Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [13]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [5]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-9099-37 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD289 (TLR9) Monoclonal Antibody (eB72-1665), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: eB72-1665 is generated against a portion of human toll-like receptor 9 (aa 273-288), a molecule reported to be expressed predominantly intracellularly. TLR9 is a ~115-120 kDa molecule, which mediates response to unmethylated CpG dinucleotides in bacterial DNA. CpG DNA induces a strong T-helper-1-like inflammatory response and the proliferation of TLR9-positive human B cells. When stimulated with CpG DNA, TLR9-deficient (TLR9-/-) mice lacked splenocyte proliferation, inflammatory cytokine production from macrophages, and dendritic cell maturation, as compared with normal mice. To date, at least twelve members of the Toll family have been identified. This family of type I transmembrane proteins is characterized by an extracellular domain with leucine-rich repeats and a cytoplasmic domain with homology to the type I IL-1 receptor. Members of the TLR family are involved in recognition and response to different microbial components including lipoproteins, peptidoglycans, and nucleic acids and play important roles in innate immunity and inflammation. TLR9 is not detected by flow cytometry using this antibody on lysed whole human blood and/or isolated human PBMC stained for cell surface or intracellular TLR9. This may be due to limitations of antigen detection by flow cytometry. Human pDCs matured in the presence of IL-3 have been reported to stain with eB72-1665 by immunofluorescence microscopy (Nat Immunol. 5:190). Human Epithelial Cell lines were also reported to stain with this mAb (J. Immunol. 173: 1219). Further studies are needed to determine the relationship between mRNA expression and protein detection by flow cytometry. Applications Reported: This eB72-1665 antibody has been reported for use in intracellular flow cytometric analysis, immunoprecipitation, and immunoblotting (WB). (Fluorochrome conjugated eB72-1665 is recommended for use in intracellular flow cytometry.) Preliminary in vitro blocking assays suggested that eB72-1665 may not be effective in blocking of CpG binding. Please contact us for further information. Applications Tested: The eB72-1665 antibody has been tested by intracellular flow cytometric analysis of hTLR9 transfected cells. This can be used at less than or equal to 1 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rat
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- eB72-1665
- Vial size
- 2 mg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references TLR9 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia identifies a promigratory subpopulation and novel therapeutic target.
Human CD40 ligand-expressing type 3 innate lymphoid cells induce IL-10-producing immature transitional regulatory B cells.
Altered Toll-like receptor expression and function in HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma.
ICOS(+) Foxp3(+) TILs in gastric cancer are prognostic markers and effector regulatory T cells associated with Helicobacter pylori.
Toll-like receptor-9 in hypoxic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and its correlation with cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Lactoferrin suppresses the Epstein-Barr virus-induced inflammatory response by interfering with pattern recognition of TLR2 and TLR9.
A consensus surface activation marker signature is partially dependent on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef expression within productively infected macrophages.
Cytoplasmic targeting motifs control localization of toll-like receptor 9.
Activation of TLR-9 induces IL-8 secretion through peroxynitrite signaling in human neutrophils.
Double-stranded RNA-mediated TLR3 activation is enhanced by CD14.
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells express TLR9 and react directly to the CpG-A oligonucleotide D19.
Human lung cancer cells express functionally active Toll-like receptor 9.
TLR9 is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum prior to stimulation.
Kennedy E, Coulter E, Halliwell E, Profitos-Peleja N, Walsby E, Clark B, Phillips EH, Burley TA, Mitchell S, Devereux S, Fegan CD, Jones CI, Johnston R, Chevassut T, Schulz R, Seiffert M, Agathanggelou A, Oldreive C, Davies N, Stankovic T, Liloglou T, Pepper C, Pepper AGS
Blood 2021 Jun 3;137(22):3064-3078
Blood 2021 Jun 3;137(22):3064-3078
Human CD40 ligand-expressing type 3 innate lymphoid cells induce IL-10-producing immature transitional regulatory B cells.
Komlósi ZI, Kovács N, van de Veen W, Kirsch AI, Fahrner HB, Wawrzyniak M, Rebane A, Stanic B, Palomares O, Rückert B, Menz G, Akdis M, Losonczy G, Akdis CA
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2018 Jul;142(1):178-194.e11
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2018 Jul;142(1):178-194.e11
Altered Toll-like receptor expression and function in HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma.
Tobouti PL, Bolt R, Radhakrishnan R, de Sousa SCOM, Hunter KD
Oncotarget 2018 Jan 2;9(1):236-248
Oncotarget 2018 Jan 2;9(1):236-248
ICOS(+) Foxp3(+) TILs in gastric cancer are prognostic markers and effector regulatory T cells associated with Helicobacter pylori.
Nagase H, Takeoka T, Urakawa S, Morimoto-Okazawa A, Kawashima A, Iwahori K, Takiguchi S, Nishikawa H, Sato E, Sakaguchi S, Mori M, Doki Y, Wada H
International journal of cancer 2017 Feb 1;140(3):686-695
International journal of cancer 2017 Feb 1;140(3):686-695
Toll-like receptor-9 in hypoxic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and its correlation with cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Zhang F, Wang D, Chen F
Oncology letters 2017 Dec;14(6):7829-7832
Oncology letters 2017 Dec;14(6):7829-7832
Lactoferrin suppresses the Epstein-Barr virus-induced inflammatory response by interfering with pattern recognition of TLR2 and TLR9.
Zheng Y, Qin Z, Ye Q, Chen P, Wang Z, Yan Q, Luo Z, Liu X, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Ma J, Li G
Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology 2014 Nov;94(11):1188-99
Laboratory investigation; a journal of technical methods and pathology 2014 Nov;94(11):1188-99
A consensus surface activation marker signature is partially dependent on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef expression within productively infected macrophages.
Babu R, Brown A
Retrovirology 2013 Dec 16;10:155
Retrovirology 2013 Dec 16;10:155
Cytoplasmic targeting motifs control localization of toll-like receptor 9.
Leifer CA, Brooks JC, Hoelzer K, Lopez J, Kennedy MN, Mazzoni A, Segal DM
The Journal of biological chemistry 2006 Nov 17;281(46):35585-92
The Journal of biological chemistry 2006 Nov 17;281(46):35585-92
Activation of TLR-9 induces IL-8 secretion through peroxynitrite signaling in human neutrophils.
József L, Khreiss T, El Kebir D, Filep JG
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Jan 15;176(2):1195-202
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Jan 15;176(2):1195-202
Double-stranded RNA-mediated TLR3 activation is enhanced by CD14.
Lee HK, Dunzendorfer S, Soldau K, Tobias PS
Immunity 2006 Feb;24(2):153-63
Immunity 2006 Feb;24(2):153-63
Human monocyte-derived dendritic cells express TLR9 and react directly to the CpG-A oligonucleotide D19.
Hoene V, Peiser M, Wanner R
Journal of leukocyte biology 2006 Dec;80(6):1328-36
Journal of leukocyte biology 2006 Dec;80(6):1328-36
Human lung cancer cells express functionally active Toll-like receptor 9.
Droemann D, Albrecht D, Gerdes J, Ulmer AJ, Branscheid D, Vollmer E, Dalhoff K, Zabel P, Goldmann T
Respiratory research 2005 Jan 4;6(1):1
Respiratory research 2005 Jan 4;6(1):1
TLR9 is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum prior to stimulation.
Leifer CA, Kennedy MN, Mazzoni A, Lee C, Kruhlak MJ, Segal DM
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2004 Jul 15;173(2):1179-83
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2004 Jul 15;173(2):1179-83
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
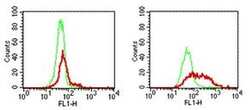
- Experimental details
- HEK 293 parent cells (left panel) and 293/hTLR9 transfected cells (right panel) were fixed and permeabilized and subsequently stained with either Anti-Rat IgG FITC (Product # 11-4811-85) alone (thin line) or with 1 µg of Anti-Human CD289 (TLR9) Purified followed by Anti-Rat IgG FITC (thick line).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
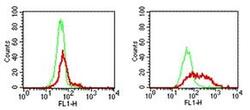
- Experimental details
- HEK 293 parent cells (left panel) and 293/hTLR9 transfected cells (right panel) were fixed and permeabilized and subsequently stained with either Anti-Rat IgG FITC (Product # 11-4811-85) alone (thin line) or with 1 µg of Anti-Human CD289 (TLR9) Purified followed by Anti-Rat IgG FITC (thick line).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
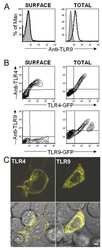
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
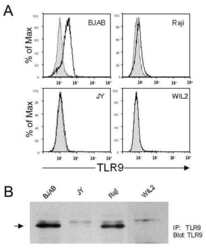
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
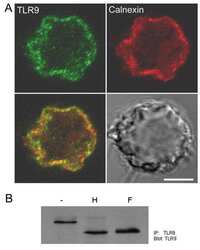
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
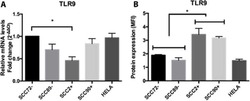
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
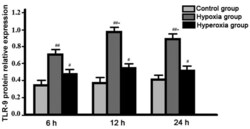
- Experimental details
- Figure 2. Expression levels of Toll-like receptor-9 (TLR-9) protein in each group at different time-points detected by western blot analysis. # Expression level of TLR-9 proetin in hyperoxia group was significantly higher than that in control group at each time-point; ## expression of TLR-9 proten in hypoxia group was significantly higher than that in hyperoxia group at each time-point; *expression level of TLR-9 protein in hypoxia group reached the peak.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry