Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [7]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 17-3879-42 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD87 (UPAR) Monoclonal Antibody (VIM5), APC, eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: This VIM5 monoclonal antibody reacts with human CD87, a GPI-linked receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA). By sequestering uPA, CD87 is involved in the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin on the leading edge of migrating cells, a process critical for chemotaxis. CD87 is expressed on the surface of monocytes, dendritic cells, and on activated T and NK cells. Interestingly, in granulocytes, CD87 expressed in the cytoplasm and on the cell surface. Non-hematopoietic cells such as endothelial cells, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts, also express this receptor. Finally, CD87 plays a role in cell adhesion and migration, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. This monoclonal antibody has been reported to have neutralization activity. Applications Reported: This VIM5 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: This VIM5 antibody has been pre-titrated and tested by flow cytometric analysis of normal human peripheral blood cells. This can be used at 5 µL (0.5 µg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. Excitation: 633-647 nm; Emission: 660 nm; Laser: Red Laser. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- VIM5
- Vial size
- 100 Tests
- Concentration
- 5 μL/Test
- Storage
- 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE!
Submitted references The transition of M-CSF-derived human macrophages to a growth-promoting phenotype.
Senolytic CAR T cells reverse senescence-associated pathologies.
Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor contribute to chemoresistance in leukemia.
Blood coagulation factor XII drives adaptive immunity during neuroinflammation via CD87-mediated modulation of dendritic cells.
Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (CD87): something old, something new.
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (CD87) is a ligand for integrins and mediates cell-cell interaction.
Expression and functional role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in normal and acute leukaemic cells.
Hamidzadeh K, Belew AT, El-Sayed NM, Mosser DM
Blood advances 2020 Nov 10;4(21):5460-5472
Blood advances 2020 Nov 10;4(21):5460-5472
Senolytic CAR T cells reverse senescence-associated pathologies.
Amor C, Feucht J, Leibold J, Ho YJ, Zhu C, Alonso-Curbelo D, Mansilla-Soto J, Boyer JA, Li X, Giavridis T, Kulick A, Houlihan S, Peerschke E, Friedman SL, Ponomarev V, Piersigilli A, Sadelain M, Lowe SW
Nature 2020 Jul;583(7814):127-132
Nature 2020 Jul;583(7814):127-132
Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor contribute to chemoresistance in leukemia.
Guo H, Zhou LX, Ma H, Liu B, Cheng J, Ma YY, Zhao L
Oncology letters 2017 Jul;14(1):383-389
Oncology letters 2017 Jul;14(1):383-389
Blood coagulation factor XII drives adaptive immunity during neuroinflammation via CD87-mediated modulation of dendritic cells.
Göbel K, Pankratz S, Asaridou CM, Herrmann AM, Bittner S, Merker M, Ruck T, Glumm S, Langhauser F, Kraft P, Krug TF, Breuer J, Herold M, Gross CC, Beckmann D, Korb-Pap A, Schuhmann MK, Kuerten S, Mitroulis I, Ruppert C, Nolte MW, Panousis C, Klotz L, Kehrel B, Korn T, Langer HF, Pap T, Nieswandt B, Wiendl H, Chavakis T, Kleinschnitz C, Meuth SG
Nature communications 2016 May 18;7:11626
Nature communications 2016 May 18;7:11626
Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (CD87): something old, something new.
Ge Y, Elghetany MT
Laboratory hematology : official publication of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology 2003;9(2):67-71
Laboratory hematology : official publication of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology 2003;9(2):67-71
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (CD87) is a ligand for integrins and mediates cell-cell interaction.
Tarui T, Mazar AP, Cines DB, Takada Y
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Feb 9;276(6):3983-90
The Journal of biological chemistry 2001 Feb 9;276(6):3983-90
Expression and functional role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in normal and acute leukaemic cells.
Lanza F, Castoldi GL, Castagnari B, Todd RF 3rd, Moretti S, Spisani S, Latorraca A, Focarile E, Roberti MG, Traniello S
British journal of haematology 1998 Oct;103(1):110-23
British journal of haematology 1998 Oct;103(1):110-23
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
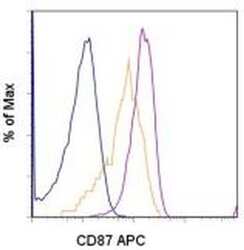
- Experimental details
- Staining of normal human peripheral blood cells with Anti-Human CD87 (UPAR) APC. Cells in the lymphocyte (blue histogram), monocyte (orange histogram), or granulocyte (pink histogram) gate were used for analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
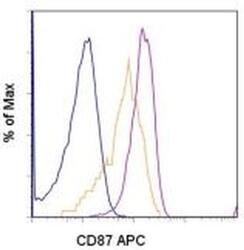
- Experimental details
- Staining of normal human peripheral blood cells with Anti-Human CD87 (UPAR) APC. Cells in the lymphocyte (blue histogram), monocyte (orange histogram), or granulocyte (pink histogram) gate were used for analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
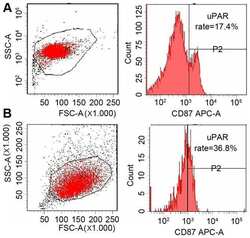
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
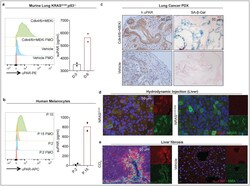
- Experimental details
- Figure 1| uPAR is a cell surface and secreted biomarker of senescence. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of mouse uPAR (m.uPAR) expression on Kras G12D ;p53 -/- murine lung adenocarcinoma cells (KP) induced to senesce by treatment with MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitors as compared to controls. Representative results of n=3 independent experiments. Levels of soluble uPAR (suPAR) as determined by ELISA in the supernatant of senescent or proliferating KP cells. Representative results of n=2 independent experiments. (b) Flow cytometric analysis comparing human uPAR (h.uPAR) expression on primary human melanocytes induced to senesce by continuous passage with proliferating controls . Representative results of n=2 independent experiments. Levels of suPAR in the supernatant of senescent (Passage 15 = P.15) or proliferating (Passage 2 = P.2) primary human melanocytes. Representative results of n=2 independent experiments. (c) Immunohistochemical stainings of h.uPAR and SA-beta-Gal of a patient-derived xenograft (PDX) from human lung adenocarcinoma orthotopically injected into NSG mice after treatment with vehicle or combined MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitors; representative of n=2 independent experiments (n=3 mice per group). (d) Co-immunofluorescence (IF) staining of m.uPAR (red) and NRAS (green) in the livers of mice 6 days after hydrodynamic tail vein injection of a plasmid encoding NRAS G12V or NRAS G12V;D38A . Representative results of n=3 independent experiments (n=5 mice per group). (e) Co-IF stai
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry