PA5-56868
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: ZDHHC9
CGI-89, CXorf11, DHHC9, ZDHHC10, ZNF379, ZNF380
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-56868 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- ZDHHC9 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant protein fragment
- Description
- Immunogen sequence: PSTQETSSSL LPQSPAPTEH LNSNEMPEDS STPEEMPPPE PPEPPQEAAE AEK Highest antigen sequence identity to the following orthologs: Mouse - 89%, Rat - 91%.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references DHHC9-mediated GLUT1 S-palmitoylation promotes glioblastoma glycolysis and tumorigenesis.
Zhang Z, Li X, Yang F, Chen C, Liu P, Ren Y, Sun P, Wang Z, You Y, Zeng YX, Li X
Nature communications 2021 Oct 7;12(1):5872
Nature communications 2021 Oct 7;12(1):5872
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
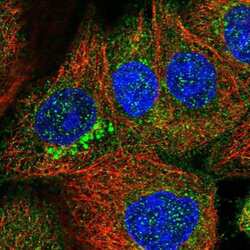
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of ZDHHC9 in human cell line A-431 shows positivity in cytoplasm & the Golgi apparatus. Samples were probed using a ZDHHC9 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-56868).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
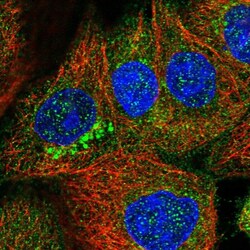
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorecent analysis of ZDHHC9 in human cell line A-431 using ZDHHC9 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-56868). Staining shows localization to cytosol and the Golgi apparatus.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
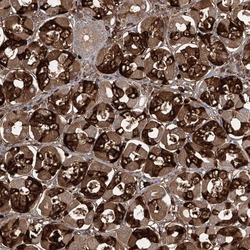
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of ZDHHC9 in human stomach using ZDHHC9 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-56868) shows strong cytoplasmic positivity in glandular cells.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
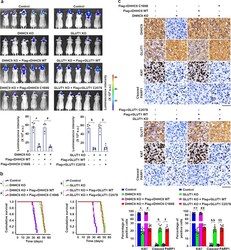
- Experimental details
- Fig. 5 DHHC9-mediated GLUT1 S-palmitoylation promotes GBM tumorigenesis. a , b Luciferase-expressing DHHC9-knockout U87 cells rescued with Flag-tagged WT rDHHC9 or rDHHC9 C169S and GLUT1-knockout GBM cells rescued with Flag-tagged WT rGLUT1 or rGLUT1 C207S were intracranially injected into athymic nude mice ( n = 5). Luminescence intensity derived from tumors was measured and relative luminescence intensity is shown ( a ). Data were collected from n = 5 mice per group, and the mean +- SD values are shown ( a ). The survival times of the mice ( n = 10) were recorded ( b ). a * P = 2.57E-06, # P = 1.16E-05, & P = 9.63E-06, $ P = 1.82E-05. b * P = 4.00E-06, # P = 3.00E-06, & P = 5.00E-06, $ P = 4.00E-06. c Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of DHHC9, GLUT1, Ki67, and cleaved PARP in paraffin-embedded xenograft tumor tissues collected from the indicated groups (top and middle). Scale bar, 50 mum. The expression levels of Ki67 and cleaved PARP1 were quantified for ten microscopic fields of the tumor samples (bottom). The mean +- SD values are shown. * P = 3.87E-19, # P = 1.44E-18, & P = 3.33E-12, $ P = 8.58E-14, ** P = 1.15E-18, ## P = 4.84E-18, && P = 5.63E-13, $$ P = 1.14E-13. P values were determined by the two-tailed Student's t test ( a , c ) and the two-tailed log-rank test ( b ). a.u., arbitrary unit ( a ). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
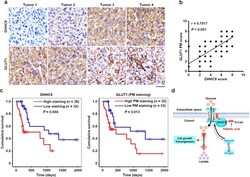
- Fig. 6 DHHC9 expression positively correlates with GLUT1 PM localization in GBM specimens and indicates clinical aggressiveness of GBM. a , b Sixty-eight human primary GBM specimens were immunohistochemically stained with indicated antibodies. Representative photos of tumors are shown ( a ). Immunohistochemistry staining scores of DHHC9 and PM-localized GLUT1 were analyzed by the two-tailed Pearson correlation ( b ). Note that some of the dots on the graphs represent more than one specimen (i.e., some scores overlapped). c Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot survival curves in human GBM specimens ( n = 68) with high (5-8 staining scores, red curve) and low (0-4 staining scores, blue curve) levels of DHHC9 and PM-localized GLUT1. The two-tailed log-rank test was used to compare the overall survival rate. Empty circles represent censored data from patients alive at the last clinical follow-up. d A mechanism of S-palmitoylated GLUT1-dependent glycolysis. GLUT1 Cys207 palmitoylation catalyzed by DHHC9 resulted in PM localization of GLUT1, leading to enhanced uptake of glucose, thereby promoting glycolysis, cell growth, and GBM tumorigenesis. P values were calculated by the two-tailed Pearson correlation ( b ) and the two-tailed log-rank test ( c ). Scale bar, 20 mum ( a ). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry