Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [19]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [16]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 33-0800 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- RANGAP1 Monoclonal Antibody (19C7)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 19C7
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references MORC3, a Component of PML Nuclear Bodies, Has a Role in Restricting Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Human Cytomegalovirus.
Analysis of the SUMO2 Proteome during HSV-1 Infection.
The SUMO proteases SENP1 and SENP2 play a critical role in nucleoporin homeostasis and nuclear pore complex function.
A pathway linking oxidative stress and the Ran GTPase system in progeria.
Down-modulation of nucleoporin RanBP2/Nup358 impaired chromosomal alignment and induced mitotic catastrophe.
Ubiquitylation-dependent localization of PLK1 in mitosis.
The interaction between importin-α and Nup153 promotes importin-α/β-mediated nuclear import.
Localization of Pom121 to the inner nuclear membrane is required for an early step of interphase nuclear pore complex assembly.
Detection of protein SUMOylation in vivo.
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is a key component of the SUMO-2/3 cycle.
Distinct and overlapping sets of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2 target proteins revealed by quantitative proteomics.
NXP-2 association with SUMO-2 depends on lysines required for transcriptional repression.
Mutation of SENP1/SuPr-2 reveals an essential role for desumoylation in mouse development.
A universal strategy for proteomic studies of SUMO and other ubiquitin-like modifiers.
Association of the human SUMO-1 protease SENP2 with the nuclear pore.
SUMO-1 targets RanGAP1 to kinetochores and mitotic spindles.
Perturbation of SUMOlation enzyme Ubc9 by distinct domain within nucleoporin RanBP2/Nup358.
Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3.
Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3.
Sloan E, Orr A, Everett RD
Journal of virology 2016 Oct 1;90(19):8621-33
Journal of virology 2016 Oct 1;90(19):8621-33
Analysis of the SUMO2 Proteome during HSV-1 Infection.
Sloan E, Tatham MH, Groslambert M, Glass M, Orr A, Hay RT, Everett RD
PLoS pathogens 2015 Jul;11(7):e1005059
PLoS pathogens 2015 Jul;11(7):e1005059
The SUMO proteases SENP1 and SENP2 play a critical role in nucleoporin homeostasis and nuclear pore complex function.
Chow KH, Elgort S, Dasso M, Powers MA, Ullman KS
Molecular biology of the cell 2014 Jan;25(1):160-8
Molecular biology of the cell 2014 Jan;25(1):160-8
A pathway linking oxidative stress and the Ran GTPase system in progeria.
Datta S, Snow CJ, Paschal BM
Molecular biology of the cell 2014 Apr;25(8):1202-15
Molecular biology of the cell 2014 Apr;25(8):1202-15
Down-modulation of nucleoporin RanBP2/Nup358 impaired chromosomal alignment and induced mitotic catastrophe.
Hashizume C, Kobayashi A, Wong RW
Cell death & disease 2013 Oct 10;4(10):e854
Cell death & disease 2013 Oct 10;4(10):e854
Ubiquitylation-dependent localization of PLK1 in mitosis.
Beck J, Maerki S, Posch M, Metzger T, Persaud A, Scheel H, Hofmann K, Rotin D, Pedrioli P, Swedlow JR, Peter M, Sumara I
Nature cell biology 2013 Apr;15(4):430-9
Nature cell biology 2013 Apr;15(4):430-9
The interaction between importin-α and Nup153 promotes importin-α/β-mediated nuclear import.
Ogawa Y, Miyamoto Y, Oka M, Yoneda Y
Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 2012 Jul;13(7):934-46
Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark) 2012 Jul;13(7):934-46
Localization of Pom121 to the inner nuclear membrane is required for an early step of interphase nuclear pore complex assembly.
Funakoshi T, Clever M, Watanabe A, Imamoto N
Molecular biology of the cell 2011 Apr;22(7):1058-69
Molecular biology of the cell 2011 Apr;22(7):1058-69
Detection of protein SUMOylation in vivo.
Tatham MH, Rodriguez MS, Xirodimas DP, Hay RT
Nature protocols 2009;4(9):1363-71
Nature protocols 2009;4(9):1363-71
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is a key component of the SUMO-2/3 cycle.
Schimmel J, Larsen KM, Matic I, van Hagen M, Cox J, Mann M, Andersen JS, Vertegaal AC
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2008 Nov;7(11):2107-22
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2008 Nov;7(11):2107-22
Distinct and overlapping sets of SUMO-1 and SUMO-2 target proteins revealed by quantitative proteomics.
Vertegaal AC, Andersen JS, Ogg SC, Hay RT, Mann M, Lamond AI
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2006 Dec;5(12):2298-310
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2006 Dec;5(12):2298-310
NXP-2 association with SUMO-2 depends on lysines required for transcriptional repression.
Rosendorff A, Sakakibara S, Lu S, Kieff E, Xuan Y, DiBacco A, Shi Y, Shi Y, Gill G
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2006 Apr 4;103(14):5308-13
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2006 Apr 4;103(14):5308-13
Mutation of SENP1/SuPr-2 reveals an essential role for desumoylation in mouse development.
Yamaguchi T, Sharma P, Athanasiou M, Kumar A, Yamada S, Kuehn MR
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Jun;25(12):5171-82
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Jun;25(12):5171-82
A universal strategy for proteomic studies of SUMO and other ubiquitin-like modifiers.
Rosas-Acosta G, Russell WK, Deyrieux A, Russell DH, Wilson VG
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2005 Jan;4(1):56-72
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2005 Jan;4(1):56-72
Association of the human SUMO-1 protease SENP2 with the nuclear pore.
Hang J, Dasso M
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 May 31;277(22):19961-6
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 May 31;277(22):19961-6
SUMO-1 targets RanGAP1 to kinetochores and mitotic spindles.
Joseph J, Tan SH, Karpova TS, McNally JG, Dasso M
The Journal of cell biology 2002 Feb 18;156(4):595-602
The Journal of cell biology 2002 Feb 18;156(4):595-602
Perturbation of SUMOlation enzyme Ubc9 by distinct domain within nucleoporin RanBP2/Nup358.
Saitoh H, Pizzi MD, Wang J
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4755-63
The Journal of biological chemistry 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4755-63
Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3.
Saitoh H, Hinchey J
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6252-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6252-8
Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3.
Saitoh H, Hinchey J
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6252-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 2000 Mar 3;275(9):6252-8
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
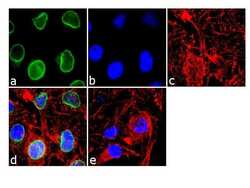
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of RanGAP-1 was done on 70% confluent log phase HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with RanGAP-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 33-0800) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d is a merged image showing Nuclear membrane localization. Panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
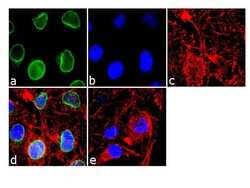
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of RanGAP-1 was done on 70% confluent log phase HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with RanGAP-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 33-0800) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d is a merged image showing Nuclear membrane localization. Panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
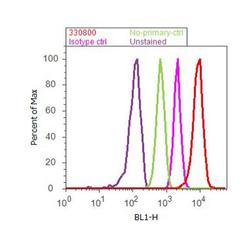
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of RanGAP-1 was done on Jurkat cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with RanGAP-1 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (330800, red histogram) or with mouse isotype control (pink histogram) at 3-5 ug/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (A11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
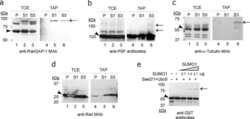
- FIGURE 4: Localization of the transmembrane proteins POM121 and Sun1 is not dependent on SENP1/2 levels, nor is interphase expansion of the nuclear envelope. (A) Control (siControl) or SENP1+2 (siSP1+2)-depleted HeLa cells were subjected to immunofluorescence analysis using antibodies against RanGAP1 and SUN1. (B) A set of similarly treated samples was probed with antibodies specific for Nup62 and Pom121. (C) Cells transfected with siRNA oligo(s) were incubated with 2 mM thymidine for 48 h before immunofluorescence analysis of Nup62 and Pom121. Bar, 10 mum.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
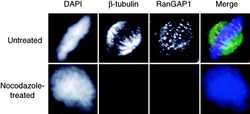
- Experimental details
- Figure 1. RanGAP1 localizes to spindles in a microtubule-dependent manner. HeLa cells were untreated or treated with 2 muM nocodazole for 2 h and then permeabilized with digitonin and fixed in formaldehyde. The cells were stained for beta-tubulin (green) and RanGAP1 (red) using specific antibodies and counterstained with DAPI (blue) for DNA.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
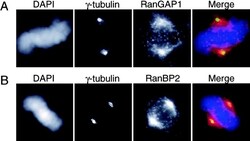
- Experimental details
- Figure 2. RanGAP1 does not localize at the immediate vicinity of spindle poles. HeLa cells were stained with either anti-RanGAP1 or anti-RanBP2 and anti-gamma-tubulin antibodies after permeabilization and fixation to observe the localization of these proteins at spindle poles. (A) gamma-Tubulin (green) and RanGAP1 (red), as recognized by corresponding antibodies. (B) gamma-Tubulin (green), RanBP2 (red), and DNA were visualized by staining with DAPI (blue).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
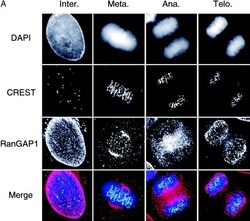
- Experimental details
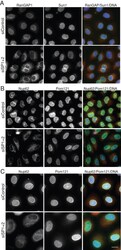
- Figure 3. RanGAP1 localization through mitosis. Deconvolution images of HeLa cells at different stages of mitosis were taken and processed. The cells were stained with DAPI (blue), CREST sera (green), and anti-RanGAP1 antibodies (red). (A) Projection images constructed from the optical sections of cells at different stages of mitosis. (B) Model generated using the Imaris/Surpass software package showing the association of RanGAP1 with the spindle in a metaphase cell. RanGAP1 associated with spindle body is indicated with arrows. Arrowheads indicate kinetochore-associated RanGAP1.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
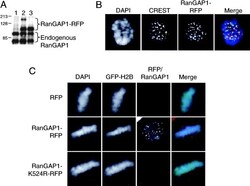
- Experimental details
- Figure 4. SUMO-1 conjugation targets RanGAP1 to the spindle during mitosis. (A) Whole cell extracts from HeLa cells transfected with pDsRed1-N1 (lane 1), pDsRed1-RanGAP1-WT (lane 2), and pDsRed1-RanGAP1-K524R (lane 3) were analyzed by Western blot using polyclonal anti-RanGAP1 antibodies. (B) A mitotic cell showing the localization pattern of RanGAP1-RFP (red) and CREST staining (green). DNA is stained using DAPI (blue). Note that RanGAP1-RFP localization is similar to untagged endogenous RanGAP1 ( Figs. 1 and 2 ). (C) HeLa cells were transfected with pDsRed1-N1 (RFP) or pDsRed1-RanGAP1-WT (RanGAP1-RFP) or pDsRed1-RanGAP1-K524R (RanGAP1-K524R-RFP). pBOS-H2BGFP (GFP-H2B) was used as a transfection marker ( Kanda et al., 1998 ). Cells were permeabilized, fixed, and stained for DNA using DAPI (blue) and observed for GFP-H2B (green) and RanGAP1-RFP (red). Note that RFP and RanGAP1-K524R-RFP do not show any specific signal on spindle or kinetochores. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with pDsRed1-RanGAP1-WT (top) and pDsRed1-RanGAP1-K524R (bottom) and fixed without digitonin permeabilization. Immunofluorescence was performed with anti-beta-tubulin antibody (green) and the cells were stained with DAPI (blue). Mutant and wild-type RanGAP1-RFP are shown in red. Note that cells expressing RanGAP1-RFP show distinct dots of RanGAP1 near the positive ends of microtubules, but these foci are absent in RanGAP1-RFP-K524R-transfected cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
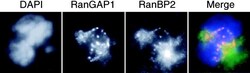
- Figure 5. RanBP2 colocalizes with RanGAP1 in mitosis. HeLa cells were stained with DAPI (blue), anti-RanBP2 (green), and anti-RanGAP1 (red). Note the strong staining of spindle poles by anti-RanBP2 antibodies but not by anti-RanGAP1.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
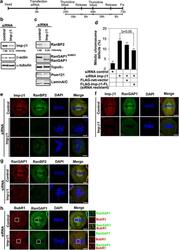
- Figure 2 Importin beta 1 siRNA treatment reduces RanBP2 and causes abnormal chromosomal congression and defective mitosis. ( a ) Schedule of fixing or collecting mitotic HeLa cells after siRNA Imp- beta 1 depletion. ( b ) Lysates of mitotic HeLa cells transfected with control or Imp- beta 1 siRNAs were analyzed 72 h later by IB with anti-Imp- beta 1 antibody. The same membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti- beta -actin and anti- alpha -tubulin (as loading control). ( c ) Effects of Imp- beta 1 depletion on the protein levels of RanBP2-associated proteins. The same membranes as in ( b ) were analyzed by IB with the indicated antibodies. RanBP2 was significantly reduced in the Imp- beta 1-depleted lysates, whereas TopoII alpha , Pom121 and Lamin A/C were not affected. ( d ) Quantification (relative percentage) of mitotic chromosomal defect phenotypes for the indicated siRNA and/or plasmid. Values are based on three independent experiments, counting 100 mitotic cells in each experiment. Mean values+-S.D. (error bars) are shown. All cells were treated with double thymidine block, stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) and visualized by confocal microscopy. ( e ) Confocal microscopic images of mitotic HeLa cells transfected with control or Imp- beta 1 siRNA and analyzed 72 h post-transfection; the cells were stained with anti-RanBP2 (green) and anti-Imp- beta 1 (red) antibodies and DAPI (blue). ( f - h ) Representative confocal microscopic images were stained
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
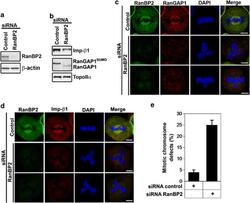
- Figure 3 RanBP2 siRNA treatment reduces importin beta 1 and causes abnormal chromosomal congression and defective mitosis. ( a ) Lysates of mitotic HeLa cells transfected with control or RanBP2 siRNAs were analyzed 72 h post transfection by IB with anti-RanBP2 antibody. The same membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti- beta -actin (as a loading control). ( b ) Effects of RanBP2 depletion on the protein levels of RanBP2-associated proteins. The same membranes as in panel ( a ) were analyzed by IB with the indicated antibodies. ( c and d ) Confocal microscopic images of mitotic HeLa cells transfected with control or RanBP2 siRNAs. At 72 h post transfection, the cells were stained with RanBP2 (green) antibody and anti-RanGAP1 (red) or Imp- beta 1 (red) antibodies and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Bar=5 mu m. ( e ) Quantification (relative percentage) of mitotic chromosomal defect phenotypes in cells transfected with control siRNA or RanBP2 siRNA. Values are based on three independent experiments, counting 100 mitotic cells in each experiment. Mean values+-S.D. (error bars) are shown. All cells were treated with double thymidine block, stained with DAPI and visualized by confocal microscopy
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
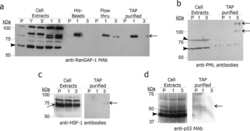
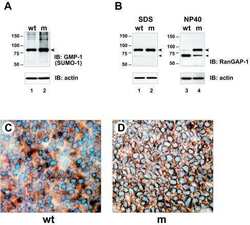
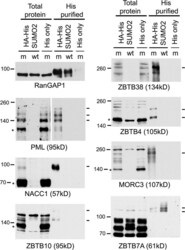
- Fig 6 Confirmation that selected proteins of interest are present in His-SUMO2 purified samples and change in abundance during HSV-1 infection. Total and purified protein fractions from mock (m) and wt HSV-1 (wt; MOI 10 12 h p.i.) infected HA-HisSUMO2 cells were analyzed by western blot, with uninfected HA-His only total protein and purified fractions included as controls. Mock infected and infected samples are indicated by m and wt respectively. Probable sumoylated species of PML, NACC1, ZBTB10, ZBTB38, ZBTB4 and MORC3 were detected in the uninfected purified samples (indicated by dashes on the right of each panel), and were reduced in abundance during HSV-1 infection. ZBTB7A exhibited apparently increased SUMO2-modification in the infected purified fraction. RanGAP1 was used as an unchanged control for SUMO2-modification following HSV-1 infection. The predicted unmodified molecular weight of each protein is indicated in each panel, and where clear the likely major unmodified form is marked by an asterisk. For PML, this refers to the major isoforms PML.I and PML.II.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
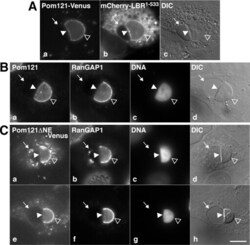
- FIGURE 7: Pom121 localizes to the INM. (A) Live imaging of full-length Pom121 1-1249 -Venus, transiently expressed in U2OS cells. Images were captured 14 h postcotransfection with Pom121-Venus and mCherry-LBR 1-533 . (B) His-tagged LBR 1-533 was transfected into U2OS cells, and 14 h after transfection cells were fixed, immunostained with antibodies raised against Pom121 and RanGAP1, and counterstained with DAPI. (C) Venus-tagged Pom121 1-1249 DeltaNE and mCherry-LBR 1-533 (unpublished data) were cotransfected into U2OS cells, which were then immunostained with an antibody raised against RanGAP1 and counterstained with DAPI (as in B). Note the separation of the INM (arrowhead) and ONM (arrow). Pom121 1-1249 -Venus and endogenous Pom121 were both detected at the intact NE (open arrowhead) and the separated INM (arrowhead), whereas RanGAP was detected only at the intact NE. Pom121 1-1249 DeltaNE-Venus localized to the INM, but at reduced levels. Bar, 10 mum.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
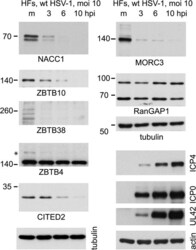
- Fig 7 Time course of degradation of selected proteins of interest during wt HSV-1 infection. HFs were infected with wt HSV-1 (MOI 10) then samples harvested at 3, 6 and 10 h after infection were analyzed by western blot for the indicated proteins. For ZBTB4, the asterisk marks a potentially sumoylated species that decreases in abundance during infection. The panels on the lower right of the figure show the analysis of selected viral proteins in these samples.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
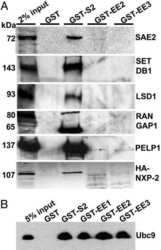
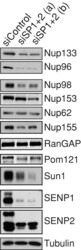
- FIGURE 5: Reduced expression of SENP1 and SENP2 results in lower levels of specific nucleoporins. Cells treated with independent siRNA oligo sets against SENP1+2 or control oligo were subjected to Western analysis using antibodies that recognize the protein indicated.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry