AHB0042
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: MAPT
DDPAC, FLJ31424, FTDP-17, MAPTL, MGC138549, MSTD, MTBT1, MTBT2, PPND, PPP1R103, tau
 Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [119]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [5]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [8]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- AHB0042 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Tau Monoclonal Antibody (TAU-5)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- TAU-5
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references DHCR24 Knockdown Induces Tau Hyperphosphorylation at Thr181, Ser199, Ser262, and Ser396 Sites via Activation of the Lipid Raft-Dependent Ras/MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway in C8D1A Astrocytes.
Identification of a reciprocal negative feedback loop between tau-modifying proteins MARK2 kinase and CBP acetyltransferase.
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Young Neural Cultures Attenuate Astrocytic Reactivity In Vitro.
Conformation-specific Antibodies Targeting Aggregated Forms of α-synuclein Block the Propagation of Synucleinopathy.
Improved Sleep, Memory, and Cellular Pathological Features of Tauopathy, Including the NLRP3 Inflammasome, after Chronic Administration of Trazodone in rTg4510 Mice.
Structural mapping techniques distinguish the surfaces of fibrillar 1N3R and 1N4R human tau.
RPS23RG1 modulates tau phosphorylation and axon outgrowth through regulating p35 proteasomal degradation.
BNIP3L/NIX-mediated mitophagy protects against glucocorticoid-induced synapse defects.
Efficient manipulation of gene dosage in human iPSCs using CRISPR/Cas9 nickases.
Dystrophic Dmd(mdx) rats show early neuronal changes (increased S100β and Tau5) at 8 months, supporting severe dystropathology in this rodent model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Tau Reduction Prevents Key Features of Autism in Mouse Models.
Correcting abnormalities in miR-124/PTPN1 signaling rescues tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease.
Fyn Kinase Controls Tau Aggregation In Vivo.
Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Tau and Related Proteins in Rats with the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.
Acetylation of Aβ42 at Lysine 16 Disrupts Amyloid Formation.
Targeting the ensemble of heterogeneous tau oligomers in cells: A novel small molecule screening platform for tauopathies.
Targeted degradation of aberrant tau in frontotemporal dementia patient-derived neuronal cell models.
REST and Neural Gene Network Dysregulation in iPSC Models of Alzheimer's Disease.
Multi-sensory Gamma Stimulation Ameliorates Alzheimer's-Associated Pathology and Improves Cognition.
Ovarian Function Modulates the Effects of Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Mouse Cerebral Cortex.
Differential Hyperphosphorylation of Tau-S199, -T231 and -S396 in Organotypic Brain Slices of Alzheimer Mice. A Model to Study Early Tau Hyperphosphorylation Using Okadaic Acid.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease: Overexpression paradigm versus knockin paradigm.
Rac1 activation links tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ dysmetabolism in Alzheimer's disease.
Tau Pathology Promotes the Reorganization of the Extracellular Matrix and Inhibits the Formation of Perineuronal Nets by Regulating the Expression and the Distribution of Hyaluronic Acid Synthases.
Tau secretion is correlated to an increase of Golgi dynamics.
Whole Genome Expression Analysis in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy Identifies MECP2 as a Possible Regulator of Tau Pathology.
The tyrosine phosphatase PTPN13/FAP-1 links calpain-2, TBI and tau tyrosine phosphorylation.
An inhibitor of the proteasomal deubiquitinating enzyme USP14 induces tau elimination in cultured neurons.
Opposing effects of progranulin deficiency on amyloid and tau pathologies via microglial TYROBP network.
Modifications of tau protein after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats are similar to those occurring in Alzheimer's disease - Hyperphosphorylation and cleavage of 4- and 3-repeat tau.
Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated protein aggregates may reduce proteasome activity and delay myotube degradation during muscle atrophy in vitro.
Liraglutide Improves Water Maze Learning and Memory Performance While Reduces Hyperphosphorylation of Tau and Neurofilaments in APP/PS1/Tau Triple Transgenic Mice.
Specific ion channels contribute to key elements of pathology during secondary degeneration following neurotrauma.
Does inactivation of USP14 enhance degradation of proteasomal substrates that are associated with neurodegenerative diseases?
No Overt Deficits in Aged Tau-Deficient C57Bl/6.Mapttm1(EGFP)Kit GFP Knockin Mice.
Loss of Tau protein affects the structure, transcription and repair of neuronal pericentromeric heterochromatin.
The Neurotoxic TAU(45-230) Fragment Accumulates in Upper and Lower Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Subjects.
Modification of Tau by 8-Nitroguanosine 3',5'-Cyclic Monophosphate (8-Nitro-cGMP): EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE-LINKED CHEMICAL MODIFICATION ON TAU AGGREGATION.
The arginylation branch of the N-end rule pathway positively regulates cellular autophagic flux and clearance of proteotoxic proteins.
A Neurogenic Perspective of Sarcopenia: Time Course Study of Sciatic Nerves From Aging Mice.
The Co-chaperone BAG2 Mediates Cold-Induced Accumulation of Phosphorylated Tau in SH-SY5Y Cells.
FRMD4A-cytohesin signaling modulates the cellular release of tau.
Open-gate mutants of the mammalian proteasome show enhanced ubiquitin-conjugate degradation.
Acetylated tau destabilizes the cytoskeleton in the axon initial segment and is mislocalized to the somatodendritic compartment.
Is phosphorylated tau unique to chronic traumatic encephalopathy? Phosphorylated tau in epileptic brain and chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
Activation of a synapse weakening pathway by human Val66 but not Met66 pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF).
Gamma frequency entrainment attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia.
Acetylated Tau Obstructs KIBRA-Mediated Signaling in Synaptic Plasticity and Promotes Tauopathy-Related Memory Loss.
Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote survival and neuronal differentiation of human BM-MSCs.
β-Secretase 1's Targeting Reduces Hyperphosphorilated Tau, Implying Autophagy Actors in 3xTg-AD Mice.
High-fat diet-induced deregulation of hippocampal insulin signaling and mitochondrial homeostasis deficiences contribute to Alzheimer disease pathology in rodents.
Activation of Cdk5/p25 and tau phosphorylation following chronic brain hypoperfusion in rats involves microRNA-195 down-regulation.
Tau phosphorylation regulates the interaction between BIN1's SH3 domain and Tau's proline-rich domain.
Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits.
Apaf1-deficient cortical neurons exhibit defects in axonal outgrowth.
HS3ST2 expression is critical for the abnormal phosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease-related tau pathology.
Facilitated Tau Degradation by USP14 Aptamers via Enhanced Proteasome Activity.
Nontoxic singlet oxygen generator as a therapeutic candidate for treating tauopathies.
Reelin protects against amyloid β toxicity in vivo.
Ccr2 deletion dissociates cavity size and tau pathology after mild traumatic brain injury.
The domestic cat as a natural animal model of Alzheimer's disease.
JSAP1/JIP3 and JLP regulate kinesin-1-dependent axonal transport to prevent neuronal degeneration.
Berberine attenuates axonal transport impairment and axonopathy induced by Calyculin A in N2a cells.
Long- and short-term CDK5 knockdown prevents spatial memory dysfunction and tau pathology of triple transgenic Alzheimer's mice.
Tau reduction prevents disease in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome.
Early alterations in energy metabolism in the hippocampus of APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Opposing effects of membrane-anchored CX3CL1 on amyloid and tau pathologies via the p38 MAPK pathway.
Long-term treadmill exercise attenuates tau pathology in P301S tau transgenic mice.
Microtubule-associated protein tau is essential for long-term depression in the hippocampus.
Presence of a neo-epitope and absence of amyloid beta and tau protein in degenerative hippocampal granules of aged mice.
Profiling murine tau with 0N, 1N and 2N isoform-specific antibodies in brain and peripheral organs reveals distinct subcellular localization, with the 1N isoform being enriched in the nucleus.
Dietary resveratrol prevents Alzheimer's markers and increases life span in SAMP8.
Cellular prion protein modulates β-amyloid deposition in aged APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induces early and chronic axonal changes in rats: its importance for the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Paraquat, but not maneb, induces synucleinopathy and tauopathy in striata of mice through inhibition of proteasomal and autophagic pathways.
Central angiotensin II-induced Alzheimer-like tau phosphorylation in normal rat brains.
Neonatal exposure to the cyanobacterial toxin BMAA induces changes in protein expression and neurodegeneration in adult hippocampus.
Differing effects of toxicants (methylmercury, inorganic mercury, lead, amyloid β, and rotenone) on cultured rat cerebrocortical neurons: differential expression of rho proteins associated with neurotoxicity.
Tau phosphorylation and sevoflurane anesthesia: an association to postoperative cognitive impairment.
The protein phosphatase PP2A/Bα binds to the microtubule-associated proteins Tau and MAP2 at a motif also recognized by the kinase Fyn: implications for tauopathies.
Pro-neural miR-128 is a glioma tumor suppressor that targets mitogenic kinases.
Salivary tau species are potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 but not of glycogen synthase kinase 3-β prevents neurite retraction and tau hyperphosphorylation caused by secretable products of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected lymphocytes.
Hyperphosphorylated Tau in an α-synuclein-overexpressing transgenic model of Parkinson's disease.
Tauopathic changes in the striatum of A53T α-synuclein mutant mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Expression of the HFE allelic variant H63D in SH-SY5Y cells affects tau phosphorylation at serine residues.
Region-specific tauopathy and synucleinopathy in brain of the alpha-synuclein overexpressing mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Ischemic preconditioning attenuates of ischemia-induced degradation of spectrin and tau: implications for ischemic tolerance.
Kinesin-1 transport reductions enhance human tau hyperphosphorylation, aggregation and neurodegeneration in animal models of tauopathies.
Transgenic mouse and cell culture models demonstrate a lack of mechanistic connection between endoplasmic reticulum stress and tau dysfunction.
Deletion of tau attenuates heat shock-induced injury in cultured cortical neurons.
Delphinidin ameliorates beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting calcium influx and tau hyperphosphorylation.
2,3,7,8-TCDD neurotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells is caused by increased oxidative stress, intracellular calcium levels, and tau phosphorylation.
Protective effect of caffeic acid against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by the inhibition of calcium influx and tau phosphorylation.
Striatal dysregulation of Cdk5 alters locomotor responses to cocaine, motor learning, and dendritic morphology.
Enhanced activity of hippocampal BACE1 in a mouse model of postmenopausal memory deficits.
Phosphorylated PP2A (tyrosine 307) is associated with Alzheimer neurofibrillary pathology.
Curcumin protected PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity through the inhibition of oxidative damage and tau hyperphosphorylation.
Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene.
Reelin signals through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt to control cortical development and through mTor to regulate dendritic growth.
Efficacy of small-molecule glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors in the postnatal rat model of tau hyperphosphorylation.
Agrin induced morphological and structural changes in growth cones of cultured hippocampal neurons.
Mitochondrial oxidative stress causes hyperphosphorylation of tau.
Identification of small molecules that interfere with radial neuronal migration and early cortical plate development.
Caspase-3- and calpain-mediated tau cleavage are differentially prevented by estrogen and testosterone in beta-amyloid-treated hippocampal neurons.
Expression of serine/threonine protein-kinases and related factors in normal monkey and human retinas: the mechanistic understanding of a CDK2 inhibitor induced retinal toxicity.
Lithium inhibits stress-induced changes in tau phosphorylation in the mouse hippocampus.
Alzheimer's disease-like tau neuropathology leads to memory deficits and loss of functional synapses in a novel mutated tau transgenic mouse without any motor deficits.
Defining Cdk5 ligand chemical space with small molecule inhibitors of tau phosphorylation.
Altered axonal architecture by removal of the heavily phosphorylated neurofilament tail domains strongly slows superoxide dismutase 1 mutant-mediated ALS.
Neurite extension in central neurons: a novel role for the receptor tyrosine kinases Ror1 and Ror2.
A Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in neurons.
Tau becomes a more favorable substrate for GSK-3 when it is prephosphorylated by PKA in rat brain.
Development of an assay to screen for inhibitors of tau phosphorylation by cdk5.
Modulation of microtubule dynamics by tau in living cells: implications for development and neurodegeneration.
Tau phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p39 during brain development reduces its affinity for microtubules.
Cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator p35 to p25 does not induce tau hyperphosphorylation.
Cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator p35 to p25 does not induce tau hyperphosphorylation.
Ubiquitin-positive neuronal and tau 2-positive glial inclusions in frontotemporal dementia of motor neuron type.
Mai M, Guo X, Huang Y, Zhang W, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Bai X, Wu J, Zu H
Molecular neurobiology 2022 Sep;59(9):5856-5873
Molecular neurobiology 2022 Sep;59(9):5856-5873
Identification of a reciprocal negative feedback loop between tau-modifying proteins MARK2 kinase and CBP acetyltransferase.
Tabassum Z, Tseng JH, Isemann C, Tian X, Chen Y, Herring LE, Cohen TJ
The Journal of biological chemistry 2022 Jun;298(6):101977
The Journal of biological chemistry 2022 Jun;298(6):101977
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Young Neural Cultures Attenuate Astrocytic Reactivity In Vitro.
Almansa D, Peinado H, García-Rodríguez R, Casadomé-Perales Á, Dotti CG, Guix FX
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Jan 25;23(3)
International journal of molecular sciences 2022 Jan 25;23(3)
Conformation-specific Antibodies Targeting Aggregated Forms of α-synuclein Block the Propagation of Synucleinopathy.
Choi M, Kim TK, Ahn J, Lee JS, Jung BC, An S, Kim D, Lee MJ, Mook-Jung I, Lee SH, Lee SJ
Experimental neurobiology 2022 Feb 28;31(1):29-41
Experimental neurobiology 2022 Feb 28;31(1):29-41
Improved Sleep, Memory, and Cellular Pathological Features of Tauopathy, Including the NLRP3 Inflammasome, after Chronic Administration of Trazodone in rTg4510 Mice.
de Oliveira P, Cella C, Locker N, Ravindran KKG, Mendis A, Wafford K, Gilmour G, Dijk DJ, Winsky-Sommerer R
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2022 Apr 20;42(16):3494-3509
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2022 Apr 20;42(16):3494-3509
Structural mapping techniques distinguish the surfaces of fibrillar 1N3R and 1N4R human tau.
Caroux E, Redeker V, Madiona K, Melki R
The Journal of biological chemistry 2021 Nov;297(5):101252
The Journal of biological chemistry 2021 Nov;297(5):101252
RPS23RG1 modulates tau phosphorylation and axon outgrowth through regulating p35 proteasomal degradation.
Zhao D, Zhou Y, Huo Y, Meng J, Xiao X, Han L, Zhang X, Luo H, Can D, Sun H, Huang TY, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu FR, Xu H, Zhang YW
Cell death and differentiation 2021 Jan;28(1):337-348
Cell death and differentiation 2021 Jan;28(1):337-348
BNIP3L/NIX-mediated mitophagy protects against glucocorticoid-induced synapse defects.
Choi GE, Lee HJ, Chae CW, Cho JH, Jung YH, Kim JS, Kim SY, Lim JR, Han HJ
Nature communications 2021 Jan 20;12(1):487
Nature communications 2021 Jan 20;12(1):487
Efficient manipulation of gene dosage in human iPSCs using CRISPR/Cas9 nickases.
Ye T, Duan Y, Tsang HWS, Xu H, Chen Y, Cao H, Chen Y, Fu AKY, Ip NY
Communications biology 2021 Feb 12;4(1):195
Communications biology 2021 Feb 12;4(1):195
Dystrophic Dmd(mdx) rats show early neuronal changes (increased S100β and Tau5) at 8 months, supporting severe dystropathology in this rodent model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Krishnan VS, Thanigaiarasu LP, White R, Crew R, Larcher T, Le Guiner C, Grounds MD
Molecular and cellular neurosciences 2020 Oct;108:103549
Molecular and cellular neurosciences 2020 Oct;108:103549
Tau Reduction Prevents Key Features of Autism in Mouse Models.
Tai C, Chang CW, Yu GQ, Lopez I, Yu X, Wang X, Guo W, Mucke L
Neuron 2020 May 6;106(3):421-437.e11
Neuron 2020 May 6;106(3):421-437.e11
Correcting abnormalities in miR-124/PTPN1 signaling rescues tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease.
Hou TY, Zhou Y, Zhu LS, Wang X, Pang P, Wang DQ, Liuyang ZY, Man H, Lu Y, Zhu LQ, Liu D
Journal of neurochemistry 2020 Aug;154(4):441-457
Journal of neurochemistry 2020 Aug;154(4):441-457
Fyn Kinase Controls Tau Aggregation In Vivo.
Briner A, Götz J, Polanco JC
Cell reports 2020 Aug 18;32(7):108045
Cell reports 2020 Aug 18;32(7):108045
Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Tau and Related Proteins in Rats with the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.
Mankhong S, Kim S, Moon S, Lee KH, Jeon HE, Hwang BH, Beak JW, Joa KL, Kang JH
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Aug 14;21(16)
International journal of molecular sciences 2020 Aug 14;21(16)
Acetylation of Aβ42 at Lysine 16 Disrupts Amyloid Formation.
Adhikari R, Yang M, Saikia N, Dutta C, Alharbi WFA, Shan Z, Pandey R, Tiwari A
ACS chemical neuroscience 2020 Apr 15;11(8):1178-1191
ACS chemical neuroscience 2020 Apr 15;11(8):1178-1191
Targeting the ensemble of heterogeneous tau oligomers in cells: A novel small molecule screening platform for tauopathies.
Lo CH, Lim CK, Ding Z, Wickramasinghe SP, Braun AR, Ashe KH, Rhoades E, Thomas DD, Sachs JN
Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2019 Nov;15(11):1489-1502
Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association 2019 Nov;15(11):1489-1502
Targeted degradation of aberrant tau in frontotemporal dementia patient-derived neuronal cell models.
Silva MC, Ferguson FM, Cai Q, Donovan KA, Nandi G, Patnaik D, Zhang T, Huang HT, Lucente DE, Dickerson BC, Mitchison TJ, Fischer ES, Gray NS, Haggarty SJ
eLife 2019 Mar 25;8
eLife 2019 Mar 25;8
REST and Neural Gene Network Dysregulation in iPSC Models of Alzheimer's Disease.
Meyer K, Feldman HM, Lu T, Drake D, Lim ET, Ling KH, Bishop NA, Pan Y, Seo J, Lin YT, Su SC, Church GM, Tsai LH, Yankner BA
Cell reports 2019 Jan 29;26(5):1112-1127.e9
Cell reports 2019 Jan 29;26(5):1112-1127.e9
Multi-sensory Gamma Stimulation Ameliorates Alzheimer's-Associated Pathology and Improves Cognition.
Martorell AJ, Paulson AL, Suk HJ, Abdurrob F, Drummond GT, Guan W, Young JZ, Kim DN, Kritskiy O, Barker SJ, Mangena V, Prince SM, Brown EN, Chung K, Boyden ES, Singer AC, Tsai LH
Cell 2019 Apr 4;177(2):256-271.e22
Cell 2019 Apr 4;177(2):256-271.e22
Ovarian Function Modulates the Effects of Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Mouse Cerebral Cortex.
Herrera JL, Ordoñez-Gutierrez L, Fabrias G, Casas J, Morales A, Hernandez G, Acosta NG, Rodriguez C, Prieto-Valiente L, Garcia-Segura LM, Alonso R, Wandosell FG
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2018;12:103
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2018;12:103
Differential Hyperphosphorylation of Tau-S199, -T231 and -S396 in Organotypic Brain Slices of Alzheimer Mice. A Model to Study Early Tau Hyperphosphorylation Using Okadaic Acid.
Foidl BM, Humpel C
Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2018;10:113
Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2018;10:113
Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease: Overexpression paradigm versus knockin paradigm.
Hashimoto S, Ishii A, Kamano N, Watamura N, Saito T, Ohshima T, Yokosuka M, Saido TC
The Journal of biological chemistry 2018 Mar 2;293(9):3118-3125
The Journal of biological chemistry 2018 Mar 2;293(9):3118-3125
Rac1 activation links tau hyperphosphorylation and Aβ dysmetabolism in Alzheimer's disease.
Borin M, Saraceno C, Catania M, Lorenzetto E, Pontelli V, Paterlini A, Fostinelli S, Avesani A, Di Fede G, Zanusso G, Benussi L, Binetti G, Zorzan S, Ghidoni R, Buffelli M, Bolognin S
Acta neuropathologica communications 2018 Jul 13;6(1):61
Acta neuropathologica communications 2018 Jul 13;6(1):61
Tau Pathology Promotes the Reorganization of the Extracellular Matrix and Inhibits the Formation of Perineuronal Nets by Regulating the Expression and the Distribution of Hyaluronic Acid Synthases.
Li Y, Li ZX, Jin T, Wang ZY, Zhao P
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2017;57(2):395-409
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2017;57(2):395-409
Tau secretion is correlated to an increase of Golgi dynamics.
Mohamed NV, Desjardins A, Leclerc N
PloS one 2017;12(5):e0178288
PloS one 2017;12(5):e0178288
Whole Genome Expression Analysis in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy Identifies MECP2 as a Possible Regulator of Tau Pathology.
Maphis NM, Jiang S, Binder J, Wright C, Gopalan B, Lamb BT, Bhaskar K
Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2017;10:69
Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2017;10:69
The tyrosine phosphatase PTPN13/FAP-1 links calpain-2, TBI and tau tyrosine phosphorylation.
Wang Y, Hall RA, Lee M, Kamgar-Parsi A, Bi X, Baudry M
Scientific reports 2017 Sep 18;7(1):11771
Scientific reports 2017 Sep 18;7(1):11771
An inhibitor of the proteasomal deubiquitinating enzyme USP14 induces tau elimination in cultured neurons.
Boselli M, Lee BH, Robert J, Prado MA, Min SW, Cheng C, Silva MC, Seong C, Elsasser S, Hatle KM, Gahman TC, Gygi SP, Haggarty SJ, Gan L, King RW, Finley D
The Journal of biological chemistry 2017 Nov 24;292(47):19209-19225
The Journal of biological chemistry 2017 Nov 24;292(47):19209-19225
Opposing effects of progranulin deficiency on amyloid and tau pathologies via microglial TYROBP network.
Takahashi H, Klein ZA, Bhagat SM, Kaufman AC, Kostylev MA, Ikezu T, Strittmatter SM, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Acta neuropathologica 2017 May;133(5):785-807
Acta neuropathologica 2017 May;133(5):785-807
Modifications of tau protein after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats are similar to those occurring in Alzheimer's disease - Hyperphosphorylation and cleavage of 4- and 3-repeat tau.
Fujii H, Takahashi T, Mukai T, Tanaka S, Hosomi N, Maruyama H, Sakai N, Matsumoto M
Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2017 Jul;37(7):2441-2457
Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2017 Jul;37(7):2441-2457
Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated protein aggregates may reduce proteasome activity and delay myotube degradation during muscle atrophy in vitro.
Shin SK, Kim JH, Lee JH, Son YH, Lee MW, Kim HJ, Noh SA, Kim KP, Kim IG, Lee MJ
Experimental & molecular medicine 2017 Jan 20;49(1):e287
Experimental & molecular medicine 2017 Jan 20;49(1):e287
Liraglutide Improves Water Maze Learning and Memory Performance While Reduces Hyperphosphorylation of Tau and Neurofilaments in APP/PS1/Tau Triple Transgenic Mice.
Chen S, Sun J, Zhao G, Guo A, Chen Y, Fu R, Deng Y
Neurochemical research 2017 Aug;42(8):2326-2335
Neurochemical research 2017 Aug;42(8):2326-2335
Specific ion channels contribute to key elements of pathology during secondary degeneration following neurotrauma.
O'Hare Doig RL, Chiha W, Giacci MK, Yates NJ, Bartlett CA, Smith NM, Hodgetts SI, Harvey AR, Fitzgerald M
BMC neuroscience 2017 Aug 14;18(1):62
BMC neuroscience 2017 Aug 14;18(1):62
Does inactivation of USP14 enhance degradation of proteasomal substrates that are associated with neurodegenerative diseases?
Ortuno D, Carlisle HJ, Miller S
F1000Research 2016;5:137
F1000Research 2016;5:137
No Overt Deficits in Aged Tau-Deficient C57Bl/6.Mapttm1(EGFP)Kit GFP Knockin Mice.
van Hummel A, Bi M, Ippati S, van der Hoven J, Volkerling A, Lee WS, Tan DC, Bongers A, Ittner A, Ke YD, Ittner LM
PloS one 2016;11(10):e0163236
PloS one 2016;11(10):e0163236
Loss of Tau protein affects the structure, transcription and repair of neuronal pericentromeric heterochromatin.
Mansuroglu Z, Benhelli-Mokrani H, Marcato V, Sultan A, Violet M, Chauderlier A, Delattre L, Loyens A, Talahari S, Bégard S, Nesslany F, Colin M, Souès S, Lefebvre B, Buée L, Galas MC, Bonnefoy E
Scientific reports 2016 Sep 8;6:33047
Scientific reports 2016 Sep 8;6:33047
The Neurotoxic TAU(45-230) Fragment Accumulates in Upper and Lower Motor Neurons in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Subjects.
Vintilescu CR, Afreen S, Rubino AE, Ferreira A
Molecular medicine (Cambridge, Mass.) 2016 Oct;22:477-486
Molecular medicine (Cambridge, Mass.) 2016 Oct;22:477-486
Modification of Tau by 8-Nitroguanosine 3',5'-Cyclic Monophosphate (8-Nitro-cGMP): EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE-LINKED CHEMICAL MODIFICATION ON TAU AGGREGATION.
Yoshitake J, Soeda Y, Ida T, Sumioka A, Yoshikawa M, Matsushita K, Akaike T, Takashima A
The Journal of biological chemistry 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22714-22720
The Journal of biological chemistry 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22714-22720
The arginylation branch of the N-end rule pathway positively regulates cellular autophagic flux and clearance of proteotoxic proteins.
Jiang Y, Lee J, Lee JH, Lee JW, Kim JH, Choi WH, Yoo YD, Cha-Molstad H, Kim BY, Kwon YT, Noh SA, Kim KP, Lee MJ
Autophagy 2016 Nov;12(11):2197-2212
Autophagy 2016 Nov;12(11):2197-2212
A Neurogenic Perspective of Sarcopenia: Time Course Study of Sciatic Nerves From Aging Mice.
Krishnan VS, White Z, McMahon CD, Hodgetts SI, Fitzgerald M, Shavlakadze T, Harvey AR, Grounds MD
Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology 2016 May;75(5):464-78
Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology 2016 May;75(5):464-78
The Co-chaperone BAG2 Mediates Cold-Induced Accumulation of Phosphorylated Tau in SH-SY5Y Cells.
de Paula CA, Santiago FE, de Oliveira AS, Oliveira FA, Almeida MC, Carrettiero DC
Cellular and molecular neurobiology 2016 May;36(4):593-602
Cellular and molecular neurobiology 2016 May;36(4):593-602
FRMD4A-cytohesin signaling modulates the cellular release of tau.
Yan X, Nykänen NP, Brunello CA, Haapasalo A, Hiltunen M, Uronen RL, Huttunen HJ
Journal of cell science 2016 May 15;129(10):2003-15
Journal of cell science 2016 May 15;129(10):2003-15
Open-gate mutants of the mammalian proteasome show enhanced ubiquitin-conjugate degradation.
Choi WH, de Poot SA, Lee JH, Kim JH, Han DH, Kim YK, Finley D, Lee MJ
Nature communications 2016 Mar 9;7:10963
Nature communications 2016 Mar 9;7:10963
Acetylated tau destabilizes the cytoskeleton in the axon initial segment and is mislocalized to the somatodendritic compartment.
Sohn PD, Tracy TE, Son HI, Zhou Y, Leite RE, Miller BL, Seeley WW, Grinberg LT, Gan L
Molecular neurodegeneration 2016 Jun 29;11(1):47
Molecular neurodegeneration 2016 Jun 29;11(1):47
Is phosphorylated tau unique to chronic traumatic encephalopathy? Phosphorylated tau in epileptic brain and chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
Puvenna V, Engeler M, Banjara M, Brennan C, Schreiber P, Dadas A, Bahrami A, Solanki J, Bandyopadhyay A, Morris JK, Bernick C, Ghosh C, Rapp E, Bazarian JJ, Janigro D
Brain research 2016 Jan 1;1630:225-40
Brain research 2016 Jan 1;1630:225-40
Activation of a synapse weakening pathway by human Val66 but not Met66 pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF).
Kailainathan S, Piers TM, Yi JH, Choi S, Fahey MS, Borger E, Gunn-Moore FJ, O'Neill L, Lever M, Whitcomb DJ, Cho K, Allen SJ
Pharmacological research 2016 Feb;104:97-107
Pharmacological research 2016 Feb;104:97-107
Gamma frequency entrainment attenuates amyloid load and modifies microglia.
Iaccarino HF, Singer AC, Martorell AJ, Rudenko A, Gao F, Gillingham TZ, Mathys H, Seo J, Kritskiy O, Abdurrob F, Adaikkan C, Canter RG, Rueda R, Brown EN, Boyden ES, Tsai LH
Nature 2016 Dec 7;540(7632):230-235
Nature 2016 Dec 7;540(7632):230-235
Acetylated Tau Obstructs KIBRA-Mediated Signaling in Synaptic Plasticity and Promotes Tauopathy-Related Memory Loss.
Tracy TE, Sohn PD, Minami SS, Wang C, Min SW, Li Y, Zhou Y, Le D, Lo I, Ponnusamy R, Cong X, Schilling B, Ellerby LM, Huganir RL, Gan L
Neuron 2016 Apr 20;90(2):245-60
Neuron 2016 Apr 20;90(2):245-60
Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote survival and neuronal differentiation of human BM-MSCs.
Urnukhsaikhan E, Cho H, Mishig-Ochir T, Seo YK, Park JK
Life sciences 2016 Apr 15;151:130-138
Life sciences 2016 Apr 15;151:130-138
β-Secretase 1's Targeting Reduces Hyperphosphorilated Tau, Implying Autophagy Actors in 3xTg-AD Mice.
Piedrahita D, Castro-Alvarez JF, Boudreau RL, Villegas-Lanau A, Kosik KS, Gallego-Gomez JC, Cardona-Gómez GP
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2015;9:498
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2015;9:498
High-fat diet-induced deregulation of hippocampal insulin signaling and mitochondrial homeostasis deficiences contribute to Alzheimer disease pathology in rodents.
Petrov D, Pedrós I, Artiach G, Sureda FX, Barroso E, Pallàs M, Casadesús G, Beas-Zarate C, Carro E, Ferrer I, Vazquez-Carrera M, Folch J, Camins A
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2015 Sep;1852(9):1687-99
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2015 Sep;1852(9):1687-99
Activation of Cdk5/p25 and tau phosphorylation following chronic brain hypoperfusion in rats involves microRNA-195 down-regulation.
Sun LH, Ban T, Liu CD, Chen QX, Wang X, Yan ML, Hu XL, Su XL, Bao YN, Sun LL, Zhao LJ, Pei SC, Jiang XM, Zong DK, Ai J
Journal of neurochemistry 2015 Sep;134(6):1139-51
Journal of neurochemistry 2015 Sep;134(6):1139-51
Tau phosphorylation regulates the interaction between BIN1's SH3 domain and Tau's proline-rich domain.
Sottejeau Y, Bretteville A, Cantrelle FX, Malmanche N, Demiaute F, Mendes T, Delay C, Alves Dos Alves H, Flaig A, Davies P, Dourlen P, Dermaut B, Laporte J, Amouyel P, Lippens G, Chapuis J, Landrieu I, Lambert JC
Acta neuropathologica communications 2015 Sep 23;3:58
Acta neuropathologica communications 2015 Sep 23;3:58
Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits.
Min SW, Chen X, Tracy TE, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang C, Shirakawa K, Minami SS, Defensor E, Mok SA, Sohn PD, Schilling B, Cong X, Ellerby L, Gibson BW, Johnson J, Krogan N, Shamloo M, Gestwicki J, Masliah E, Verdin E, Gan L
Nature medicine 2015 Oct;21(10):1154-62
Nature medicine 2015 Oct;21(10):1154-62
Apaf1-deficient cortical neurons exhibit defects in axonal outgrowth.
De Zio D, Molinari F, Rizza S, Gatta L, Ciotti MT, Salvatore AM, Mathiassen SG, Cwetsch AW, Filomeni G, Rosano G, Ferraro E
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 2015 Nov;72(21):4173-91
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 2015 Nov;72(21):4173-91
HS3ST2 expression is critical for the abnormal phosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease-related tau pathology.
Sepulveda-Diaz JE, Alavi Naini SM, Huynh MB, Ouidja MO, Yanicostas C, Chantepie S, Villares J, Lamari F, Jospin E, van Kuppevelt TH, Mensah-Nyagan AG, Raisman-Vozari R, Soussi-Yanicostas N, Papy-Garcia D
Brain : a journal of neurology 2015 May;138(Pt 5):1339-54
Brain : a journal of neurology 2015 May;138(Pt 5):1339-54
Facilitated Tau Degradation by USP14 Aptamers via Enhanced Proteasome Activity.
Lee JH, Shin SK, Jiang Y, Choi WH, Hong C, Kim DE, Lee MJ
Scientific reports 2015 Jun 4;5:10757
Scientific reports 2015 Jun 4;5:10757
Nontoxic singlet oxygen generator as a therapeutic candidate for treating tauopathies.
Sheik Mohideen S, Yamasaki Y, Omata Y, Tsuda L, Yoshiike Y
Scientific reports 2015 Jun 1;5:10821
Scientific reports 2015 Jun 1;5:10821
Reelin protects against amyloid β toxicity in vivo.
Lane-Donovan C, Philips GT, Wasser CR, Durakoglugil MS, Masiulis I, Upadhaya A, Pohlkamp T, Coskun C, Kotti T, Steller L, Hammer RE, Frotscher M, Bock HH, Herz J
Science signaling 2015 Jul 7;8(384):ra67
Science signaling 2015 Jul 7;8(384):ra67
Ccr2 deletion dissociates cavity size and tau pathology after mild traumatic brain injury.
Gyoneva S, Kim D, Katsumoto A, Kokiko-Cochran ON, Lamb BT, Ransohoff RM
Journal of neuroinflammation 2015 Dec 3;12:228
Journal of neuroinflammation 2015 Dec 3;12:228
The domestic cat as a natural animal model of Alzheimer's disease.
Chambers JK, Tokuda T, Uchida K, Ishii R, Tatebe H, Takahashi E, Tomiyama T, Une Y, Nakayama H
Acta neuropathologica communications 2015 Dec 10;3:78
Acta neuropathologica communications 2015 Dec 10;3:78
JSAP1/JIP3 and JLP regulate kinesin-1-dependent axonal transport to prevent neuronal degeneration.
Sato T, Ishikawa M, Mochizuki M, Ohta M, Ohkura M, Nakai J, Takamatsu N, Yoshioka K
Cell death and differentiation 2015 Aug;22(8):1260-74
Cell death and differentiation 2015 Aug;22(8):1260-74
Berberine attenuates axonal transport impairment and axonopathy induced by Calyculin A in N2a cells.
Liu X, Zhou J, Abid MD, Yan H, Huang H, Wan L, Feng Z, Chen J
PloS one 2014;9(4):e93974
PloS one 2014;9(4):e93974
Long- and short-term CDK5 knockdown prevents spatial memory dysfunction and tau pathology of triple transgenic Alzheimer's mice.
Castro-Alvarez JF, Uribe-Arias SA, Kosik KS, Cardona-Gómez GP
Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2014;6:243
Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2014;6:243
Tau reduction prevents disease in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome.
Gheyara AL, Ponnusamy R, Djukic B, Craft RJ, Ho K, Guo W, Finucane MM, Sanchez PE, Mucke L
Annals of neurology 2014 Sep;76(3):443-56
Annals of neurology 2014 Sep;76(3):443-56
Early alterations in energy metabolism in the hippocampus of APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Pedrós I, Petrov D, Allgaier M, Sureda F, Barroso E, Beas-Zarate C, Auladell C, Pallàs M, Vázquez-Carrera M, Casadesús G, Folch J, Camins A
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2014 Sep;1842(9):1556-66
Biochimica et biophysica acta 2014 Sep;1842(9):1556-66
Opposing effects of membrane-anchored CX3CL1 on amyloid and tau pathologies via the p38 MAPK pathway.
Lee S, Xu G, Jay TR, Bhatta S, Kim KW, Jung S, Landreth GE, Ransohoff RM, Lamb BT
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2014 Sep 10;34(37):12538-46
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2014 Sep 10;34(37):12538-46
Long-term treadmill exercise attenuates tau pathology in P301S tau transgenic mice.
Ohia-Nwoko O, Montazari S, Lau YS, Eriksen JL
Molecular neurodegeneration 2014 Nov 28;9:54
Molecular neurodegeneration 2014 Nov 28;9:54
Microtubule-associated protein tau is essential for long-term depression in the hippocampus.
Kimura T, Whitcomb DJ, Jo J, Regan P, Piers T, Heo S, Brown C, Hashikawa T, Murayama M, Seok H, Sotiropoulos I, Kim E, Collingridge GL, Takashima A, Cho K
Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences 2014 Jan 5;369(1633):20130144
Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological sciences 2014 Jan 5;369(1633):20130144
Presence of a neo-epitope and absence of amyloid beta and tau protein in degenerative hippocampal granules of aged mice.
Manich G, del Valle J, Cabezón I, Camins A, Pallàs M, Pelegrí C, Vilaplana J
Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 2014 Feb;36(1):151-65
Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 2014 Feb;36(1):151-65
Profiling murine tau with 0N, 1N and 2N isoform-specific antibodies in brain and peripheral organs reveals distinct subcellular localization, with the 1N isoform being enriched in the nucleus.
Liu C, Götz J
PloS one 2013;8(12):e84849
PloS one 2013;8(12):e84849
Dietary resveratrol prevents Alzheimer's markers and increases life span in SAMP8.
Porquet D, Casadesús G, Bayod S, Vicente A, Canudas AM, Vilaplana J, Pelegrí C, Sanfeliu C, Camins A, Pallàs M, del Valle J
Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 2013 Oct;35(5):1851-65
Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands) 2013 Oct;35(5):1851-65
Cellular prion protein modulates β-amyloid deposition in aged APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Ordóñez-Gutiérrez L, Torres JM, Gavín R, Antón M, Arroba-Espinosa AI, Espinosa JC, Vergara C, Del Río JA, Wandosell F
Neurobiology of aging 2013 Dec;34(12):2793-804
Neurobiology of aging 2013 Dec;34(12):2793-804
Transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induces early and chronic axonal changes in rats: its importance for the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Zhang Q, Gao T, Luo Y, Chen X, Gao G, Gao X, Zhou Y, Dai J
PloS one 2012;7(3):e33722
PloS one 2012;7(3):e33722
Paraquat, but not maneb, induces synucleinopathy and tauopathy in striata of mice through inhibition of proteasomal and autophagic pathways.
Wills J, Credle J, Oaks AW, Duka V, Lee JH, Jones J, Sidhu A
PloS one 2012;7(1):e30745
PloS one 2012;7(1):e30745
Central angiotensin II-induced Alzheimer-like tau phosphorylation in normal rat brains.
Tian M, Zhu D, Xie W, Shi J
FEBS letters 2012 Oct 19;586(20):3737-45
FEBS letters 2012 Oct 19;586(20):3737-45
Neonatal exposure to the cyanobacterial toxin BMAA induces changes in protein expression and neurodegeneration in adult hippocampus.
Karlsson O, Berg AL, Lindström AK, Hanrieder J, Arnerup G, Roman E, Bergquist J, Lindquist NG, Brittebo EB, Andersson M
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2012 Dec;130(2):391-404
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2012 Dec;130(2):391-404
Differing effects of toxicants (methylmercury, inorganic mercury, lead, amyloid β, and rotenone) on cultured rat cerebrocortical neurons: differential expression of rho proteins associated with neurotoxicity.
Fujimura M, Usuki F
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2012 Apr;126(2):506-14
Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2012 Apr;126(2):506-14
Tau phosphorylation and sevoflurane anesthesia: an association to postoperative cognitive impairment.
Le Freche H, Brouillette J, Fernandez-Gomez FJ, Patin P, Caillierez R, Zommer N, Sergeant N, Buée-Scherrer V, Lebuffe G, Blum D, Buée L
Anesthesiology 2012 Apr;116(4):779-87
Anesthesiology 2012 Apr;116(4):779-87
The protein phosphatase PP2A/Bα binds to the microtubule-associated proteins Tau and MAP2 at a motif also recognized by the kinase Fyn: implications for tauopathies.
Sontag JM, Nunbhakdi-Craig V, White CL 3rd, Halpain S, Sontag E
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14984-93
The Journal of biological chemistry 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14984-93
Pro-neural miR-128 is a glioma tumor suppressor that targets mitogenic kinases.
Papagiannakopoulos T, Friedmann-Morvinski D, Neveu P, Dugas JC, Gill RM, Huillard E, Liu C, Zong H, Rowitch DH, Barres BA, Verma IM, Kosik KS
Oncogene 2012 Apr 12;31(15):1884-95
Oncogene 2012 Apr 12;31(15):1884-95
Salivary tau species are potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease.
Shi M, Sui YT, Peskind ER, Li G, Hwang H, Devic I, Ginghina C, Edgar JS, Pan C, Goodlett DR, Furay AR, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Zhang J
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2011;27(2):299-305
Journal of Alzheimer's disease : JAD 2011;27(2):299-305
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 but not of glycogen synthase kinase 3-β prevents neurite retraction and tau hyperphosphorylation caused by secretable products of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected lymphocytes.
Maldonado H, Ramírez E, Utreras E, Pando ME, Kettlun AM, Chiong M, Kulkarni AB, Collados L, Puente J, Cartier L, Valenzuela MA
Journal of neuroscience research 2011 Sep;89(9):1489-98
Journal of neuroscience research 2011 Sep;89(9):1489-98
Hyperphosphorylated Tau in an α-synuclein-overexpressing transgenic model of Parkinson's disease.
Haggerty T, Credle J, Rodriguez O, Wills J, Oaks AW, Masliah E, Sidhu A
The European journal of neuroscience 2011 May;33(9):1598-610
The European journal of neuroscience 2011 May;33(9):1598-610
Tauopathic changes in the striatum of A53T α-synuclein mutant mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Wills J, Credle J, Haggerty T, Lee JH, Oaks AW, Sidhu A
PloS one 2011 Mar 21;6(3):e17953
PloS one 2011 Mar 21;6(3):e17953
Expression of the HFE allelic variant H63D in SH-SY5Y cells affects tau phosphorylation at serine residues.
Hall EC 2nd, Lee SY, Mairuae N, Simmons Z, Connor JR
Neurobiology of aging 2011 Aug;32(8):1409-19
Neurobiology of aging 2011 Aug;32(8):1409-19
Region-specific tauopathy and synucleinopathy in brain of the alpha-synuclein overexpressing mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
Kaul T, Credle J, Haggerty T, Oaks AW, Masliah E, Sidhu A
BMC neuroscience 2011 Aug 3;12:79
BMC neuroscience 2011 Aug 3;12:79
Ischemic preconditioning attenuates of ischemia-induced degradation of spectrin and tau: implications for ischemic tolerance.
Nakajima T, Ochi S, Oda C, Ishii M, Ogawa K
Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology 2011 Apr;32(2):229-39
Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology 2011 Apr;32(2):229-39
Kinesin-1 transport reductions enhance human tau hyperphosphorylation, aggregation and neurodegeneration in animal models of tauopathies.
Falzone TL, Gunawardena S, McCleary D, Reis GF, Goldstein LS
Human molecular genetics 2010 Nov 15;19(22):4399-408
Human molecular genetics 2010 Nov 15;19(22):4399-408
Transgenic mouse and cell culture models demonstrate a lack of mechanistic connection between endoplasmic reticulum stress and tau dysfunction.
Spatara ML, Robinson AS
Journal of neuroscience research 2010 Jul;88(9):1951-61
Journal of neuroscience research 2010 Jul;88(9):1951-61
Deletion of tau attenuates heat shock-induced injury in cultured cortical neurons.
Miao Y, Chen J, Zhang Q, Sun A
Journal of neuroscience research 2010 Jan;88(1):102-10
Journal of neuroscience research 2010 Jan;88(1):102-10
Delphinidin ameliorates beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting calcium influx and tau hyperphosphorylation.
Kim HS, Sul D, Lim JY, Lee D, Joo SS, Hwang KW, Park SY
Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2009 Jul;73(7):1685-9
Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2009 Jul;73(7):1685-9
2,3,7,8-TCDD neurotoxicity in neuroblastoma cells is caused by increased oxidative stress, intracellular calcium levels, and tau phosphorylation.
Sul D, Kim HS, Cho EK, Lee M, Kim HS, Jung WW, Hwang KW, Park SY
Toxicology 2009 Jan 8;255(1-2):65-71
Toxicology 2009 Jan 8;255(1-2):65-71
Protective effect of caffeic acid against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by the inhibition of calcium influx and tau phosphorylation.
Sul D, Kim HS, Lee D, Joo SS, Hwang KW, Park SY
Life sciences 2009 Feb 27;84(9-10):257-62
Life sciences 2009 Feb 27;84(9-10):257-62
Striatal dysregulation of Cdk5 alters locomotor responses to cocaine, motor learning, and dendritic morphology.
Meyer DA, Richer E, Benkovic SA, Hayashi K, Kansy JW, Hale CF, Moy LY, Kim Y, O'Callaghan JP, Tsai LH, Greengard P, Nairn AC, Cowan CW, Miller DB, Antich P, Bibb JA
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2008 Nov 25;105(47):18561-6
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2008 Nov 25;105(47):18561-6
Enhanced activity of hippocampal BACE1 in a mouse model of postmenopausal memory deficits.
Fukuzaki E, Takuma K, Himeno Y, Yoshida S, Funatsu Y, Kitahara Y, Mizoguchi H, Ibi D, Koike K, Inoue M, Yamada K
Neuroscience letters 2008 Mar 12;433(2):141-5
Neuroscience letters 2008 Mar 12;433(2):141-5
Phosphorylated PP2A (tyrosine 307) is associated with Alzheimer neurofibrillary pathology.
Liu R, Zhou XW, Tanila H, Bjorkdahl C, Wang JZ, Guan ZZ, Cao Y, Gustafsson JA, Winblad B, Pei JJ
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2008 Jan-Feb;12(1):241-57
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2008 Jan-Feb;12(1):241-57
Curcumin protected PC12 cells against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity through the inhibition of oxidative damage and tau hyperphosphorylation.
Park SY, Kim HS, Cho EK, Kwon BY, Phark S, Hwang KW, Sul D
Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2008 Aug;46(8):2881-7
Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2008 Aug;46(8):2881-7
Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene.
Bai Q, Garver JA, Hukriede NA, Burton EA
Nucleic acids research 2007;35(19):6501-16
Nucleic acids research 2007;35(19):6501-16
Reelin signals through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt to control cortical development and through mTor to regulate dendritic growth.
Jossin Y, Goffinet AM
Molecular and cellular biology 2007 Oct;27(20):7113-24
Molecular and cellular biology 2007 Oct;27(20):7113-24
Efficacy of small-molecule glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors in the postnatal rat model of tau hyperphosphorylation.
Selenica ML, Jensen HS, Larsen AK, Pedersen ML, Helboe L, Leist M, Lotharius J
British journal of pharmacology 2007 Nov;152(6):959-79
British journal of pharmacology 2007 Nov;152(6):959-79
Agrin induced morphological and structural changes in growth cones of cultured hippocampal neurons.
Bergstrom RA, Sinjoanu RC, Ferreira A
Neuroscience 2007 Nov 9;149(3):527-36
Neuroscience 2007 Nov 9;149(3):527-36
Mitochondrial oxidative stress causes hyperphosphorylation of tau.
Melov S, Adlard PA, Morten K, Johnson F, Golden TR, Hinerfeld D, Schilling B, Mavros C, Masters CL, Volitakis I, Li QX, Laughton K, Hubbard A, Cherny RA, Gibson B, Bush AI
PloS one 2007 Jun 20;2(6):e536
PloS one 2007 Jun 20;2(6):e536
Identification of small molecules that interfere with radial neuronal migration and early cortical plate development.
Zhou L, Jossin Y, Goffinet AM
Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 2007 Jan;17(1):211-20
Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 2007 Jan;17(1):211-20
Caspase-3- and calpain-mediated tau cleavage are differentially prevented by estrogen and testosterone in beta-amyloid-treated hippocampal neurons.
Park SY, Tournell C, Sinjoanu RC, Ferreira A
Neuroscience 2007 Jan 5;144(1):119-27
Neuroscience 2007 Jan 5;144(1):119-27
Expression of serine/threonine protein-kinases and related factors in normal monkey and human retinas: the mechanistic understanding of a CDK2 inhibitor induced retinal toxicity.
Saturno G, Pesenti M, Cavazzoli C, Rossi A, Giusti AM, Gierke B, Pawlak M, Venturi M
Toxicologic pathology 2007 Dec;35(7):972-83
Toxicologic pathology 2007 Dec;35(7):972-83
Lithium inhibits stress-induced changes in tau phosphorylation in the mouse hippocampus.
Yoshida S, Maeda M, Kaku S, Ikeya H, Yamada K, Nakaike S
Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2006 Nov;113(11):1803-14
Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 2006 Nov;113(11):1803-14
Alzheimer's disease-like tau neuropathology leads to memory deficits and loss of functional synapses in a novel mutated tau transgenic mouse without any motor deficits.
Schindowski K, Bretteville A, Leroy K, Bégard S, Brion JP, Hamdane M, Buée L
The American journal of pathology 2006 Aug;169(2):599-616
The American journal of pathology 2006 Aug;169(2):599-616
Defining Cdk5 ligand chemical space with small molecule inhibitors of tau phosphorylation.
Ahn JS, Radhakrishnan ML, Mapelli M, Choi S, Tidor B, Cuny GD, Musacchio A, Yeh LA, Kosik KS
Chemistry & biology 2005 Jul;12(7):811-23
Chemistry & biology 2005 Jul;12(7):811-23
Altered axonal architecture by removal of the heavily phosphorylated neurofilament tail domains strongly slows superoxide dismutase 1 mutant-mediated ALS.
Lobsiger CS, Garcia ML, Ward CM, Cleveland DW
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Jul 19;102(29):10351-6
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 Jul 19;102(29):10351-6
Neurite extension in central neurons: a novel role for the receptor tyrosine kinases Ror1 and Ror2.
Paganoni S, Ferreira A
Journal of cell science 2005 Jan 15;118(Pt 2):433-46
Journal of cell science 2005 Jan 15;118(Pt 2):433-46
A Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and apoptosis in neurons.
Zheng YL, Kesavapany S, Gravell M, Hamilton RS, Schubert M, Amin N, Albers W, Grant P, Pant HC
The EMBO journal 2005 Jan 12;24(1):209-20
The EMBO journal 2005 Jan 12;24(1):209-20
Tau becomes a more favorable substrate for GSK-3 when it is prephosphorylated by PKA in rat brain.
Liu SJ, Zhang JY, Li HL, Fang ZY, Wang Q, Deng HM, Gong CX, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wang JZ
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Nov 26;279(48):50078-88
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Nov 26;279(48):50078-88
Development of an assay to screen for inhibitors of tau phosphorylation by cdk5.
Ahn JS, Musacchio A, Mapelli M, Ni J, Scinto L, Stein R, Kosik KS, Yeh LA
Journal of biomolecular screening 2004 Mar;9(2):122-31
Journal of biomolecular screening 2004 Mar;9(2):122-31
Modulation of microtubule dynamics by tau in living cells: implications for development and neurodegeneration.
Bunker JM, Wilson L, Jordan MA, Feinstein SC
Molecular biology of the cell 2004 Jun;15(6):2720-8
Molecular biology of the cell 2004 Jun;15(6):2720-8
Tau phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p39 during brain development reduces its affinity for microtubules.
Takahashi S, Saito T, Hisanaga S, Pant HC, Kulkarni AB
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Mar 21;278(12):10506-15
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Mar 21;278(12):10506-15
Cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator p35 to p25 does not induce tau hyperphosphorylation.
Kerokoski P, Suuronen T, Salminen A, Soininen H, Pirttilä T
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2002 Nov 15;298(5):693-8
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2002 Nov 15;298(5):693-8
Cleavage of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator p35 to p25 does not induce tau hyperphosphorylation.
Kerokoski P, Suuronen T, Salminen A, Soininen H, Pirttilä T
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2002 Nov 15;298(5):693-8
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2002 Nov 15;298(5):693-8
Ubiquitin-positive neuronal and tau 2-positive glial inclusions in frontotemporal dementia of motor neuron type.
Forno LS, Langston JW, Herrick MK, Wilson JD, Murayama S
Acta neuropathologica 2002 Jun;103(6):599-606
Acta neuropathologica 2002 Jun;103(6):599-606
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
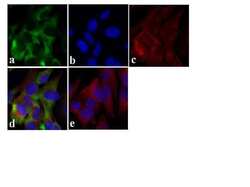
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Tau (Tau-5) was done on 70% confluent log phase SHSY5Y cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Tau (Tau-5) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # AHB0042) at 1 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d is a merged image showing cytoplasmic localization and panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
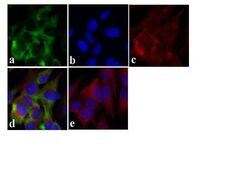
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Tau (Tau-5) was done on 70% confluent log phase SHSY5Y cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Tau (Tau-5) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # AHB0042) at 1 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Product # A-11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor 594 Phalloidin (Product # A12381). Panel d is a merged image showing cytoplasmic localization and panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
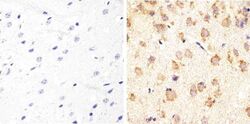
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of Tau showing staining in the cytoplasm of paraffin-embedded mouse brain tissue (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a Tau (Product # AHB0042) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
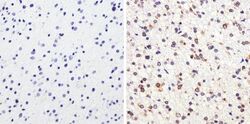
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of Tau showing staining in the cytoplasm of paraffin-embedded human astroglioma (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a Tau (Product # AHB0042) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:50 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
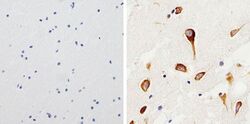
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of Tau showing staining in the cytoplasm and weak nuclear staining of paraffin-embedded human brain tissue (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a Tau (Product # AHB0042) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:200 overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
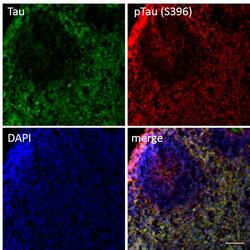
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of p-Tau (S396) and Tau in human iPSC-derived forebrain organoids derived at Day 40. The organoids were fixed with 4% PFA for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by incubation with 30% sucrose solution overnight at 4°C. The organoids were then embedded in OCT and cryosectioned at 5 µm, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 20 min, and blocked with 10% donkey serum in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. Organoid slices were stained with a Mouse Tau (TAU-5) monoclonal antibody (green; Product # AHB0042) at a dilution of 1:500 and a Rabbit p-Tau (Ser396) polyclonal antibody (red; Product # 44-752G) at a dilution of 1:500 in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C, and then incubated with Donkey anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (Product # R37114), Donkey anti-Rabbit Alexa Fluor 568 (Product # A10042) at a dilution of 1:1000 as well as DAPI (blue; 1:25000) in blocking solution at room temperature for 1 hour. Images were taken at 20X magnification. Scale bar: 50 µm. Data courtesy of Dr. Zhexing Wen at Emory University.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
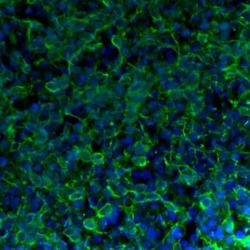
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Tau in human iPSC-derived forebrain organoids derived at Day 40. The organoids were fixed with 4% PFA for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by incubation with 30% sucrose solution overnight at 4°C. The organoids were then embedded in OCT and cryosectioned at 5 µm, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 20 min, and blocked with 10% donkey serum in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. Organoid slices were stained with a Mouse Tau monoclonal antibody (green; Product # AHB0042) at a dilution of 1:500 in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C, and then incubated with Donkey anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 (Product # R37114) at a dilution of 1:1000 as well as DAPI (blue; 1:25000) in blocking solution at room temperature for 1 hour. Images were taken at 20X magnification. Data courtesy of Dr. Zhexing Wen at Emory University.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
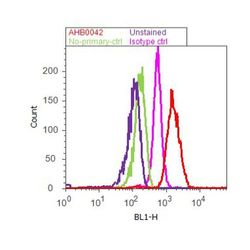
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Tau-5 was done on SH-SY5Y cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Tritonª X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. Cells were labeled with Tau-5 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (AHB0042, red histogram) or with mouse isotype control (pink histogram) at 1-3 µg/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2-3 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor¨ 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (A11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune¨ Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
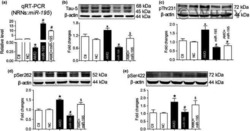
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
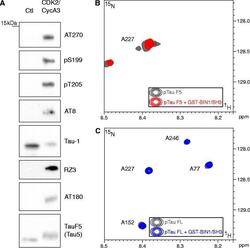
- Experimental details
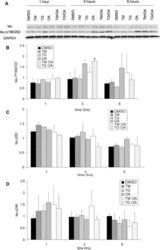
- Fig. 2 Tau phosphorylation precludes the BIN1-Tau interaction in vitro . a . Tau-F5 fragment phosphorylation analysis after in vitro phosphorylation by CDK2/CycA3 kinase. Representative immunoblots using various antibodies against phosphorylation epitopes in Tau. The total amount of Tau-F5 was revealed by the phosphorylation-independent antibody Tau5. The significant shift in molecular weight observed in CDK2/CycA3-treated samples indicates Tau hyperphosphorylation. In contrast to other antibodies, the Tau-1 antibody binds to various non-phosphorylated Tau sites; the signal thus decreases when Tau is hyperphosphorylated [ 31 ]. b . 2D [ 1 H, 15 N] HSQC spectra of 125 muM 15 N CDK-phosphorylated Tau-F5[165-245] free in solution (gray) and with a 1 molar amount of GST-BIN1/SH3 (red, superimposed): Overlaid details of 2D [ 1 H, 15 N] HSQC spectra presented in Additional file 6 . c . 2D [ 1 H, 15 N] HSQC spectra of 60 muM 15 N CDK-phosphorylated 2N4R Tau free in solution (gray) and with a 2 molar amount of GST-BIN1/SH3 (blue, superimposed): Overlaid details of full spectra presented in Additional file 7
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
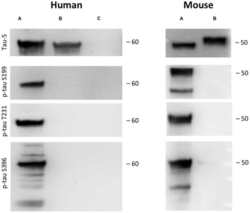
- Experimental details
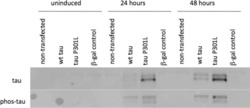
- Figure 2 Tau phosphorylation in vitro . One microgram recombinant human tau (left, A) or mouse tau (right, A) was incubated with glycogensynthase-kinase-3beta (GSK-3ss) and ATP in kinase buffer and analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against total tau (tau-5) phospho-tau-S199, phospho-tau-T231 and phospho-tau-S396. Lanes B and C served as a control omitting either the enzyme GSK-3beta (Lane B) or tau protein (Lane C). Size markers are given as kDa.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
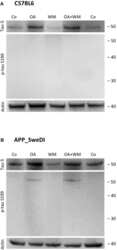
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 Western blot for p-tau S199. Brain slices of adult WT mice (A) or transgenic (TG) mice (B) were incubated for 14 days at 37degC without (Co) or with Okadaic acid (OA), wortmannin (WM), or combination of OA+WM. Extracted brain slices were subsequently analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against total tau (tau-5) and phospho-tau-S199. Size markers are given as kDa on the right side. Actin served as a control.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn