Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [3]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [3]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-16887 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- eNOS Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- PA5-16887 targets eNOS in immunohistochemistry (paraffin) applications and shows reactivity with Bovine, Canine, Human, mouse, Porcine, and Rat samples. Suggested positive control is capillary endothelium and regenerative endothelium. The PA5-16887 immunogen is a synthetic peptide derived from C-ternimal of human eNOS.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 500 μL
- Concentration
- 0.081 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Mechanically reinforced biotubes for arterial replacement and arteriovenous grafting inspired by architectural engineering.
Targeted Repair of Vascular Injury by Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Modified with P-Selectin Binding Peptide.
Telomerase reverse transcriptase protects against angiotensin II-induced microvascular endothelial dysfunction.
Zhi D, Cheng Q, Midgley AC, Zhang Q, Wei T, Li Y, Wang T, Ma T, Rafique M, Xia S, Cao Y, Li Y, Li J, Che Y, Zhu M, Wang K, Kong D
Science advances 2022 Mar 18;8(11):eabl3888
Science advances 2022 Mar 18;8(11):eabl3888
Targeted Repair of Vascular Injury by Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Modified with P-Selectin Binding Peptide.
Yan H, Mi X, Midgley AC, Du X, Huang Z, Wei T, Liu R, Ma T, Zhi D, Zhu D, Wang T, Feng G, Zhao Y, Zhang W, He J, Zhu M, Kong D, Wang K
Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2020 Jun;7(11):1903516
Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2020 Jun;7(11):1903516
Telomerase reverse transcriptase protects against angiotensin II-induced microvascular endothelial dysfunction.
Ait-Aissa K, Kadlec AO, Hockenberry J, Gutterman DD, Beyer AM
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2018 May 1;314(5):H1053-H1060
American journal of physiology. Heart and circulatory physiology 2018 May 1;314(5):H1053-H1060
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
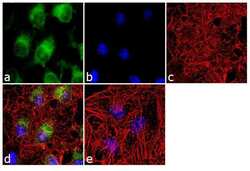
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of eNOS was done on 70% confluent log phase HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with eNOS Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-16887) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d is a merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
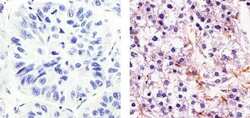
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of eNOS showing weak staining in the cytoplasm of paraffin-embedded human hepatocarcinoma (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a eNOS Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-16887) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 for 1 hour at 37°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
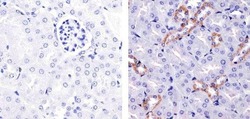
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis of eNOS showing staining in the cytoplasm of paraffin-embedded mouse kidney tissue (right) compared to a negative control without primary antibody (left). To expose target proteins, antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min. Following antigen retrieval, tissues were blocked in 3% H2O2-methanol for 15 min at room temperature, washed with ddH2O and PBS, and then probed with a eNOS Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA5-16887) diluted in 3% BSA-PBS at a dilution of 1:20 for 1 hour at 37°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively in PBST and detection was performed using an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody followed by colorimetric detection using a DAB kit. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and dehydrated with ethanol and xylene to prep for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
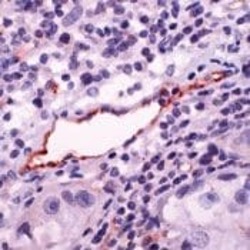
- Experimental details
- Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human Lung Ca stained with eNOS antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and AEC. Note staining of endothelium of vessel.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
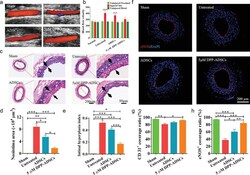
- Figure 4 The effect of DPP-ADSCs treatment on reparation of injured arteries after 21 days. The a) patency and b) blood flow of injured arteries in sham, untreated, ADSCs injection. and 5 x 10 -6 m DPP-ADSCs injection groups was measured by color Doppler ultrasound. c) VVG staining of cross sections of injured arteries with different treatment. The d) neointima area and e) intimal hyperplasia index were calculated based on the VVG staining to reflect the histopathological characteristics of injured arteries in the different treatment groups. f) Refunctional endothelialization of injured arteries was analyzed by immunofluorescence staining with anti-eNOS. The quantitative analysis of g) CD31-positive and h) eNOS-positive endothelial coverage rate based on merge images at 21 days. All data are representative of ( n = 5) animals per group.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
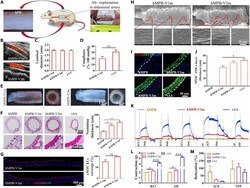
- Fig. 2. Evaluation of the potential of hMPB as autologous grafts in rAA replacement model. ( A ) Subcutaneously prepared hPBs were used as autologous abdominal artery replacements in rats. ( B ) CDU images of hMPB-V1m and hMPB-V3m and ( C ) corresponding measurement of luminal diameter. ( D ) Quantification of in vivo compliance of implanted hMPB and rAA. ( E ) Lumen and enface views of hMPB-V1m and hMPB-V3m. ( F ) H&E images of hMPB-V1m, hMPB-V3m, and rAA cross sections; quantification of hMPB neointima thickness shown alongside. Black dashed lines represent PS wall boundary (hMPB, hMPB-V1m, and hMPB-V3m) or boundary between tunicae media and adventitia layers (rAA). ( G ) EC coverage was visualized and calculated on the basis of anti-eNOS IF staining of hMPB longitudinal sections before and after VI. ( H ) EC coverage of lumen surfaces of hMPB-V1m and hMPB-V3m observed by SEM. ( I ) Co-stained cross sections show the distribution of ECs (eNOS, red) and SMCs (MYH, green) in hMPB-V1m, hMPB-V3m, and rAA. White dashed lines represent PS wall boundary (hMPB, hMPB-V1m, and hMPB-V3m) or the boundary between tunicae media and adventitia layers (rAA). ( J ) MYH + SMC layer thickness calculated from eNOS/MYH co-staining. ( K ) Representative curves of physiological functions of hMPB, hMPB-V3m, and rAA in response to vasodilators and vasoconstrictors. ( L ) Quantification of constriction in response to KCl and AD; ( M ) Quantification of relaxation in response to ACh and SNP. Samples
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry