ABIN252619
antibody from antibodies-online
Targeting: TP73
P73
 Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Chromatin ImmunoprecipitationAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [28]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- ABIN252619 - Provider product page

- Provider
- antibodies-online
- Product name
- anti-Tumor Protein P73 (TP73) antibody
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Description
- Protein G purified
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 5B1288
- Vial size
- 0.1 mg
- Storage
- Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
- Handling
- Avoid freeze-thaw cycles
Submitted references TP53INP1 Downregulation Activates a p73-Dependent DUSP10/ERK Signaling Pathway to Promote Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
IAPP-driven metabolic reprogramming induces regression of p53-deficient tumours in vivo.
Dysregulated ΔNp63α negatively regulates the maspin promoter in keratinocytes via blocking endogenous p73 binding.
CK2 phosphorylates and inhibits TAp73 tumor suppressor function to promote expression of cancer stem cell genes and phenotype in head and neck cancer.
The sodium/iodide symporter NIS is a transcriptional target of the p53-family members in liver cancer cells.
TAp73 enhances the pentose phosphate pathway and supports cell proliferation.
ΔNp73 enhances promoter activity of TGF-β induced genes.
ΔNp63α regulates keratinocyte proliferation by controlling PTEN expression and localization.
p73 is essential for vitamin D-mediated osteoblastic differentiation.
p63 and p73 transcriptionally regulate genes involved in DNA repair.
Evaluation of p63 and p73 antibodies for cross-reactivity.
A gene signature-based approach identifies mTOR as a regulator of p73.
Regulation of p73-mediated apoptosis by c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Skin human papillomavirus type 38 alters p53 functions by accumulation of deltaNp73.
DNp73alpha protects myogenic cells from apoptosis.
MEK1 inhibition sensitizes primary acute myelogenous leukemia to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis.
c-Abl-independent p73 stabilization during gemcitabine- or 4'-thio-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-induced apoptosis in wild-type and p53-null colorectal cancer cells.
MDM2 is required for suppression of apoptosis by activated Akt1 in salivary acinar cells.
Melanocyte and keratinocyte carcinogenesis: p53 family protein activities and intersecting mRNA expression profiles.
TP53INP1 is a novel p73 target gene that induces cell cycle arrest and cell death by modulating p73 transcriptional activity.
A role of p73 in mitotic exit.
New antibodies recognizing p73: comparison with commercial antibodies.
Treatment with arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibitor activates the p73-p53AIP1 apoptotic pathway in leukemia cells.
The p73 gene is an anti-tumoral target of the RARbeta/gamma-selective retinoid tazarotene.
Adenosine deaminase, a key enzyme in DNA precursors control, is a new p73 target.
Exclusion of c-Abl from the nucleus restrains the p73 tumor suppression function.
p73 is regulated by phosphorylation at the G2/M transition.
DNA damage-dependent acetylation of p73 dictates the selective activation of apoptotic target genes.
Ng KY, Chan LH, Chai S, Tong M, Guan XY, Lee NP, Yuan Y, Xie D, Lee TK, Dusetti NJ, Carrier A, Ma S
Cancer research 2017 Sep 1;77(17):4602-4612
Cancer research 2017 Sep 1;77(17):4602-4612
IAPP-driven metabolic reprogramming induces regression of p53-deficient tumours in vivo.
Venkatanarayan A, Raulji P, Norton W, Chakravarti D, Coarfa C, Su X, Sandur SK, Ramirez MS, Lee J, Kingsley CV, Sananikone EF, Rajapakshe K, Naff K, Parker-Thornburg J, Bankson JA, Tsai KY, Gunaratne PH, Flores ER
Nature 2015 Jan 29;517(7536):626-30
Nature 2015 Jan 29;517(7536):626-30
Dysregulated ΔNp63α negatively regulates the maspin promoter in keratinocytes via blocking endogenous p73 binding.
King KE, Reddi DM, Ponnamperuma RM, Gerdes M, Weinberg WC
Molecular carcinogenesis 2014 Sep;53(9):698-710
Molecular carcinogenesis 2014 Sep;53(9):698-710
CK2 phosphorylates and inhibits TAp73 tumor suppressor function to promote expression of cancer stem cell genes and phenotype in head and neck cancer.
Lu H, Yan C, Quan XX, Yang X, Zhang J, Bian Y, Chen Z, Van Waes C
Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) 2014 Oct;16(10):789-800
Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) 2014 Oct;16(10):789-800
The sodium/iodide symporter NIS is a transcriptional target of the p53-family members in liver cancer cells.
Guerrieri F, Piconese S, Lacoste C, Schinzari V, Testoni B, Valogne Y, Gerbal-Chaloin S, Samuel D, Bréchot C, Faivre J, Levrero M
Cell death & disease 2013 Sep 19;4:e807
Cell death & disease 2013 Sep 19;4:e807
TAp73 enhances the pentose phosphate pathway and supports cell proliferation.
Du W, Jiang P, Mancuso A, Stonestrom A, Brewer MD, Minn AJ, Mak TW, Wu M, Yang X
Nature cell biology 2013 Aug;15(8):991-1000
Nature cell biology 2013 Aug;15(8):991-1000
ΔNp73 enhances promoter activity of TGF-β induced genes.
Niemantsverdriet M, Nagle P, Chiu RK, Langendijk JA, Kampinga HH, Coppes RP
PloS one 2012;7(12):e50815
PloS one 2012;7(12):e50815
ΔNp63α regulates keratinocyte proliferation by controlling PTEN expression and localization.
Leonard MK, Kommagani R, Payal V, Mayo LD, Shamma HN, Kadakia MP
Cell death and differentiation 2011 Dec;18(12):1924-33
Cell death and differentiation 2011 Dec;18(12):1924-33
p73 is essential for vitamin D-mediated osteoblastic differentiation.
Kommagani R, Whitlatch A, Leonard MK, Kadakia MP
Cell death and differentiation 2010 Mar;17(3):398-407
Cell death and differentiation 2010 Mar;17(3):398-407
p63 and p73 transcriptionally regulate genes involved in DNA repair.
Lin YL, Sengupta S, Gurdziel K, Bell GW, Jacks T, Flores ER
PLoS genetics 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000680
PLoS genetics 2009 Oct;5(10):e1000680
Evaluation of p63 and p73 antibodies for cross-reactivity.
Rosenbluth JM, Johnson K, Tang L, Triplett T, Pietenpol JA
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2009 Nov 15;8(22):3702-6
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2009 Nov 15;8(22):3702-6
A gene signature-based approach identifies mTOR as a regulator of p73.
Rosenbluth JM, Mays DJ, Pino MF, Tang LJ, Pietenpol JA
Molecular and cellular biology 2008 Oct;28(19):5951-64
Molecular and cellular biology 2008 Oct;28(19):5951-64
Regulation of p73-mediated apoptosis by c-Jun N-terminal kinase.
Jones EV, Dickman MJ, Whitmarsh AJ
The Biochemical journal 2007 Aug 1;405(3):617-23
The Biochemical journal 2007 Aug 1;405(3):617-23
Skin human papillomavirus type 38 alters p53 functions by accumulation of deltaNp73.
Accardi R, Dong W, Smet A, Cui R, Hautefeuille A, Gabet AS, Sylla BS, Gissmann L, Hainaut P, Tommasino M
EMBO reports 2006 Mar;7(3):334-40
EMBO reports 2006 Mar;7(3):334-40
DNp73alpha protects myogenic cells from apoptosis.
Belloni L, Moretti F, Merlo P, Damalas A, Costanzo A, Blandino G, Levrero M
Oncogene 2006 Jun 15;25(25):3606-12
Oncogene 2006 Jun 15;25(25):3606-12
MEK1 inhibition sensitizes primary acute myelogenous leukemia to arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis.
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Salvatore L, Noguera N, Mazzera L, Tabilio A, Lo-Coco F, Levrero M, Bonati A
Blood 2006 Jun 1;107(11):4549-53
Blood 2006 Jun 1;107(11):4549-53
c-Abl-independent p73 stabilization during gemcitabine- or 4'-thio-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-induced apoptosis in wild-type and p53-null colorectal cancer cells.
Thottassery JV, Westbrook L, Someya H, Parker WB
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2006 Feb;5(2):400-10
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2006 Feb;5(2):400-10
MDM2 is required for suppression of apoptosis by activated Akt1 in salivary acinar cells.
Limesand KH, Schwertfeger KL, Anderson SM
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Dec;26(23):8840-56
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Dec;26(23):8840-56
Melanocyte and keratinocyte carcinogenesis: p53 family protein activities and intersecting mRNA expression profiles.
Kulesz-Martin M, Lagowski J, Fei S, Pelz C, Sears R, Powell MB, Halaban R, Johnson J
The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings 2005 Nov;10(2):142-52
The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings 2005 Nov;10(2):142-52
TP53INP1 is a novel p73 target gene that induces cell cycle arrest and cell death by modulating p73 transcriptional activity.
Tomasini R, Seux M, Nowak J, Bontemps C, Carrier A, Dagorn JC, Pébusque MJ, Iovanna JL, Dusetti NJ
Oncogene 2005 Dec 8;24(55):8093-104
Oncogene 2005 Dec 8;24(55):8093-104
A role of p73 in mitotic exit.
Merlo P, Fulco M, Costanzo A, Mangiacasale R, Strano S, Blandino G, Taya Y, Lavia P, Levrero M
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Aug 26;280(34):30354-60
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Aug 26;280(34):30354-60
New antibodies recognizing p73: comparison with commercial antibodies.
Sayan AE, Paradisi A, Vojtesek B, Knight RA, Melino G, Candi E
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2005 Apr 29;330(1):186-93
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2005 Apr 29;330(1):186-93
Treatment with arsenic trioxide (ATO) and MEK1 inhibitor activates the p73-p53AIP1 apoptotic pathway in leukemia cells.
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Bonati A
Blood 2004 Jul 15;104(2):519-25
Blood 2004 Jul 15;104(2):519-25
The p73 gene is an anti-tumoral target of the RARbeta/gamma-selective retinoid tazarotene.
Papoutsaki M, Lanza M, Marinari B, Nisticò S, Moretti F, Levrero M, Chimenti S, Costanzo A
The Journal of investigative dermatology 2004 Dec;123(6):1162-8
The Journal of investigative dermatology 2004 Dec;123(6):1162-8
Adenosine deaminase, a key enzyme in DNA precursors control, is a new p73 target.
Tullo A, Mastropasqua G, Bourdon JC, Centonze P, Gostissa M, Costanzo A, Levrero M, Del Sal G, Saccone C, Sbisà E
Oncogene 2003 Nov 27;22(54):8738-48
Oncogene 2003 Nov 27;22(54):8738-48
Exclusion of c-Abl from the nucleus restrains the p73 tumor suppression function.
Vella V, Zhu J, Frasca F, Li CY, Vigneri P, Vigneri R, Wang JY
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Jul 4;278(27):25151-7
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Jul 4;278(27):25151-7
p73 is regulated by phosphorylation at the G2/M transition.
Fulco M, Costanzo A, Merlo P, Mangiacasale R, Strano S, Blandino G, Balsano C, Lavia P, Levrero M
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49196-202
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 5;278(49):49196-202
DNA damage-dependent acetylation of p73 dictates the selective activation of apoptotic target genes.
Costanzo A, Merlo P, Pediconi N, Fulco M, Sartorelli V, Cole PA, Fontemaggi G, Fanciulli M, Schiltz L, Blandino G, Balsano C, Levrero M
Molecular cell 2002 Jan;9(1):175-86
Molecular cell 2002 Jan;9(1):175-86
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image
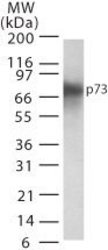
- Experimental details
- WB
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image
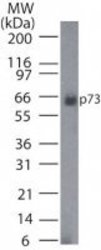
- Experimental details
- WB
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- WB
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn