Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [8]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [2]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-5273-82 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD8b Monoclonal Antibody (SIDI8BEE), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The SIDI8BEE monoclonal antibody reacts with human and rhesus macaque CD8 beta. The CD8b chain associates with the CD8a chain to form the CD8ab heterodimer expressed on the surface of a majority of thymocytes, and on peripheral cytotoxic alpha beta TCR T cells. The CD8 receptor complex binds to MHC class I and plays a role in T cell development and activation of mature T cells. Long been thought to exist either as a heterodimer of the alpha and beta chain or as a homodimer of alpha chains, beta chains have now been shown to homodimerize as well. SIDI8BEE can detect the CD8 beta chain in both the CD8ab heterodimer and the CD8bb homodimer. SIDI8BEE is cross-reactive to human and rhesus macaque CD8b. Other non-human primate species have not been tested. Applications Reported: This SIDI8BEE antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis, immunoprecipitation, and western blotting. Applications Tested: This SIDI8BEE antibody has been tested by flow cytometric analysis of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. This can be used at less than or equal to 0.125 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- SIDI8BEE
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Fingerprints of CD8+ T cells on human pre-plasma and memory B cells.
Antigen receptor-redirected T cells derived from hematopoietic precursor cells lack expression of the endogenous TCR/CD3 receptor and exhibit specific antitumor capacities.
CD103+ intraepithelial T cells in high-grade serous ovarian cancer are phenotypically diverse TCRαβ+ CD8αβ+ T cells that can be targeted for cancer immunotherapy.
GATA3 induces human T-cell commitment by restraining Notch activity and repressing NK-cell fate.
Normalizing the environment recapitulates adult human immune traits in laboratory mice.
Differential expression of the human CD8beta splice variants and regulation of the M-2 isoform by ubiquitination.
Mapping the binding site on CD8 beta for MHC class I reveals mutants with enhanced binding.
Human CD8 beta, but not mouse CD8 beta, can be expressed in the absence of CD8 alpha as a beta beta homodimer.
Strittmatter-Keller U, Walter C, Rauld C, Egli N, Regairaz C, Rabe S, Zenke G, Carballido J, Schweighoffer T
PloS one 2018;13(12):e0208187
PloS one 2018;13(12):e0208187
Antigen receptor-redirected T cells derived from hematopoietic precursor cells lack expression of the endogenous TCR/CD3 receptor and exhibit specific antitumor capacities.
Van Caeneghem Y, De Munter S, Tieppo P, Goetgeluk G, Weening K, Verstichel G, Bonte S, Taghon T, Leclercq G, Kerre T, Debets R, Vermijlen D, Abken H, Vandekerckhove B
Oncoimmunology 2017;6(3):e1283460
Oncoimmunology 2017;6(3):e1283460
CD103+ intraepithelial T cells in high-grade serous ovarian cancer are phenotypically diverse TCRαβ+ CD8αβ+ T cells that can be targeted for cancer immunotherapy.
Komdeur FL, Wouters MC, Workel HH, Tijans AM, Terwindt AL, Brunekreeft KL, Plat A, Klip HG, Eggink FA, Leffers N, Helfrich W, Samplonius DF, Bremer E, Wisman GB, Daemen T, Duiker EW, Hollema H, Nijman HW, de Bruyn M
Oncotarget 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75130-75144
Oncotarget 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75130-75144
GATA3 induces human T-cell commitment by restraining Notch activity and repressing NK-cell fate.
Van de Walle I, Dolens AC, Durinck K, De Mulder K, Van Loocke W, Damle S, Waegemans E, De Medts J, Velghe I, De Smedt M, Vandekerckhove B, Kerre T, Plum J, Leclercq G, Rothenberg EV, Van Vlierberghe P, Speleman F, Taghon T
Nature communications 2016 Apr 6;7:11171
Nature communications 2016 Apr 6;7:11171
Normalizing the environment recapitulates adult human immune traits in laboratory mice.
Beura LK, Hamilton SE, Bi K, Schenkel JM, Odumade OA, Casey KA, Thompson EA, Fraser KA, Rosato PC, Filali-Mouhim A, Sekaly RP, Jenkins MK, Vezys V, Haining WN, Jameson SC, Masopust D
Nature 2016 Apr 28;532(7600):512-6
Nature 2016 Apr 28;532(7600):512-6
Differential expression of the human CD8beta splice variants and regulation of the M-2 isoform by ubiquitination.
Thakral D, Dobbins J, Devine L, Kavathas PB
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Jun 1;180(11):7431-42
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2008 Jun 1;180(11):7431-42
Mapping the binding site on CD8 beta for MHC class I reveals mutants with enhanced binding.
Devine L, Thakral D, Nag S, Dobbins J, Hodsdon ME, Kavathas PB
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Sep 15;177(6):3930-8
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2006 Sep 15;177(6):3930-8
Human CD8 beta, but not mouse CD8 beta, can be expressed in the absence of CD8 alpha as a beta beta homodimer.
Devine L, Kieffer LJ, Aitken V, Kavathas PB
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2000 Jan 15;164(2):833-8
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2000 Jan 15;164(2):833-8
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
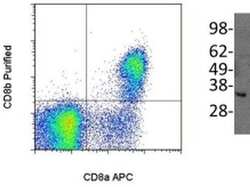
- Experimental details
- (Left) Staining of normal human peripheral blood cells either with Anti-Human CD8a (Product # 12-0086) and Anti-Human/Non-Human Primate CD8b Purified. F(ab')2 Anti-Mouse IgG PE (Product # 12-4012) was used to detect Anti-CD8b Purified. Cells in the lymphocyte gate were used for analysis. (Right) Immunoblotting of reduced cell lysate prepared from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with 5 µg/mL of Anti-Human/Non-Human Primate CD8b antibody. Bands were visualized using Anti-Mouse IgG HRP.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
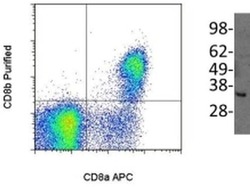
- Experimental details
- (Left) Staining of normal human peripheral blood cells either with Anti-Human CD8a (Product # 12-0086) and Anti-Human/Non-Human Primate CD8b Purified. F(ab')2 Anti-Mouse IgG PE (Product # 12-4012) was used to detect Anti-CD8b Purified. Cells in the lymphocyte gate were used for analysis. (Right) Immunoblotting of reduced cell lysate prepared from normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells with 5 µg/mL of Anti-Human/Non-Human Primate CD8b antibody. Bands were visualized using Anti-Mouse IgG HRP.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
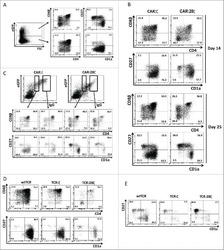
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
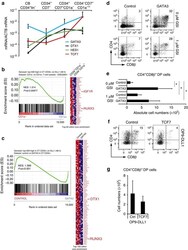
- Experimental details
- Figure 4 GATA3 restrains Notch activation at the T-lineage commitment stage. ( a ) Quantitative PCR of GATA3 , DTX1 , HES1 and TCF7 expression in different stages of in vitro generated T cell precursors from CB CD34 + lin - HPCs after 7 days of OP9-DLL4 coculture. Data shows the average expression in 3-4 independent samples on a log scale and erros bars indicate s.e.m. ( b , c ) GSEA shows a significant enrichment of the top 500 Notch-dependent genes in human CD34 + thymocytes in the set of genes higher expressed in ( b ) uncommitted CD34 + CD1a - versus CD34 + CD1a + committed T-cell precursors 50 , and genes expressed higher in ( c ) control versus GATA3-transduced CD34 + thymocytes as determined by microarray after 48 h of transduction. ( d ) Flow cytometry analysis of control and GATA3 -transduced CD34 + CD1 - uncommitted thymocytes in OP9-DLL1 cocultures with addition of 0 or 1 muM GSI and in the presence of IL7, SCF and FLT3L, showing the development of CD4 + CD8beta + DP thymocytes after 6 days of coculture. ( e ) Graph show absolute number of CD4 + CD8beta + DP thymocytes, generated in corresponding cultures shown in d . Data shows the average of four independent experiments and errors bars show s.e.m. * P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
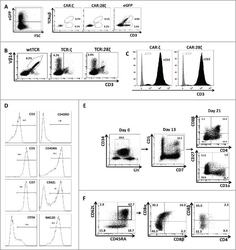
- Experimental details
- Figure 3. Phenotype and endogenous TCR expression of CD34 + HPC-derived transgenic AR + T cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the AR-transgenic T cells. (A) CAR-transgenic GFP + cells of cultures transduced to express either the CAR:zeta or the CAR:28zeta were analyzed on day 26 of OP9-DL1 culture for CD3 and TCRalphabeta expression. As a control, GFP - cells are shown from the OP9-DL1 culture transduced to express the CAR:zeta ( N = 5). (B) Dot plots show CD3 expression of cells from the OP9-DL1 cultures transgenic for the wtTCR, TCR:zeta and TCR:28zeta. Vbeta14 staining is used to mark transgene expression, as no GFP is expressed by the transgenic cells ( N = 5). (C) Surface and cytoplasmic staining for CD3 of in vitro generated mature T cells that were expanded for one cycle on feeder cells in the presence of cytokines. (D) Expression of various membrane markers by the CD27 + CD1a - mature T cells at the end of OP9-DL1 culture (46 d) ( N = 2). (E) Day 0: fresh cord blood after MACS CD34 enrichment sorted using the sorting window shown. Day 13: cord blood cells cultured on OP9-DL1 were sorted for CD5 CD7 double positive cells, using the indicated sorting window. The cells were then transduced to express CAR:28zeta and further differentiated on OP9-DL1 feeder layer. Day 21: analysis of the transgenic GFP + cultured cells for DP cells and CD27 + CD1a - mature cells. (F) Flow cytometric analysis of GFP + CAR:28zeta-transgenic cultures, gated on GFP + CD27 + CD1a
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry