Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [20]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [14]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-9948-82 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD278 (ICOS) Monoclonal Antibody (ISA-3), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The ISA-3 monoclonal antibody reacts with human ICOS (Inducible COStimulatory molecule), also known as H4, CRP-1 and AILIM. ICOS is a T cell specific activation molecule and a third member of the CD28/CTLA-4 family. Human ICOS has a relative molecular mass of 55-60 kDa, composed of 27 kDa and 29 kDa chains. Human ICOS on activated T cells has potent costimulatory activity for T cell activation and is required for humoral immune responses, in particular for memory B cell and plasma cell generation. ICOS binds to its ligand, B7h/B7RP-1 expressed on activated APCs (antigen presenting cells) and on a number of inflamed peripheral tissues. Plate-bound ISA-3 is costimulatory for T cells and induces production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 and other cytokines, but not IL-2. ISA-3 has the same reactivity pattern and characteristics as F44. ISA-3 was generated against the human ICOS antigen. C398.4A, anti-mouse ICOS/H4 (Product # 14-9949-82), was shown to cross-react with human ICOS but binds to an epitope different from ISA-3. C398.4A stains activated cells brighter than ISA-3; however, it also exhibits higher staining of non-activated human peripheral blood or isolated PBMC. To achieve the brightest staining of ICOS on activated human T cells, please use Product # 13-9948-82 or Product # 12-9948-42 rather than Product # 11-9948-42 . Applications Reported: The ISA-3 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections. It has also been reported in in vitro functional assays. (Please use Functional Grade purified ISA-3, Product # 16-9948-82, in functional assays). Applications Tested: The ISA-3 antibody has been tested by flow cytometric analysis of unstimulated and PHA-activated (2 days) human blood cells. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.5 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- ISA-3
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Inducible Costimulator-C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 3 Signaling is Involved in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Pathogenesis.
Impaired HA-specific T follicular helper cell and antibody responses to influenza vaccination are linked to inflammation in humans.
Functional SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immune Memory Persists after Mild COVID-19.
IL-21-Deficient T Follicular Helper Cells Support B Cell Responses Through IL-27 in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B.
The adjuvant GLA-SE promotes human Tfh cell expansion and emergence of public TCRβ clonotypes.
Distribution of circulating follicular helper T cells and expression of interleukin-21 and chemokine C-X-C ligand 13 in gastric cancer.
Dysregulated ICOS(+) proinflammatory and suppressive regulatory T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
CXCL13-producing TFH cells link immune suppression and adaptive memory in human breast cancer.
ICOS(+) Foxp3(+) TILs in gastric cancer are prognostic markers and effector regulatory T cells associated with Helicobacter pylori.
Polyfunctional Melan-A-specific tumor-reactive CD8(+) T cells elicited by dacarbazine treatment before peptide-vaccination depends on AKT activation sustained by ICOS.
CD28 family of receptors on T cells in chronic HBV infection: Expression characteristics, clinical significance and correlations with PD-1 blockade.
PD-1 marks dysfunctional regulatory T cells in malignant gliomas.
Tumor-infiltrating plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote immunosuppression by Tr1 cells in human liver tumors.
Stromal cells' B7-1 is a key stimulatory molecule for interleukin-10 production by HOZOT, a multifunctional regulatory T-cell line.
Inducible costimulator: a modulator of IFN-gamma production in human tuberculosis.
Inducible costimulator: a modulator of IFN-gamma production in human tuberculosis.
Homozygous loss of ICOS is associated with adult-onset common variable immunodeficiency.
Induction, binding specificity and function of human ICOS.
The T cell activation molecule H4 and the CD28-like molecule ICOS are identical.
ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28.
Li DY, Chen L, Miao SY, Zhou M, Wu JH, Sun SW, Liu LL, Qi C, Xiong XZ
International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2022;17:1847-1861
International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2022;17:1847-1861
Impaired HA-specific T follicular helper cell and antibody responses to influenza vaccination are linked to inflammation in humans.
Hill DL, Whyte CE, Innocentin S, Lee JL, Dooley J, Wang J, James EA, Lee JC, Kwok WW, Zand MS, Liston A, Carr EJ, Linterman MA
eLife 2021 Nov 2;10
eLife 2021 Nov 2;10
Functional SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immune Memory Persists after Mild COVID-19.
Rodda LB, Netland J, Shehata L, Pruner KB, Morawski PA, Thouvenel CD, Takehara KK, Eggenberger J, Hemann EA, Waterman HR, Fahning ML, Chen Y, Hale M, Rathe J, Stokes C, Wrenn S, Fiala B, Carter L, Hamerman JA, King NP, Gale M Jr, Campbell DJ, Rawlings DJ, Pepper M
Cell 2021 Jan 7;184(1):169-183.e17
Cell 2021 Jan 7;184(1):169-183.e17
IL-21-Deficient T Follicular Helper Cells Support B Cell Responses Through IL-27 in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B.
Khanam A, Ayithan N, Tang L, Poonia B, Kottilil S
Frontiers in immunology 2020;11:599648
Frontiers in immunology 2020;11:599648
The adjuvant GLA-SE promotes human Tfh cell expansion and emergence of public TCRβ clonotypes.
Hill DL, Pierson W, Bolland DJ, Mkindi C, Carr EJ, Wang J, Houard S, Wingett SW, Audran R, Wallin EF, Jongo SA, Kamaka K, Zand M, Spertini F, Daubenberger C, Corcoran AE, Linterman MA
The Journal of experimental medicine 2019 Aug 5;216(8):1857-1873
The Journal of experimental medicine 2019 Aug 5;216(8):1857-1873
Distribution of circulating follicular helper T cells and expression of interleukin-21 and chemokine C-X-C ligand 13 in gastric cancer.
Meng X, Yu X, Dong Q, Xu X, Li J, Xu Q, Ma J, Zhou C
Oncology letters 2018 Sep;16(3):3917-3922
Oncology letters 2018 Sep;16(3):3917-3922
Dysregulated ICOS(+) proinflammatory and suppressive regulatory T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Wang HX, Kang X, Chu S, Li H, Li X, Yin X, Qiu YR, Lai W
Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2018 Oct;16(4):3728-3734
Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2018 Oct;16(4):3728-3734
CXCL13-producing TFH cells link immune suppression and adaptive memory in human breast cancer.
Gu-Trantien C, Migliori E, Buisseret L, de Wind A, Brohée S, Garaud S, Noël G, Dang Chi VL, Lodewyckx JN, Naveaux C, Duvillier H, Goriely S, Larsimont D, Willard-Gallo K
JCI insight 2017 Jun 2;2(11)
JCI insight 2017 Jun 2;2(11)
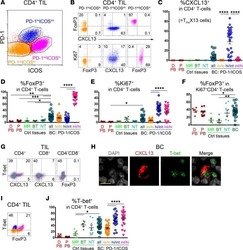
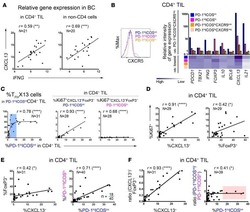
ICOS(+) Foxp3(+) TILs in gastric cancer are prognostic markers and effector regulatory T cells associated with Helicobacter pylori.
Nagase H, Takeoka T, Urakawa S, Morimoto-Okazawa A, Kawashima A, Iwahori K, Takiguchi S, Nishikawa H, Sato E, Sakaguchi S, Mori M, Doki Y, Wada H
International journal of cancer 2017 Feb 1;140(3):686-695
International journal of cancer 2017 Feb 1;140(3):686-695
Polyfunctional Melan-A-specific tumor-reactive CD8(+) T cells elicited by dacarbazine treatment before peptide-vaccination depends on AKT activation sustained by ICOS.
Franzese O, Palermo B, Di Donna C, Sperduti I, Ferraresi V, Stabile H, Gismondi A, Santoni A, Nisticò P
Oncoimmunology 2016 May;5(5):e1114203
Oncoimmunology 2016 May;5(5):e1114203
CD28 family of receptors on T cells in chronic HBV infection: Expression characteristics, clinical significance and correlations with PD-1 blockade.
Tang ZS, Hao YH, Zhang EJ, Xu CL, Zhou Y, Zheng X, Yang DL
Molecular medicine reports 2016 Aug;14(2):1107-16
Molecular medicine reports 2016 Aug;14(2):1107-16
PD-1 marks dysfunctional regulatory T cells in malignant gliomas.
Lowther DE, Goods BA, Lucca LE, Lerner BA, Raddassi K, van Dijk D, Hernandez AL, Duan X, Gunel M, Coric V, Krishnaswamy S, Love JC, Hafler DA
JCI insight 2016 Apr 21;1(5)
JCI insight 2016 Apr 21;1(5)
Tumor-infiltrating plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote immunosuppression by Tr1 cells in human liver tumors.
Pedroza-Gonzalez A, Zhou G, Vargas-Mendez E, Boor PP, Mancham S, Verhoef C, Polak WG, Grünhagen D, Pan Q, Janssen H, Garcia-Romo GS, Biermann K, Tjwa ET, IJzermans JN, Kwekkeboom J, Sprengers D
Oncoimmunology 2015 Jun;4(6):e1008355
Oncoimmunology 2015 Jun;4(6):e1008355
Stromal cells' B7-1 is a key stimulatory molecule for interleukin-10 production by HOZOT, a multifunctional regulatory T-cell line.
Otani T, Tsuji-Takayama K, Okochi A, Yamamoto M, Takeuchi M, Yamasaki F, Nakamura S, Kibata M
Immunology and cell biology 2011 Feb;89(2):246-54
Immunology and cell biology 2011 Feb;89(2):246-54
Inducible costimulator: a modulator of IFN-gamma production in human tuberculosis.
Quiroga MF, Pasquinelli V, Martínez GJ, Jurado JO, Zorrilla LC, Musella RM, Abbate E, Sieling PA, García VE
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 May 15;176(10):5965-74
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 May 15;176(10):5965-74
Inducible costimulator: a modulator of IFN-gamma production in human tuberculosis.
Quiroga MF, Pasquinelli V, Martínez GJ, Jurado JO, Zorrilla LC, Musella RM, Abbate E, Sieling PA, García VE
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 May 15;176(10):5965-74
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 May 15;176(10):5965-74
Homozygous loss of ICOS is associated with adult-onset common variable immunodeficiency.
Grimbacher B, Hutloff A, Schlesier M, Glocker E, Warnatz K, Dräger R, Eibel H, Fischer B, Schäffer AA, Mages HW, Kroczek RA, Peter HH
Nature immunology 2003 Mar;4(3):261-8
Nature immunology 2003 Mar;4(3):261-8
Induction, binding specificity and function of human ICOS.
Beier KC, Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Heuck C, Rauch A, Büchner K, Ludewig B, Ochs HD, Mages HW, Kroczek RA
European journal of immunology 2000 Dec;30(12):3707-17
European journal of immunology 2000 Dec;30(12):3707-17
The T cell activation molecule H4 and the CD28-like molecule ICOS are identical.
Buonfiglio D, Bragardo M, Redoglia V, Vaschetto R, Bottarel F, Bonissoni S, Bensi T, Mezzatesta C, Janeway CA Jr, Dianzani U
European journal of immunology 2000 Dec;30(12):3463-7
European journal of immunology 2000 Dec;30(12):3463-7
ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28.
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC, Eljaschewitsch B, Kraft R, Anagnostopoulos I, Kroczek RA
Nature 1999 Jan 21;397(6716):263-6
Nature 1999 Jan 21;397(6716):263-6
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
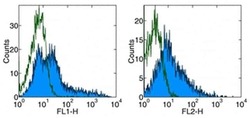
- Experimental details
- Staining of CD3 + CD28 stimulated human PBMC with Anti-Human CD278 (ICOS) FITC (left), and Anti-Human CD278 (ICOS) PE (right).Appropriate isotype controls were used (open histogram).Total viable cells were used for analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
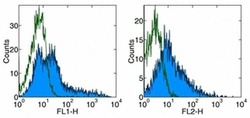
- Experimental details
- Staining of CD3 + CD28 stimulated human PBMC with Anti-Human CD278 (ICOS) FITC (left), and Anti-Human CD278 (ICOS) PE (right).Appropriate isotype controls were used (open histogram).Total viable cells were used for analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
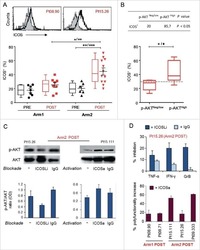
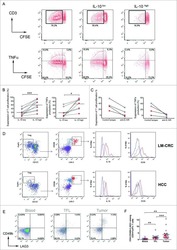
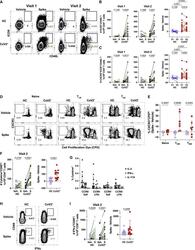
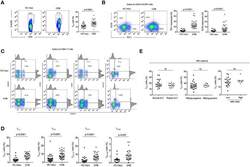
- Figure 3 SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces Durable, Functional Spike-Reactive CD4 + T Cells (A) Representative flow cytometry plots of ICOS and CD40L expression on antigen-experienced (non-CD45RA + CCR7 + ) CD4 + T cells 20 h after incubation of PBMCs from HC and CoV2 + individuals at V1 and V2 with vehicle or SARS-CoV-2 spike. (B) Number of antigen-experienced ICOS + CD40L + CD4 + T cells per 1x10 6 CD4 + T cells from HC and CoV2 + samples after incubation with vehicle (Veh.) or spike (S) at both time points (right) and calculated number of spike-responsive CD4 + T cells (number after incubation with spike minus number after incubation with vehicle) compared across time points (left). (C) Number of antigen-experienced CXCR5 + ICOS + CD40L + CD4 + T cells (cTfh) per 1 x 10 6 CD4 + T cells from HC and CoV2 + samples after incubation with Veh. or S at both time points (right) and calculated number of spike-responsive cTfh cells (number after incubation with spike minus number after incubation with vehicle) compared across time points (left). (D) Representative flow cytometry plots of sorted CD4 + naive (CD45RA + CCR7 + ), T CM (CD45RA - CCR7 + ), or T EM (CD45RA - CCR7 - ) T cells from HC and CoV2 + PBMCs after 5-6 days of co-culture with SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein-pulsed autologous monocytes and measuring proliferation by CPD dilution. (E) SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific expansion of sorted CD4 + naive T, T CM , and T EM cells from V1 (circles) and V2 (squares) reported as frequency of CXC
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
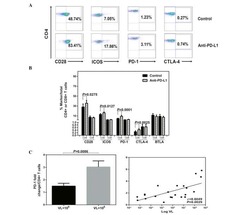
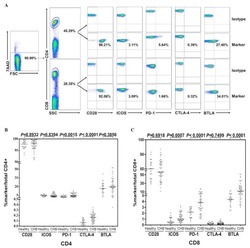
- Figure 1 T FH cell compartment was altered during chronic HBV infection. (A, B) Representative flow cytometry plot indicates the percent frequencies of circulating T FH cells, PD-1 as well as ICOS expression in HC-vacc (n = 21) and CHB patients (n = 32) respectively. Throughout the flow cytometry plots, gates were placed based on single-color controls. (C, D) T FH cell subtypes were analyzed on the basis of expression of different cell surface molecules. Values in the quadrant designate the percent frequency of different T FH cell subsets. Cumulative data has been shown in scatter plot (HC-vacc: n = 21 and CHB: n = 32) and expressed as median. Each symbol on scatter plot represents an individual subject. Statistical analysis was performed using non-parametric, two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. (E) Frequency of T FH cells in HBV patients with different ALT and HBV DNA levels, HBeAg-negative and positive patients was analyzed. Levels of ALT were divided as normal (range, 22-40; n=21) vs. raised (range, 41-193; n=15)). HBV DNA levels were divided as 10 4 (n = 8). Unpaired t-test was used for statistical significance.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
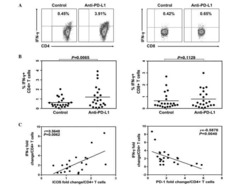
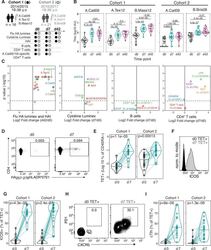
- Figure 1. Robust haemagglutinin (HA)-specific CD4 + T cells' response to seasonal influenza vaccination. ( A ) Overview of cohort characteristics, vaccination strains, and immune variables measured before (d0), 7 days (d7), and 42 days (d42) after seasonal influenza vaccination. ( B ) IgG responses to HA proteins from vaccine influenza strains measured by Luminex. Dashed line indicates limit of detection in Luminex assay. ( C ) Log 2 fold change versus -log10 false discovery rate (FDR)-adjusted p-value of Flu HA Luminex, Cytokine Luminex, B cell and CD4 + T cell immunophenotyping parameters before and after vaccination at indicated time points for cohort 1. Dashed line represents the p-value cut-off at FDR-adjusted p=0.05. ( D ) Representative flow cytometry plots of HA 257-276 HLADR*0701 staining on CD4 + CD45RA - cells, gate corresponds to HA-specific TET + T cells, and ( E ) the frequency of HA-specific TET + T cells among all CD4 + CD45RA - cells on d0 compared to d7. ( F ) Representative ICOS staining and ( G ) the percentage of ICOS + cells among HA-specific TET + T cells on d0 and d7. ( H ) CXCR5 and PD1 staining on HA-specific TET + T cells on d0 and d7, gate corresponds to 'TET + cTfh' T cells, and ( I ) the percentage of circulating T follicular helper (cTfh) cells among HA-specific TET + T cells on d0 and d7 for each cohort. In parts ( D-I ), cohort 1 n = 16; cohort 2 n = 19. Paired p-values determined using Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Figure 1--figure supplement 1.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
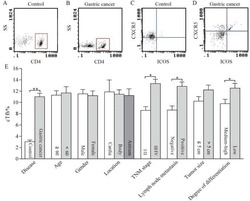
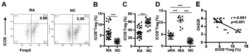
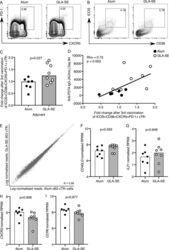
- Inducible costimulator (ICOS) signaling induces C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3) expression in vivo and in vitro. ( A ) Representative flow cytometric dot plots of the frequencies of CXCR3 + CD4 + T cells and CXCR3 + CD4 + CD25 + FOXP3 + Tregs within patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (SCOPD). Comparisons of the percentage of CXCR3 + T cells within CD4 + T cells ( B ) and CD4 + CD25 + FOXP3 + Tregs ( C ) in the peripheral blood from 15 healthy controls (HC), 11 healthy smokers (HS), 22 patients with SCOPD (SCOPD), and 14 patients with acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD). ( D ) Representative gating of CXCR3 + ICOS + CD4 + T cells and CXCR3 + ICOS - CD4 + T cells and the corresponding histograms (n = 22). ( E ) Naive CD4 + T cells obtained from the peripheral blood of healthy people were cultured with plate-bound anti-CD3/28 mAbs in the presence of IL-2 with or without anti-ICOS mAb (ISA-3) for four days. The frequency of CXCR3 + CD4 + T cells was analyzed with flow cytometry. Comparable results were obtained from six independent experiments. ( F ) The percentage of CXCR3 + CD4 + T cells in the peripheral blood and corresponding BALF of four patients with SCOPD. *p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
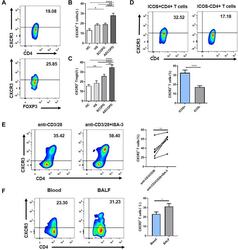
- Figure 3. A GLA-SE adjuvanted vaccine promotes cTfh expansion. (A and B) Flow cytometric contour plots of (A) PD-1 and CXCR5 on total CD45RA - CD4 + CD3 + cells and (B) ICOS and CD38 on the population gated in A on peripheral blood cells from individuals 7 d after the third P27A vaccination. Alum group, n = 7; GLA-SE group, n = 8. (C) Fold change of CD38 + ICOS + CXCR5 + PD-1 + cTfh cells 7 d after the third P27A vaccination (frequency of cTfh cells at day 63/baseline). Alum group, n = 7; GLA-SE, group n = 8. P = 0.027. The P value is from an unpaired Student's t test. (D) Correlation of anti-P27A IgG antibody titer 28 d after the third vaccination against fold change in CD38 + ICOS + CXCR5 + PD-1 + cTfh cells 7 d after the third vaccination. Rho = 0.73; P = 0.003 by Spearman's correlation (Rho = coefficient); n = 15. (E) Scatterplot of RNA-sequencing data comparing all genes expressed in CD38 + ICOS + CXCR5 + PD-1 + cTfh cells 7 d after the third P27A vaccination in either Alum- (x axis) or GLA-SE- (y axis) vaccinated groups. Alum group, n = 7; GLA-SE group, n = 8. (F-I) Bar plots showing log-normalized reads from RNA-sequencing data of CD40LG . P = 0.593 (F), IL21 P = 0.846 (G), CXCR3 P = 0.606 (H), and CCR6 P = 0.977 (I) for transcripts in ICOS in CD38 + ICOS + CXCR5 + PD-1 + cTfh cells 7 d after the third P27A vaccination; Alum group, n = 7; GLA-SE group, n = 8. P values were calculated using DESeq2 with a false discovery rate corr
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry