guide RNA for 24 h prior to harvest for western blot analysis (E) or treated with TPA or VPA to induce lytic activation. Cells were harvested at 24 h (F) or 36 h (G,H) to analyze lytic readouts as in (B-D) , respectively. Data represent averages of three independent experiments; error bars, SEM; * p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
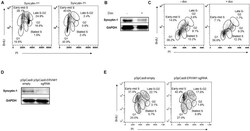
- FIGURE 7 Syncytin-1 supports proliferation of EBV + cells. (A) Syncytin-1 positive HH514-16 cells were sub-gated equally into Syncytin-1 hi and Syncytin-1 lo sub-populations, which were then further examined for cell cycle analysis via flow cytometry. (B,C) A stably integrated doxycycline-inducible Syncytin-1 knockdown HH514-16 cell line was induced with doxycycline or left untreated for 24 h to reduce Syncytin-1 expression followed by western blot to analyze Syncytin-1 levels (B) and cell cycle analysis as in (A) for each treatment group (C) . (D,E) HH514-16 cells were nucleofected with pSpCas9 BB-2A-puro or pSpCas9 BB-2A-puro ERVW-1 guide RNA for 24 h to knockdown Syncytin-1 expression followed by western blot to analyze Syncytin-1 levels (D) and cell cycle analysis (E) .
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Other assay
Other assay