Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [1]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [4]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-51640 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant protein fragment
- Description
- Immunogen sequence: KDNEQHVFKV KDMENLEDVF YQMIDESQSL SLCGMVWEHR KGTDYHKQPW QAKISVIRPS KGHESCMGAV VSEYFVLTAA HCFTVDDKEH SIKVSVGGEK RDLEIEVVLF HPNYNINGKK EAGIPEFYDY DVALIKLKNK LKYG Highest antigen sequence identity to the following orthologs: Mouse - 86%, Rat - 81%.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.10 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Challenge of Bovine Foot Skin Fibroblasts With Digital Dermatitis Treponemes Identifies Distinct Pathogenic Mechanisms.
Newbrook K, Carter SD, Crosby-Durrani H, Evans NJ
Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2020;10:538591
Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2020;10:538591
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
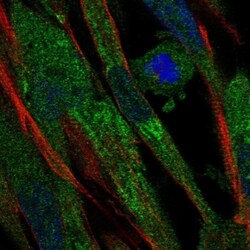
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of Complement Factor B in human cell line ASC TERT1 using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows localization to endoplasmic reticulum.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
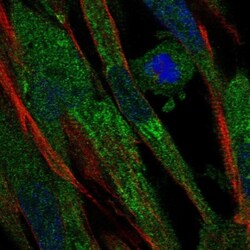
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of Complement Factor B in human cell line ASC TERT1 using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows localization to endoplasmic reticulum.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
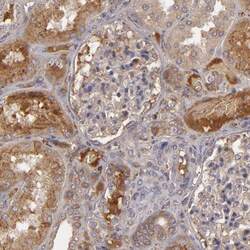
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of Complement Factor B in human kidney using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows moderate positivity in secretion surrounding cells in tubules.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
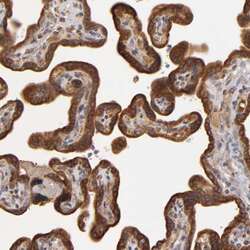
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of Complement Factor B in human placenta using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows strong positivity in trophoblastic cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
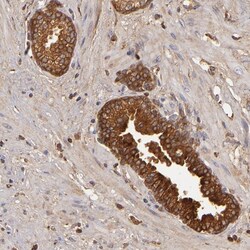
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of Complement Factor B in human prostate using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows strong cytoplasmic positivity in glandular cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
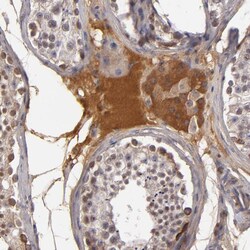
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of Complement Factor B in human testis using Complement Factor B Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-51640) shows moderate cytoplasmic positivity in Leydig cells.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
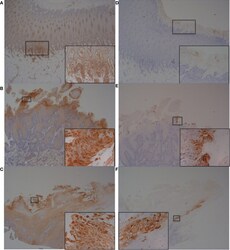
- Experimental details
- Figure 7 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of CFB and RND1 on bovine foot skin from the site of BDD lesions. Low power images accompanied with high power inserts. Images shown are representatives of three independent experimental replicates (n = 3) for each tissue lesion type (no BDD, acute BDD, chronic BDD). (A-C) IHC for CFB. (A) No BDD. Labeling of lymphocytes and plasma cells at the dermal-epidermal junction (x20), with insert confirming identification of labeled mononuclear cells (x100). (B) Acute BDD. Intense labeling of the most superficial keratinocytes (x20), with insert showing intense cytoplasmic and membranous labeling of the most superficial keratinocytes (xx400). (C) Chronic BDD lesion (x20, x400) exhibiting similar findings to (B) . (D-F) IHC for RND1. (D) No BDD. Multifocally, the stratum corneum has granular background labeling of the stratum corneum keratinocytes (x20, x100). (E) Acute BDD. Multifocally, there are intensely labeled keratinocytes near to ulcerated regions (x20), with insert highlighting view of intense labeling (x400). (F) Chronic BDD. Multifocal mild granular labeling of the stratum corneum keratinocytes similar to (D) ; however, note most of the thickened stratum corneum is not labeled (20). Insert shows background labeling of some stratum corneum keratinocytes (400).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
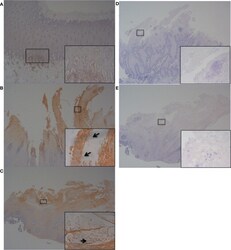
- Experimental details
- Figure 8 Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of IL-6 on bovine foot skin tissue from the site of BDD lesions. Low power images accompanied with high power inserts. Images shown are representatives of three independent experimental replicates (n = 3) for each tissue lesion type (no BDD, acute BDD, chronic BDD). (A-C) IHC for IL-6. (A) No BDD. Lymphocytes and plasma cells at the dermal-epidermal junction are intensely labelled (x20, x100). (B) Acute BDD. Positive labeling of the stratum corneum and some stratum spinosum keratinocytes (x40), with insert showing intense labeling of spirochaetal structures (x400). Arrow denotes labeling showing similar morphology and location to that observed with DD treponeme IHC ( Figure S4E ) (C) Chronic BDD lesion (x20, x400) exhibiting similar findings to (B) . Arrow denotes labeling showing similar morphology and location to that observed with DD treponeme IHC ( Figure S4F ). (D-E) IL-6 negative antibody (no primary antibody) control. (D) Acute BDD (x20, x400). (E) Chronic BDD (x20, x400).
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry