Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [11]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [8]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 44-1071G - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Phospho-AS160 (Thr642) Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Inhibition of AMPK activity in response to insulin in adipocytes: involvement of AMPK pS485, PDEs, and cellular energy levels.
Glucose Sensing by Skeletal Myocytes Couples Nutrient Signaling to Systemic Homeostasis.
Skeletal Muscle TRIB3 Mediates Glucose Toxicity in Diabetes and High- Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance.
PKB-Mediated Thr649 Phosphorylation of AS160/TBC1D4 Regulates the R-Wave Amplitude in the Heart.
TBC1D1 reduces palmitate oxidation by inhibiting β-HAD activity in skeletal muscle.
6-Mercaptopurine augments glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle cells in part via a mechanism dependent upon orphan nuclear receptor NR4A3.
Thr649Ala-AS160 knock-in mutation does not impair contraction/AICAR-induced glucose transport in mouse muscle.
Recovered insulin response by 2 weeks of leptin administration in high-fat fed rats is associated with restored AS160 activation and decreased reactive lipid accumulation.
Loss of 50% of excess weight using a very low energy diet improves insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and skeletal muscle insulin signalling in obese insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients.
Distinct signals regulate AS160 phosphorylation in response to insulin, AICAR, and contraction in mouse skeletal muscle.
Insulin-mediated phosphorylation of the proline-rich Akt substrate PRAS40 is impaired in insulin target tissues of high-fat diet-fed rats.
Kopietz F, Rupar K, Berggreen C, Säll J, Vertommen D, Degerman E, Rider MH, Göransson O
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2020 Sep 1;319(3):E459-E471
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2020 Sep 1;319(3):E459-E471
Glucose Sensing by Skeletal Myocytes Couples Nutrient Signaling to Systemic Homeostasis.
Meng ZX, Gong J, Chen Z, Sun J, Xiao Y, Wang L, Li Y, Liu J, Xu XZS, Lin JD
Molecular cell 2017 May 4;66(3):332-344.e4
Molecular cell 2017 May 4;66(3):332-344.e4
Skeletal Muscle TRIB3 Mediates Glucose Toxicity in Diabetes and High- Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance.
Zhang W, Wu M, Kim T, Jariwala RH, Garvey WJ, Luo N, Kang M, Ma E, Tian L, Steverson D, Yang Q, Fu Y, Garvey WT
Diabetes 2016 Aug;65(8):2380-91
Diabetes 2016 Aug;65(8):2380-91
PKB-Mediated Thr649 Phosphorylation of AS160/TBC1D4 Regulates the R-Wave Amplitude in the Heart.
Quan C, Xie B, Wang HY, Chen S
PloS one 2015;10(4):e0124491
PloS one 2015;10(4):e0124491
TBC1D1 reduces palmitate oxidation by inhibiting β-HAD activity in skeletal muscle.
Maher AC, McFarlan J, Lally J, Snook LA, Bonen A
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2014 Nov 1;307(9):R1115-23
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2014 Nov 1;307(9):R1115-23
6-Mercaptopurine augments glucose transport activity in skeletal muscle cells in part via a mechanism dependent upon orphan nuclear receptor NR4A3.
Liu Q, Zhu X, Xu L, Fu Y, Garvey WT
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2013 Nov 1;305(9):E1081-92
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2013 Nov 1;305(9):E1081-92
Thr649Ala-AS160 knock-in mutation does not impair contraction/AICAR-induced glucose transport in mouse muscle.
Ducommun S, Wang HY, Sakamoto K, MacKintosh C, Chen S
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2012 May 15;302(9):E1036-43
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism 2012 May 15;302(9):E1036-43
Recovered insulin response by 2 weeks of leptin administration in high-fat fed rats is associated with restored AS160 activation and decreased reactive lipid accumulation.
Stefanyk LE, Gulli RA, Ritchie IR, Chabowski A, Snook LA, Bonen A, Dyck DJ
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2011 Jul;301(1):R159-71
American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 2011 Jul;301(1):R159-71
Loss of 50% of excess weight using a very low energy diet improves insulin-stimulated glucose disposal and skeletal muscle insulin signalling in obese insulin-treated type 2 diabetic patients.
Jazet IM, Schaart G, Gastaldelli A, Ferrannini E, Hesselink MK, Schrauwen P, Romijn JA, Maassen JA, Pijl H, Ouwens DM, Meinders AE
Diabetologia 2008 Feb;51(2):309-19
Diabetologia 2008 Feb;51(2):309-19
Distinct signals regulate AS160 phosphorylation in response to insulin, AICAR, and contraction in mouse skeletal muscle.
Kramer HF, Witczak CA, Fujii N, Jessen N, Taylor EB, Arnolds DE, Sakamoto K, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ
Diabetes 2006 Jul;55(7):2067-76
Diabetes 2006 Jul;55(7):2067-76
Insulin-mediated phosphorylation of the proline-rich Akt substrate PRAS40 is impaired in insulin target tissues of high-fat diet-fed rats.
Nascimento EB, Fodor M, van der Zon GC, Jazet IM, Meinders AE, Voshol PJ, Vlasblom R, Baan B, Eckel J, Maassen JA, Diamant M, Ouwens DM
Diabetes 2006 Dec;55(12):3221-8
Diabetes 2006 Dec;55(12):3221-8
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
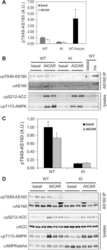
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
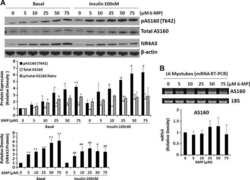
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
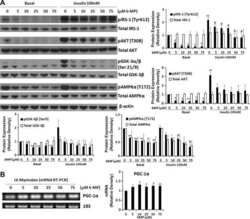
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
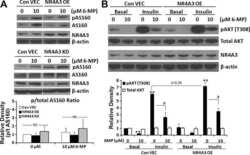
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
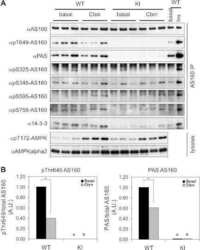
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
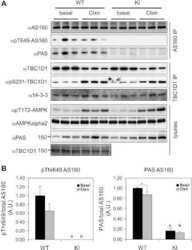
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
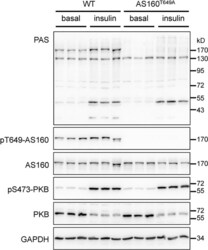
- Experimental details
- Fig 2 Phosphorylation of AS160/TBC1D4 in mouse heart in response to insulin. PAS-binding signals, phosphorylation of AS160-Thr 649 and PKB-Ser 473 , and total AS160 and PKB were detected in the lysates (40 mug) of hearts from the wild-type and AS160 Thr649Ala knockin mice that were intraperitoneally injected with PBS (basal) or insulin (150 mU per kg of body weight) for 20 min. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
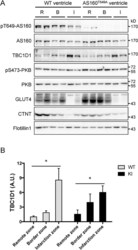
- Experimental details
- Fig 4 Expression and phosphorylation of AS160 and TBC1D1 in the infarct heart. Immunoblotting analyses of phosphorylation of AS160-Thr 649 and PKB-Ser 473 , and total AS160, TBC1D1, PKB, GLUT4 and cTnT in the lysates (40 mug) of the infarct zone (I), border zone (B) and remote zone (R) of mouse heart 4 weeks after myocardial infarction. Flotillin-1 was used as a loading control. A, representative blots. B, quantitation of TBC1D1 signals, n = 4. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05 (infarct zone versus remote zone).
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Other assay
Other assay