Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-27188 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- p27 Kip1 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- Recommended positive controls: HeLa, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, Neuro 2A, C8D30, NIH-3T3, Raw264.7, C2C12. Predicted reactivity: Mouse (80%), Dog (87%), Cat (87%), Pig (84%), Rhesus Monkey (98%), Bovine (84%). Store product as a concentrated solution. Centrifuge briefly prior to opening the vial.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.07 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Human 3D cellular model of hypoxic brain injury of prematurity.
CDKN1B/p27 is localized in mitochondria and improves respiration-dependent processes in the cardiovascular system-New mode of action for caffeine.
ESRP1 Mutations Cause Hearing Loss due to Defects in Alternative Splicing that Disrupt Cochlear Development.
Context-Dependent Functional Divergence of the Notch Ligands DLL1 and DLL4 In Vivo.
Pașca AM, Park JY, Shin HW, Qi Q, Revah O, Krasnoff R, O'Hara R, Willsey AJ, Palmer TD, Pașca SP
Nature medicine 2019 May;25(5):784-791
Nature medicine 2019 May;25(5):784-791
CDKN1B/p27 is localized in mitochondria and improves respiration-dependent processes in the cardiovascular system-New mode of action for caffeine.
Ale-Agha N, Goy C, Jakobs P, Spyridopoulos I, Gonnissen S, Dyballa-Rukes N, Aufenvenne K, von Ameln F, Zurek M, Spannbrucker T, Eckermann O, Jakob S, Gorressen S, Abrams M, Grandoch M, Fischer JW, Köhrer K, Deenen R, Unfried K, Altschmied J, Haendeler J
PLoS biology 2018 Jun;16(6):e2004408
PLoS biology 2018 Jun;16(6):e2004408
ESRP1 Mutations Cause Hearing Loss due to Defects in Alternative Splicing that Disrupt Cochlear Development.
Rohacek AM, Bebee TW, Tilton RK, Radens CM, McDermott-Roe C, Peart N, Kaur M, Zaykaner M, Cieply B, Musunuru K, Barash Y, Germiller JA, Krantz ID, Carstens RP, Epstein DJ
Developmental cell 2017 Nov 6;43(3):318-331.e5
Developmental cell 2017 Nov 6;43(3):318-331.e5
Context-Dependent Functional Divergence of the Notch Ligands DLL1 and DLL4 In Vivo.
Preuße K, Tveriakhina L, Schuster-Gossler K, Gaspar C, Rosa AI, Henrique D, Gossler A, Stauber M
PLoS genetics 2015 Jun;11(6):e1005328
PLoS genetics 2015 Jun;11(6):e1005328
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
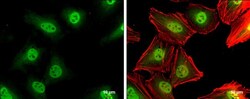
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence analysis of p27 Kip1 was performed in HeLa cells fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: p27 Kip1 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5 27188) diluted at 1:500. Red: phalloidin, a cytoskeleton marker. Scale bar = 10 µm.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
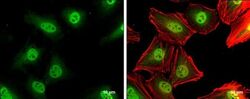
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence analysis of p27 Kip1 was performed in HeLa cells fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: p27 Kip1 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5 27188) diluted at 1:500. Red: phalloidin, a cytoskeleton marker. Scale bar = 10 µm.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
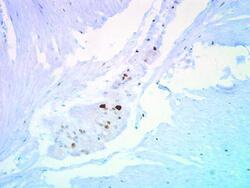
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical staining of human ulcerative colitis tissue using anti-p27 Kip1 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-27188).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
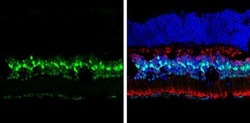
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry (Frozen) analysis of p27-Kip1 was performed in frozen sectioned adult mouse retina tissue using p27 Kip1 Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-27188) at a dilution of 1:250 (Green). Red: Protein kinase C alpha staining. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
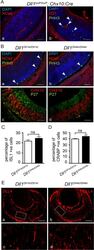
- Experimental details
- Fig 4 DLL4 expressed from the Dll1 locus rescues DLL1 loss-of-function in the retina. (A) Dll1 mutant retinas show epithelial disruption with formation of polarised rosettes in which the apical markers N-Cadherin (NCad, a) and ZO-1 (ZO1, b) are abnormally present at the central lumen. Ectopic proliferating progenitors, labelled with PHH3 (b, arrowheads), are located close to the apical lumen of these rosettes. (B) In contrast, the neuroepithelium of homozygous Dll1 Dll1ki and Dll1 Dll4ki embryos is correctly organised without rosettes, and N-Cadherin shows the normal apical localisation close to the retinal pigmented epithelium (a,b). Mitotic progenitors (PHH3+) are only detected at the apical region of the neuroepithelium (a,b arrowheads). A normal stratification of CHX10+ progenitors and P27+ differentiating neurons is also observed (c,d). (C, D) E13.5 homozygous Dll1 Dll1ki and Dll1 Dll4ki retinas show no significant difference in the number of ISL1+ RGCs (C) and CRABP+ amacrine cells (D). Cells immunopositive for Islet-1 and Crabp were counted and related to the total number of cells in the retina (DAPI+). Percentages are shown as mean +- SEM; ns, not significant. (E) Expression of DLL4 in homozygous Dll1 Dll1ki (a,c) and in homozygous Dll1 Dll4ki (b,d) E13.5 retinas as detected by an anti-DLL4 antibody. (c) and (d) are magnifications of (a) and (b), respectively. Endogenous plus transgenic DLL4 is expressed in more cells in Dll1 Dll4ki/Dll4ki as compared to endogeno
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry