Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-33103 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- NeuN Monoclonal Antibody (1B7)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 1B7
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Icarisid II rescues cognitive dysfunction via activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway promoting hippocampal neurogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Use of high-content imaging to quantify transduction of AAV-PHP viruses in the brain following systemic delivery.
Active constituent of Polygala tenuifolia attenuates cognitive deficits by rescuing hippocampal neurogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
UNC-45A Is Highly Expressed in the Proliferative Cells of the Mouse Genital Tract and in the Microtubule-Rich Areas of the Mouse Nervous System.
Xiao HH, Chen JC, Li H, Li RH, Wang HB, Song HP, Li HY, Shan GS, Tian Y, Zhao YM, Tian JM, Yang JX
Phytotherapy research : PTR 2022 May;36(5):2095-2108
Phytotherapy research : PTR 2022 May;36(5):2095-2108
Use of high-content imaging to quantify transduction of AAV-PHP viruses in the brain following systemic delivery.
Smith EJ, Farshim PP, Flomen R, Jones ST, McAteer SJ, Deverman BE, Gradinaru V, Bates GP
Brain communications 2021;3(2):fcab105
Brain communications 2021;3(2):fcab105
Active constituent of Polygala tenuifolia attenuates cognitive deficits by rescuing hippocampal neurogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Wang XF, Xiao HH, Wu YT, Kong L, Chen JC, Yang JX, Hu XL
BMC complementary medicine and therapies 2021 Oct 25;21(1):267
BMC complementary medicine and therapies 2021 Oct 25;21(1):267
UNC-45A Is Highly Expressed in the Proliferative Cells of the Mouse Genital Tract and in the Microtubule-Rich Areas of the Mouse Nervous System.
Clemente V, Hoshino A, Meints J, Shetty M, Starr T, Lee M, Bazzaro M
Cells 2021 Jun 26;10(7)
Cells 2021 Jun 26;10(7)
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
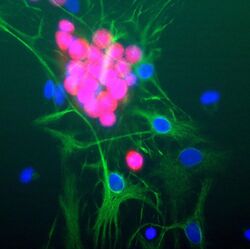
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemistry analysis of NeuN in cultured rat neurons showing strong nuclear and distal cytoplasmic labeling with NeuN monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-33103) using a dilution of 1:1,000 (red). The complete absence of astrocyte staining is shown using Anti-GFAP with a dilution of 1:1,000 (green) and nuclear staining was done with DAPI (blue).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
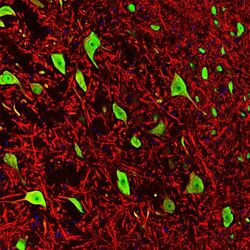
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of NeuN in rat brain stem co-labeled with NeuN monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-33103) using a dilution of 1:1,000 (green) and Anti-MAP2 using a dilution of 1:5,000 (red). The Anti-FOX3 specifically labels the nuclei and the proximal cytoplasm of neuronal cells while the Anti-MAP2 labels dendrites and overlaps with FOX3 labeling the perikarya of neurons. The blue is DAPI staining of nuclear DNA.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Figure 2 Building an automated analysis tree to quantify AAV transduction . ( A ) Brain sections were stained with Hoechst and immunostained for NeuN and GFP and images were captured on the Opera Phenix. Whole brain composites were generated by stitching together a panel of images with a 10% overlap. This was performed for 19 optical slices captured throughout the Z-plane at 1.2 mum intervals. ( B ) Each channel was analysed separately to identify positive signals for cell nuclei (Hoechst, blue), neurons (NeuN, orange) and AAV transduced cells (GFP, green). The Harmony software pseudo-labels positive signals with a coloured border as shown in the lower right-hand side of the thumbnails. ( C ) Positive signals for NeuN and GFP were further gated based on user input and machine learning to remove false positives. A combination of these gated outputs were used to identify NeuN+, GFP+ and NeuN+/GFP+ cells. ( D ) Data from each optical slice throughout the Z-stack were combined to locate neurons and transduced cells throughout the entire section. ( E-G ) The percentage of the Hoechst+ cells found in each section that were NeuN+, GFP+ or both NeuN+/GFP+ for each mouse strain. (H) The automated analysis of the data collected from all brain sections was reanalyzed using less stringent gating criteria for GFP+. Allowing more cells to be registered as GFP+ increased the transduction efficiency in the C57BL/6J mice. However, a small percentage of the Hoechst+ cells in the CBA/Ca section
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
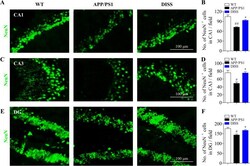
- Experimental details
- Fig. 9 DISS promoted the neuronal differentiation of hippocampal NSCs in APP/PS1 mice. IF analysis against NeuN was carried out to detect the mature NSCs in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice. (A, C and E) Representative immunostaining images of NeuN + cells in the hippocampal CA1 (A), CA3 (C) and DG (E) regions, respectively. Scale bar = 100 mum. (B, D and F). Quantitative analysis of NeuN + cells in the hippocampal CA1 (B), CA3 (D) and DG (F) regions, respectively. # P < 0.05; ## P < 0.01 vs. WT group; * P < 0.05 vs. APP/PS1 group. Data are represented as mean +- sem. n = 6 mice in each group; 6 slices per animal were analyzed by one-way ANOVA
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
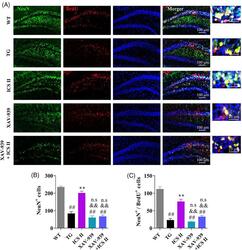
- Experimental details
- 8 FIGURE ICS II promoted the neuronal differentiation of NSCs in the hippocampus by activation of Wnt/beta-actenin signaling pathway. Mice were administrated with ICS II (10 mg/kg) accompanied with or without XAV-939 (5 mg/kg) for 4 weeks, followed by intraperitoneal injection of BrdU (100 mg/kg) to label the proliferation cells. After treatment for another 3 weeks, immunostaining against NeuN and BrdU were carried out to detect the mature neurons derived from proliferative NSCs in the hippocampal DG regions. (a) Representative images of NeuN + /BrdU + cells; (b) Quantification of NeuN + cells as shown in A; (c) Quantification of NeuN + /BrdU + cells as shown in A. Data are represented as mean +- SEM ( n = 3/group). ## p < .01 versus WT group; ** p < .01 versus TG group; && p < .01 versus ICS II group; n.s p > .05 versus TG group. ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test was used
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry