Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-21006 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- VENTX Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- A suggested positive control is mouse brain tissue lysate. PA5-21006 can be used with blocking peptide PEP-1120.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 3 months. For long term storage store at -20°C
Submitted references NKL Homeobox Gene VENTX Is Part of a Regulatory Network in Human Conventional Dendritic Cells.
Nagel S, Pommerenke C, Meyer C, Drexler HG
International journal of molecular sciences 2021 May 31;22(11)
International journal of molecular sciences 2021 May 31;22(11)
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
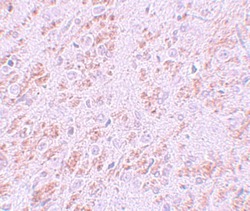
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry of VENTX in rat brain tissue with VENTX Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-21006) at 5 µg/mL.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
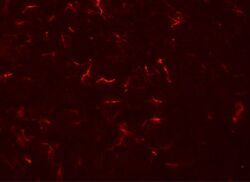
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence of VENTX in rat brain tissue with VENTX Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-21006) at 20 µg/mL.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
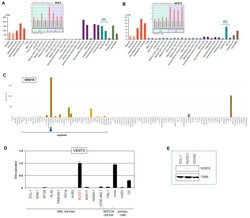
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 VENTX and HHEX expression. Expression analyses of NKL homeobox genes HHEX ( A ) and VENTX ( B ) were performed using public datasets from GEO (GSE24759) and the Human Protein Atlas. The data show that HHEX is active in both pDC and cDC entities while VENTX is expressed in cDCs but not pDCs. ( C ) VENTX expression analysis was performed using RNA-seq dataset LL-100. Conspicuous VENTX levels are shown for AML cell line MUTZ-3 (blue arrow head). The myeloid cell lines are indicated. ( D ) RQ-PCR analysis of VENTX in selected AML and BPDCN cell lines and primary cells including monocytes (mono), monocyte-derived DCs (moDC), and DCs. The indicated fold expression levels are relative to MUTZ-3 which was set to unity. ( E ) Western blot analysis of VENTX and alpha-Tubulin (TUBA) which served as loading control. VENTX protein was detected in MUTZ-3 while two control cell lines tested negative.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
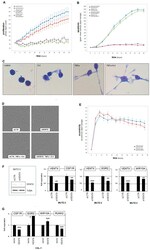
- Experimental details
- Figure 6 Functional analyses of VENTX. ( A ) MUTZ-3 cells treated for siRNA-mediated knockdown of VENTX were analyzed by live-cell imaging, demonstrating a supportive input for VENTX in proliferation. Additional stimulation with TNFa and IL4 inhibited proliferation but showed no difference between VENTX-knockdown and control. ( B ) Additional treatment with apoptosis-inducer etoposide increased apoptosis, showing no difference between VENTX-knockdown and control. ( C ) May-Grunwald-Giemsa staining of MUTZ-3 cells showed distinct morphological alterations after two days stimulation with IL4 and/or TNFa. These cell extensions and formations of dendrites were interpreted as dendritic cell differentiation. ( D ) Microscopic images of MUTZ-3 cells after VENTX-knockdown and stimulation with/without IL4 and TNFa performed by the live-cell imager. ( E ) TNFa-induced alteration of the cell morphology from MUTZ-3 was quantified using the eccentricity-tool from the live-cell imager. The eccentricity increased strongly after TNFa-stimulation. However, no difference between VENTX-knockdown and control cells were detected. ( F ) Western blot analysis of VENTX and TUBA-control confirmed reduced VENTX expression after knockdown at the protein level in MUTZ-3 cells (left). RQ-PCR analyses of CSFR1, EGR2, and MIR10A after VENTX-knockdown in MUTZ-3 cells demonstrated that VENTX activated these genes. ( G ) RQ-PCR analyses of CSFR1, EGR2, MIR10A, and RUNX2 after forced expression of VENTX in BPD
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry