Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [9]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [3]
- Immunohistochemistry [4]
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [5]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-17057 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Cytokeratin 5 Monoclonal Antibody (2C2)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- MA5-17057 targets CK5 in indirect ELISA, FACS, ICC, IHC, IF and WB applications and shows reactivity with Human, Mouse, and Non-human primate samples. The MA5-17057 immunogen is purified recombinant fragment of human CK5 expressed in E. Coli. MA5-17057 detects CK5 which has a predicted molecular weight of approximately 62.3kDa.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 2C2
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Novel insights linking BRCA1-IRIS role in mammary gland development to formation of aggressive PABCs: the case for longer breastfeeding.
Modelling aggressive prostate cancers of young men in immune-competent mice, driven by isogenic Trp53 alterations and Pten loss.
Excessive Polyamine Generation in Keratinocytes Promotes Self-RNA Sensing by Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis.
Enhanced Tropism of Species B1 Adenoviral-Based Vectors for Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cells.
Lats1 and Lats2 are required for the maintenance of multipotency in the Müllerian duct mesenchyme.
The pro- and anti-tumor roles of mesenchymal stem cells toward BRCA1-IRIS-overexpressing TNBC cells.
Recurrent hotspot mutations in HRAS Q61 and PI3K-AKT pathway genes as drivers of breast adenomyoepitheliomas.
Urothelial cell expansion and differentiation are improved by exposure to hypoxia.
Conditional ablation of TGF-β signaling inhibits tumor progression and invasion in an induced mouse bladder cancer model.
Castillo P, Aisagbonhi O, Saenz CC, ElShamy WM
American journal of cancer research 2022;12(1):396-426
American journal of cancer research 2022;12(1):396-426
Modelling aggressive prostate cancers of young men in immune-competent mice, driven by isogenic Trp53 alterations and Pten loss.
Mejía-Hernández JO, Keam SP, Saleh R, Muntz F, Fox SB, Byrne D, Kogan A, Pang L, Huynh J, Litchfield C, Caramia F, Lozano G, He H, You JM, Sandhu S, Williams SG, Haupt Y, Haupt S
Cell death & disease 2022 Sep 8;13(9):777
Cell death & disease 2022 Sep 8;13(9):777
Excessive Polyamine Generation in Keratinocytes Promotes Self-RNA Sensing by Dendritic Cells in Psoriasis.
Lou F, Sun Y, Xu Z, Niu L, Wang Z, Deng S, Liu Z, Zhou H, Bai J, Yin Q, Cai X, Sun L, Wang H, Li Q, Wu Z, Chen X, Gu J, Shi YL, Tao W, Ginhoux F, Wang H
Immunity 2020 Jul 14;53(1):204-216.e10
Immunity 2020 Jul 14;53(1):204-216.e10
Enhanced Tropism of Species B1 Adenoviral-Based Vectors for Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cells.
Li N, Cooney AL, Zhang W, Ehrhardt A, Sinn PL
Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development 2019 Sep 13;14:228-236
Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development 2019 Sep 13;14:228-236
Lats1 and Lats2 are required for the maintenance of multipotency in the Müllerian duct mesenchyme.
St-Jean G, Tsoi M, Abedini A, Levasseur A, Rico C, Morin M, Djordjevic B, Miinalainen I, Kaarteenaho R, Paquet M, Gévry N, Boyer A, Vanderhyden B, Boerboom D
Development (Cambridge, England) 2019 Oct 18;146(20)
Development (Cambridge, England) 2019 Oct 18;146(20)
The pro- and anti-tumor roles of mesenchymal stem cells toward BRCA1-IRIS-overexpressing TNBC cells.
Ryan D, Paul BT, Koziol J, ElShamy WM
Breast cancer research : BCR 2019 Apr 24;21(1):53
Breast cancer research : BCR 2019 Apr 24;21(1):53
Recurrent hotspot mutations in HRAS Q61 and PI3K-AKT pathway genes as drivers of breast adenomyoepitheliomas.
Geyer FC, Li A, Papanastasiou AD, Smith A, Selenica P, Burke KA, Edelweiss M, Wen HC, Piscuoglio S, Schultheis AM, Martelotto LG, Pareja F, Kumar R, Brandes A, Fan D, Basili T, Da Cruz Paula A, Lozada JR, Blecua P, Muenst S, Jungbluth AA, Foschini MP, Wen HY, Brogi E, Palazzo J, Rubin BP, Ng CKY, Norton L, Varga Z, Ellis IO, Rakha EA, Chandarlapaty S, Weigelt B, Reis-Filho JS
Nature communications 2018 May 8;9(1):1816
Nature communications 2018 May 8;9(1):1816
Urothelial cell expansion and differentiation are improved by exposure to hypoxia.
Chabaud S, Saba I, Baratange C, Boiroux B, Leclerc M, Rousseau A, Bouhout S, Bolduc S
Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine 2017 Nov;11(11):3090-3099
Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine 2017 Nov;11(11):3090-3099
Conditional ablation of TGF-β signaling inhibits tumor progression and invasion in an induced mouse bladder cancer model.
Liang Y, Zhu F, Zhang H, Chen D, Zhang X, Gao Q, Li Y
Scientific reports 2016 Jul 5;6:29479
Scientific reports 2016 Jul 5;6:29479
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
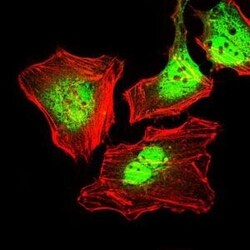
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) (Green). Red: actin filaments have been labeled with phalloidin.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
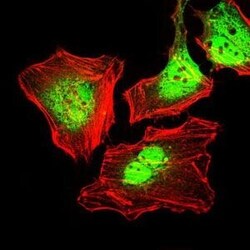
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) (Green). Red: actin filaments have been labeled with phalloidin.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
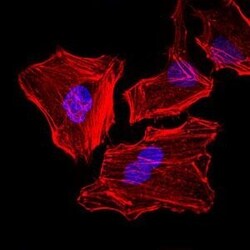
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057). Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye. Red: actin filaments have been labeled with phalloidin.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
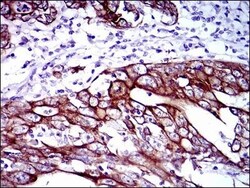
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded stomach cancer tissues using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) followed with DAB staining.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
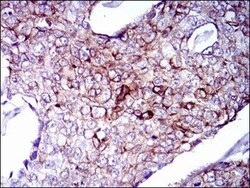
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) followed with DAB staining.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
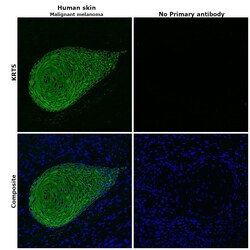
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of KRT5 was performed using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human skin (malignant melanoma) tissue sections. To expose the target protein, heat-induced epitope retrieval was performed on de-paraffinized sections using eBioscience™ IHC Antigen Retrieval Solution - High pH (10X) (Product # 00-4956-58) diluted to 1X solution in water in a decloaking chamber at 110 degree Celsius for 15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval, the sections were blocked with 2% normal goat serum in 1X PBS for 45 minutes at room temperature and then probed with or without Cytokeratin 5 Monoclonal Antibody (2C2) (Product # MA5-17057) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% normal goat serum overnight at 4 degree Celsius in a humidified chamber. Detection was performed using Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32723) at a dilution of 1:2000 in 0.1% normal goat serum for 45 minutes at room temperature. ReadyProbes™ Tissue Autofluorescence Quenching Kit (Product # R37630) was used to quench autofluorescence from the tissues. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Product # D1306) and the sections were mounted using ProLong™ Glass Antifade Mountant (Product # P36984). The images were captured on EVOS™ M7000 Imaging System (Product # AMF7000) at 20X magnification and deconvoluted externally.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
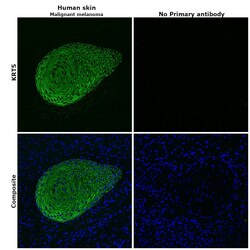
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of KRT5 was performed using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human skin (malignant melanoma) tissue sections. To expose the target protein, heat-induced epitope retrieval was performed on de-paraffinized sections using eBioscience™ IHC Antigen Retrieval Solution - Low pH (10X) (Product # 00-4955-58) diluted to 1X solution in water in a decloaking chamber at 110 degree Celsius for 15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval, the sections were blocked with 2% normal goat serum in 1X PBS for 45 minutes at room temperature and then probed with or without Cytokeratin 5 Monoclonal Antibody (2C2) (Product # MA5-17057) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% normal goat serum overnight at 4 degree Celsius in a humidified chamber. Detection was performed using Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32723) at a dilution of 1:2000 in 0.1% normal goat serum for 45 minutes at room temperature. ReadyProbes™ Tissue Autofluorescence Quenching Kit (Product # R37630) was used to quench autofluorescence from the tissues. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Product # D1306) and the sections were mounted using ProLong™ Glass Antifade Mountant (Product # P36984). The images were captured on EVOS™ M7000 Imaging System (Product # AMF7000) at 20X magnification and deconvoluted externally.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
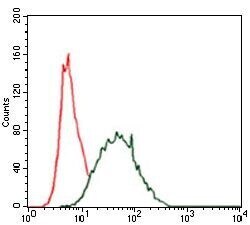
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cells using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) (green) and negative control (red).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
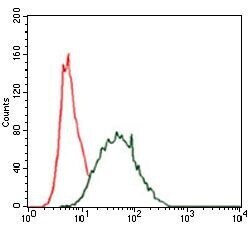
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometric analysis of HeLa cells using CK5 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-17057) (green) and negative control (red).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
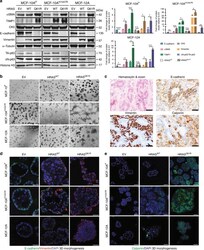
- Experimental details
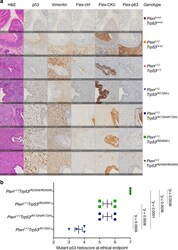
- Fig. 6 Expression of mutant HRAS Q61R results in the acquisition of a partial myoepithelial phenotype in non-malignant breast epithelial cells. a Representative western blot (left) analysis of total protein expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA), TIMP1, cytokeratin 5 (CK5), E-cadherin, vimentin, and nuclear protein expression of N-p63 and TA-p63 in MCF-10A P , MCF-10A H1047R , and MCF-12A cells stably expressing empty vector (EV), HRAS WT , or mutant HRAS Q61R . alpha-Tubulin and Histone H3 were used as protein loading controls for total and nuclear protein expression, respectively. Quantification (right) using LI-COR is shown based on experiments done in triplicate. Comparisons of protein levels were performed between HRAS WT and mutant HRAS Q61R , both relative to EV. Error bars, s.d. of mean ( n = 3). n.s. = not significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001; two-tailed unpaired t -test. b Representative micrographs of cells cultured in three-dimensional basement membrane for 10 days showing the effects of EV, HRAS WT , or mutant HRAS Q61R expression in MCF-10A P , MCF-10A H1047R , and MCF-12A cells on growth and glandular architecture (scale bars, 400 um). c Representative micrographs of E-cadherin, vimentin, and calponin immunohistochemical expression in a HRAS and PIK3CA mutant adenomyoepithelioma (AM32). Note the bi-layered glandular architecture where E-cadherin is preferentially expressed in the inner epithelial layer, whereas viment
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical detection of cancer progression markers in anterior prostate lobes reveals characteristics displayed in aggressive human PC tumours. a Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and serially-matched immunohistochemical staining of sections of anterior prostate (AP) sections at ethical endpoint from mice of indicated genotype with antibodies against p53, vimentin, CK5 and p63. Flex-negative corresponds to CK5 and p63 immunohistochemical staining control. IHC staining was performed in >6 mice per genotype. Scale bar equivalent to 100 um. b p53 staining intensity ranged from 0 (minimum) to 3 (maximum), whereas the proportion of cells stained was evaluated on a scale of 0 to 4 ((1) 80%). Scores were summed to a final possible maximum histoscore of 7. p -values resulting from of statistical comparison of genotypes using ANOVA and Tukey's tests. Error bars indicate mean +- SEM ( n = 4 mice per genotype).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
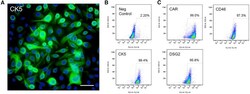
- Figure 6 Basal Cell Markers and Ad Receptor Expression in Primary Human Airway Basal Cells (A and B) Immunohistochemistry (A) or flow cytometry (B) was used to visualize cytokeratin (CK5) in primary basal cells. Scale bar, 50 mum. (C) Flow cytometry was used to quantify CAR, DSG2, and CD46 in primary basal cells.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry