Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [2]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-6496-95 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Actin (muscle) Monoclonal Antibody (HHF35), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The monoclonal antibody HHF35 recognizes muscle actin; specifically the alpha and gamma form found in skeletal cardiac, and smooth muscle. No reactivity to the beta form is observed. The 42 kDa protein is a main component of the cytoskeletal structural network. The HHF35 antibody has been shown to recognize actin from smooth muscle cells of the heart, bladder, uterus, gastrointestinal tract, and diaphragm. The antibody stains tumors of muscle origin such as leiomyomas, leiosarcomes and rhabdomyosacromas.
- Antibody clone number
- HHF35
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
Submitted references Restoration of Corneal Transparency by Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
Morphological characterisation of portal myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells in the normal dog liver.
Mittal SK, Omoto M, Amouzegar A, Sahu A, Rezazadeh A, Katikireddy KR, Shah DI, Sahu SK, Chauhan SK
Stem cell reports 2016 Oct 11;7(4):583-590
Stem cell reports 2016 Oct 11;7(4):583-590
Morphological characterisation of portal myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells in the normal dog liver.
Ijzer J, Roskams T, Molenbeek RF, Ultee T, Penning LC, Rothuizen J, van den Ingh TS
Comparative hepatology 2006 Nov 16;5:7
Comparative hepatology 2006 Nov 16;5:7
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
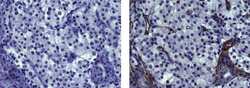
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed paraffin embedded human pancreas using 10 µg/mL of Mouse IgG1 Isotype Control Purified (Product # 14-4714-82) (left) or 10 µg/mL Anti-Actin (muscle) Purified (right) followed by biotinylated Anti-Mouse IgG, and DAB visualization.Nuclei are counterstained with hematoxylin.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
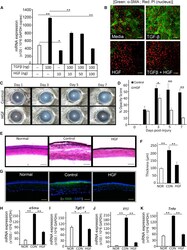
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 HGF Alone Is Sufficient to Inhibit Corneal Opacity and Inflammation (A and B) A corneal fibroblast cell line (MK/T1) was stimulated with TGF-beta1 in the presence or absence of HGF for 24 hr. alpha-SMA expression was assessed (A) at mRNA level using real-time PCR and (B) at protein level by immunohistochemistry. The values shown are the mean +- SD of three independent experiments. (C-K) Corneal injury was induced by mechanical removal of corneal epithelium and anterior stroma in C57BL/6 mice. Thereafter, 5 muL of 0.1% murine recombinant HGF in PBS per eye was applied topically to the injured eye twice a day up to 7 days after injury. A control group received a similar dosage of mouse serum albumin. At days 1, 3, 5, and 7 post injury, bright-field photographs of injured corneas were captured to evaluate corneal opacity using slit-lamp biomicroscopy. Representative bright-field images of injured corneas (C) were quantitated using Image J software to assess corneal opacity scores (D). Corneas were harvested at 7 days post injury. Cross-sections were stained with H&E to visualize corneal tissue structure and infiltration of inflammatory cells (E), and measure corneal tissue thickness (F). For immunocytochemistry analysis (G), cross-sections were immunostained with the fibrosis marker alpha-SMA (green). In addition, harvested corneas were analyzed for their mRNA expression of (H) alpha-Sma , (I) Tgf-beta1 , (J) Il-1beta , and (K) Tnf-alpha using real-time PCR. The values
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
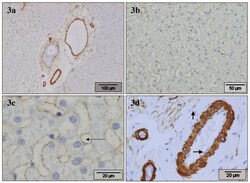
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 alpha-SMA . Normal canine liver, stained with alpha-SMA antibody. a) Portal areas show positivity around the bile ducts, in the arterial tunica media, and in the wall of the portal veins. There is slightly irregular moderate staining in the perisinusoidal spaces throughout the parenchyma. b) HSC stain positive, producing a thin irregular positive band lining the sinusoids. c) HSC stain positive. A positive cell containing one large vacuole (arrow-head is placed in vacuole) and a dislocated nucleus is seen. d) In the portal area there is strong positivity around the bile ducts and in the arterial tunica media, and moderate positivity in the wall of the portal veins, while endothelial cells remain negative (horizontal arrow). A portal MF with moderate positivity (vertical arrow) is present.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry