Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [13]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA1-825 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- C/EBP alpha Monoclonal Antibody (15C8)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- MA1-825 detects C/EBP alpha protein in human, mouse and rat samples. MA1-825 has successfully been used in Western blot and immunoprecipitation procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects a 45 kDa protein representing C/EBP alpha in transfected hu293T cells. MA1-825 is specific to the amino terminal region of C/EBP alpha. The MA1-825 immunogen is a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues M(1) E S A D F Y E V E P R P P(14) of mouse C/EBP alpha. This peptide (Cat. # PEP-242) is available for use in neutralization and control experiments.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 15C8
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Antiobesity and antidiabetic effects of the dairy bacterium Propionibacterium freudenreichii MJ2 in high-fat diet-induced obese mice by modulating lipid metabolism.
The histone methyltransferase Suv39h regulates 3T3-L1 adipogenesis.
Nucleolar retention of a translational C/EBPalpha isoform stimulates rDNA transcription and cell size.
C/EBPalpha or C/EBPalpha oncoproteins regulate the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways by direct interaction with NF-kappaB p50 bound to the bcl-2 and FLIP gene promoters.
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) and C/EBPalpha myeloid oncoproteins induce bcl-2 via interaction of their basic regions with nuclear factor-kappaB p50.
An M, Park YH, Lim YH
Scientific reports 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2481
Scientific reports 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2481
The histone methyltransferase Suv39h regulates 3T3-L1 adipogenesis.
Jing J, Li F, Zha L, Yang X, Wu R, Wang S, Xue B, Shi H
Adipocyte 2020 Dec;9(1):401-414
Adipocyte 2020 Dec;9(1):401-414
Nucleolar retention of a translational C/EBPalpha isoform stimulates rDNA transcription and cell size.
Müller C, Bremer A, Schreiber S, Eichwald S, Calkhoven CF
The EMBO journal 2010 Mar 3;29(5):897-909
The EMBO journal 2010 Mar 3;29(5):897-909
C/EBPalpha or C/EBPalpha oncoproteins regulate the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways by direct interaction with NF-kappaB p50 bound to the bcl-2 and FLIP gene promoters.
Paz-Priel I, Ghosal AK, Kowalski J, Friedman AD
Leukemia 2009 Feb;23(2):365-74
Leukemia 2009 Feb;23(2):365-74
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) and C/EBPalpha myeloid oncoproteins induce bcl-2 via interaction of their basic regions with nuclear factor-kappaB p50.
Paz-Priel I, Cai DH, Wang D, Kowalski J, Blackford A, Liu H, Heckman CA, Gombart AF, Koeffler HP, Boxer LM, Friedman AD
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2005 Oct;3(10):585-96
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2005 Oct;3(10):585-96
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
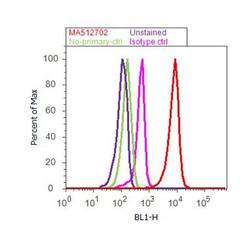
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of CEBP alpha was done on THP-1 cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with CEBP alpha Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (MA1825, red histogram) or with mouse isotype control (pink histogram) at 3-5 ug/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (A11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
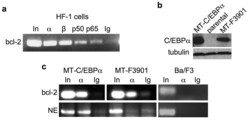
- Experimental details
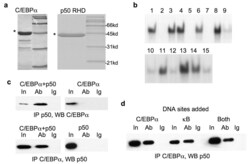
- Figure 1 C/EBPalpha and a C/EBPalphaLZ oncoprotein bind the endogenous bcl-2 promoter ( a ) HF-1 cells were subjected to ChIP analysis using antisera against C/EBPalpha (alpha), C/EBPbeta (beta), NF-kappaB p50, NF-kappaB p65, or IgG control. PCR products were subjected to agarose gel electropheresis and visualized using ethidium bromide. In - input, 1% of DNA used for ChIP. ( b ) Total cellular proteins from Ba/F3 lines expressing the indicated MT-C/EBPalpha isoform or from parental cells were subjected to Western blotting using C/EBPalpha and beta-tubulin antisera. ( c ) Ba/F3 cells expressing MT-C/EBPalpha or MT-F3901, or parental Ba/F3 cells, were cultured with zinc chloride for 16 hours and subjected to ChIP analysis. After immunoprecipitation with antiserum against C/EBPalpha (alpha) or rabbit IgG, the precipitated DNAs were subjected to PCR for the bcl-2 or neutrophil elastase (NE) promoters, as indicated. Data representative of 3 independent experiments is shown.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
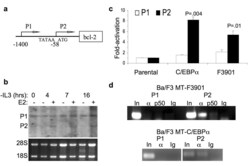
- Experimental details
- Figure 2 C/EBPalpha preferentially binds and activates the endogenous bcl-2 gene P2 promoter ( a ) Diagram of the human bcl-2 gene. P2 transcription initiates at -58 relative to the initial ATG codon, and P1 initiates at several sites in the vicinity of -1400. The P2, but not the P1, promoter contains a TATAA box (at -88). ( b ) Ba/F3-C/EBPalpha-ER cells withdrawn from IL-3 were cultured with (+) or without (-) estradiol (E2). The expression of bcl-2 mRNA at the indicated time points was assessed by Northern blot analysis (top). The positions of P1 and P2 bcl-2 transcripts are indicated and RNA loading was assessed by ethidium bromide staining of the 28S and 18S ribosomal RNAs (bottom). ( c ) Ba/F3 MT-C/EBPalpha, MT-F3901, or parental Ba/F3 cells were cultured with zinc for 16 hours and then withdrawn from IL-3. RNA was extracted 24 hours after IL-3 removal. The levels of P1 and P2 transcripts were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR and normalized to mS16 expression. Fold-activation relative to the parental Ba/F3 cells is presented. ( d ) Ba/F3 MT-F3901 or MT-C/EBPalpha cells were treated with zinc for 16 hours and subjected to ChIP using antisera against C/EBPalpha (alpha), NF-kappaB p50, or normal rabbit IgG and primers specific for the P1 or P2 bcl-2 promoters. Data representative of two independent experiments is shown.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
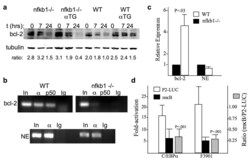
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 C/EBPalpha and a C/EBPalphaLZ oncoprotein depend on NF-kappaB p50 for binding to the bcl-2 promoter ( a ) Splenocytes from mice with the indicated genotype were exposed to 200 cGy and cultured for 0, 7, or 24 hours. Total cellular proteins extracts were obtained and subjected to Western blotting for bcl-2 and beta-tubulin. The ratio of bcl-2:tubulin in each sample is shown. ( b ) Total bone marrow cells extracted from nfkb1 -/- or wild-type control mice were subjected to ChIP using C/EBPalpha (alpha) or NF-kappaB p50 (p50) antisera or IgG control and primers specific for the bcl-2 P2 or neutrophil elastase (NE) promoters. ( c ) RNA isolated from total bone marrow cells from the hind limbs of age, sex, and strain-matched nfkb1 -/- or wild-type (WT) mice were subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis of bcl-2 or NE expression, normalized to mS16. Relative mRNA expression between WT and nfkb1 -/- mice is shown, with expression in nfkb1 -/- marrow set to 1. Data from four comparisons are shown. ( d ) F9 cells were transiently co-transfected with 1.5 ug of P2-LUC or its variant harboring clustered point mutations in the -170 kappaB site (mkappaB), with 100 ng of CMV, CMV-C/EBPalpha, or CMV-F3901, and 5 with ng of CMV-beta-galactosidase as an internal control. Activation of the wild type and mutant promoters by C/EBPalpha or F3901 was analyzed 48 after transfection. Fold-activation compared to the empty CMV vector was determined after adjustment for beta-galactosidase acti
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
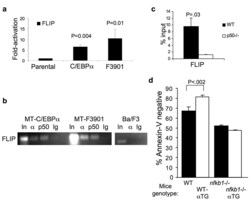
- Figure 4 C/EBPalpha induces FLIP expression and binds its endogenous promoter ( a ) Parental Ba/F3 cells and lines expressing C/EBPalpha or C/EBPalphaF3901 from the MT promoter were cultured in zinc chloride for 16 hours and then withdrawn from IL-3. RNA was extracted 16 hours after IL-3 removal. FLIP transcripts were measured using quantitative RT-PCR and expressed as fold-activation compared with parental cells. ( b ) Ba/F3 MT-C/EBPalpha or MT-C/EBPalphaF3901 or parental Ba/F3 cells were cultured with zinc for 16 hours and subjected to ChIP using C/EBPalpha (alpha) or NF-kappaB p50 (p50) antisera or control rabbit IgG and primers corresponding to the FLIP promoter. Data representative of two independent experiments is shown. ( c ) Splenocytes from H2K-C/EBPalpha-Eu transgenic (alphaTG) or nfkb1 -/-;alphaTG mice were subjected to ChIP using C/EBPalpha antiserum. Shown is the ratio of signal detected in the immunoprecipitate compared with input in three repetitions. ( d ) Single cell suspensions of splenocytes were obtained from mice with the indicated genotypes, stimulated with LPS for 30 hours and cultured with 200 ng/mL of soluble FasL for 16 hours. The cells were then stained with APC-Annexin V and PI. Shown are the percent of cells that were Annexin V-negative, all of which excluded PI (mean and SD from three experiments).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 C/EBPalpha binds NF-kappaB p50 directly ( a ) Histidine tagged C/EBPalpha and the Rel homology domain (RHD) of NF-kappaB p50 were expressed in E. coli , purified, resolved on an acrylamide gel, and stained with Coomassie blue. The positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated. ( b ) Refolding of purified C/EBPalpha in 15 different solutions, containing a range of salt, pH, and detergents, was examined. Activities of the renatured proteins were assessed by their ability to bind a consensus C/EBPalpha DNA sequence from the NE promoter in a gel shift assay. The lane numbers correspond to that of each buffer (QuickFold Protein Refolding Kit). A complete list of the buffers is available at http://athenaes.com/osc/QuickFoldAppMan.php . ( c ) Purified C/EBPalpha and NF-kappaB p50 RHD were co-incubated, subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with C/EBPalpha or p50 antisera, as indicated, followed by Western blot (WB) analysis with the reciprocal antibody (left panels). Purified C/EBPalpha alone was subjected to IP with p50 antisera, and purified RHD alone was subjected to IP with C/EBPalpha antisera as additional controls (right panels). ( d ) Co-immunoprecipitation was assessed after coincubation of purified C/EBPalpha and NF-kappaB p50 with double stranded oligonucleotides containing consensus DNA binding sites for C/EBPalpha or p50 (kappaB), or with both oligonucleotides.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
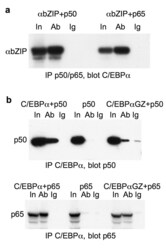
- Figure 6 The C/EBPalpha basic region mediates its interaction with NF-kappaB p50 or p65 ( a ) 293T cells in 100 mm dishes were cotransfected with 2 ug CMV-C/EBPalphabZIP and 2 ug of either CMV-NFkappaB p50 or CMV-NF-kappaB p65. Two days later, cells extracts were immunoprecipitated with p50 or p65 rabbit antisera (Ab) or rabbit IgG control (Ig) and immunoblotted with rabbit antiserum raised against the C/EBPalpha COOH-terminal sequence. ( b ) Extracts from cells transfected with CMV-C/EBPalpha or CMV-C/EBPalphaGZ and either CMV-NF-kappaB p50 or CMV-NF-kappaB p65 were immunoprecipitated with C/EBPalpha antiserum or rabbit IgG and immunoblotted with monoclonal p50 or p65 antibodies, as indicated (right and left panels). Extracts from cells transfected with p50 or p65 alone were assayed similarly as additional controls (center panel).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
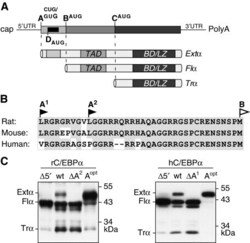
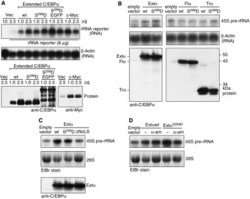
- Figure 1 The extended-C/EBPalpha isoform is translated from a non-AUG codon. ( A ) Schematic representation of the C/EBPalpha messenger RNA with three alternative translation initiation sites, indicated as A (CUG or GUG), B (AUG) and C (AUG), and the initiation site for the cis -regulatory uORF, indicated as D (AUG), respectively. The mRNA can be translated into three separate protein isoforms extended- (Extalpha), full-length- (Flalpha) or truncated-C/EBPalpha (Tralpha) that contain different sets of the functional domains TAD (Transactivation Domain), BD (Basic Domain) and LZ (Leucine Zipper). ( B ) Amino-acid sequence comparison of the extended domains of rat, mouse and human C/EBPalpha; conserved amino-acid residues are shaded in grey. ( C ) Immunoblots comparing expression from wild-type and mutant rat (rC/EBPalpha) and human (hC/EBPalpha) C/EBPalpha constructs in COS-1 cells: Wild-types (wt), mutants lacking the translation initiation site A (DeltaA 1/2 ), constructs devoid of the 5'leader (Delta5'), and constructs with the CUG or GUG exchanged by an AUG codon (A opt ).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
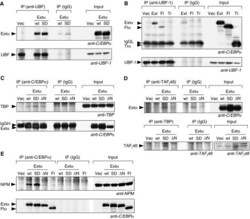
- Figure 5 Extended-C/EBPalpha interacts with UBF-1, SL1 and NPM. Immunoprecipitations (IPs) were performed with specific antibodies or with mouse IgG as control from total lysates of HEK293 cells expressing one of the C/EBPalpha isoforms encoded: wild type (wt) extended-C/EBPalpha (Extalpha or Ext), extended-C/EBPalpha S299D (SD), extended-C/EBPalpha S299D DeltaNoLS (DeltaN), full-length-C/EBPalpha (Fl), truncated-C/EBPalpha (Tr). Immunoblots of immunoprecipitates (IP) and total lysates (Input) were stained as indicated. ( A ) Extended-C/EBPalpha co-precipitates with UBF-1 using anti-UBF-1 antibodies ( B ) extended- and full-length-C/EBPalpha but not truncated-C/EBPalpha co-precipitate with UBF-1 using anti-UBF-1 antibodies. Immunoglobulin light chain is marked by IgGL. ( C ) TBP co-precipitates with extended-C/EBPalpha using anti-C/EBPalpha antibodies. Immunoglobulin heavy chain is marked by IgGH. ( D ) Extended-C/EBPalpha S299D but not the DeltaNoLS mutation co-precipitates with TAF I 48 using anti-TAF I 48 antibodies (upper panel). TAF I 48 co-precipitates more efficiently with TBP using anti-TBP antibodies only in cells expressing extended-C/EBPalpha S299D (lower panel). ( E ) NPM co-precipitates with extended-C/EBPalpha S299D but not with the extended-C/EBPalpha S299D DeltaNoLS using anti-C/EBPalpha antibodies.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure 7 Extended-C/EBPalpha stimulates RNA Pol I-dependent rDNA transcription. ( A ) Hek293T cells were transiently transfected with the human rRNA minigene reporter construct pHrP2-BH together with expression constructs for wild type extended-C/EBPalpha (wt), the extended-C/EBPalpha S299D (S 299 D) mutant, the latter fused to EGFP (S 299 D EGFP), c-Myc or the empty vector (Vec) as control as indicated. Half of the cells were analysed for transcription from the rRNA minigene reporter by Northern blotting using 10 mug of total RNA and a construct-specific probe. The other half of the cells were used for protein analysis. ( B ) The levels of the endogenous 45S rRNA precursor in C33A cells stably expressing wild type (wt) extended-, full-length-, truncated-C/EBPalpha or the S229D mutants thereof (S 299 D), or the empty vector as control was analysed by Northern blotting from 30 mug of total RNA. ( C ) The levels 45S rRNA precursor in C33A cells stably expressing wild type (wt) extended-C/EBPalpha or the S229D or DeltaNoLS mutants thereof, or the empty vector as control was analysed by Northern blotting from 30 mug of total RNA. ( D ) The levels 45S rRNA precursor in C33A cells stably expressing wild type (wt) extended-C/EBPalpha, the S229D mutant or the empty vector as control untreated or treated with 50 mug/ml alpha-amanitin (alpha-am) was analysed by Northern blotting from 30 mug of total RNA. A human beta-actin probe or ethidium bromide (EtBr) inverted staining of the gel w
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
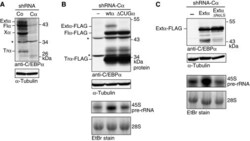
- Figure 8 Selective elimination of extended-C/EBPalpha impedes rRNA synthesis. ( A ) Lentiviral shRNA-mediated knock-down of endogenous human C/EBPalpha (Calpha) compared with control scrambled shRNA (Co) in HL-60 cells. ( B ) Retroviral-mediated expression in C/EBPalpha knock-down HL-60 (shRNA-Calpha) cells from rat C/EBPalpha (wtalpha) or the DeltaCUGalpha mutant cDNAs. ( C ) Retroviral-mediated expression of extended-C/EBPalpha and the DeltaNoLS mutant thereof in C/EBPalpha knock-down HL-60 (shRNA-Calpha) cells. Immunoblots were probed with anti-C/EBPalpha antibodies (14AA), and with anti-alpha-tubulin antibodies for loading control. The Xalpha-labelled band is of indefinite C/EBPalpha origin; possibly sumoylated truncated-C/EBPalpha (data not shown). Asterisk ( * ) indicates non-specific bands. Levels of 45S pre-rRNA were measured by Northern blotting of 15 mug of total RNA. Ethidium bromide (EtBr) inverted staining of the gel was used for loading control.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
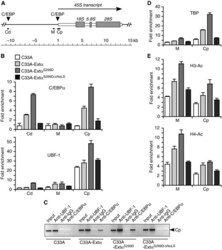
- Figure 9 Occupation of rDNA sequences by extended-C/EBPalpha facilitates UBF-1 and TBP recruitment and induces histone acetylation. ( A ) Schematic representation of part of the rDNA repeat with the transcribed rRNA and C/EBP consensus recognition sequences as indicated. The rDNA sequences analysed in the ChIP assays are designated Cd (C/EBP distal), Cp (C/EBP promoter) and M (c-Myc). ( B ) Fold enrichment of rDNA obtained with chromatin cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis for the regions Cd, M and Cp with anti-C/EBPalpha or anti-UBF-1 as indicated versus non-specific rabbit IgG. ChIP assays were done with C33A cells expressing empty vector, extended-C/EBPalpha-wt, -S299D or -S299D-DeltaNoLS mutant as indicated. ( C ) DNA gel of semi-quantitative PCR of region Cp with input, and ChIP assays with the antibodies as indicated for C33A cells expressing empty vector, extended-C/EBPalpha-wt, -S299D or -S299D-DeltaNoLS mutant. ( D ) Fold enrichment of rDNA obtained with ChIP analysis for the regions M and Cp with anti-TBP versus non-specific rabbit IgG. ( E ) Fold enrichment of rDNA obtained with ChIP analysis for the regions M and Cp with anti-H3-AC or anti-H4-AC as indicated versus non-specific rabbit IgG. DNA was quantitated by real-time PCR and data are presented as means and standard deviation from two independent ChIP experiments each analyses by two independent PCR reactions.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
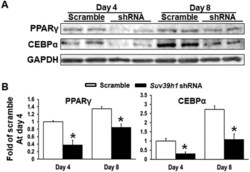
- Experimental details
- Figure 3. Suv39h1 knockdown inhibits adipogenic protein expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. (a) Immunoblots of PPARgamma and CEBPalpha protein. (b) Density quantitation of the immunoblots. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were infected with Suv39h1 shRNA lentivirus, selected with puromycin and differentiated as described in the Methods. Protein levels were measured by immunoblotting. All data are expressed as mean +- SEM, n = 4. * p < 0.05 vs. scramble control
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
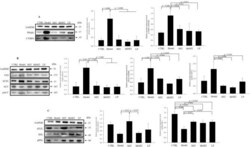
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 Effects of MJ2 and hkMJ2 on protein expression levels related to adipogenesis and lipid metabolism in eWAT. Total protein was extracted from eWAT in each group, and the relative protein expression levels of the factors related to ( A ) adipogenesis (PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha), ( B ) lipogenesis (FAS, SCD-1 and ACC) and ( C ) lipolysis (ATGL and HSL) were investigated by western blot. Representative images of each protein are shown, and the relative quantified expression levels indicate the mean +- SD. The p values were determined by ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test. The full-length blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 3 .
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry