Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [37]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunocytochemistry [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA001893 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA001893, RRID:AB_1079991
- Product name
- Anti-SIX1
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human SIX1, Gene description: SIX homeobox 1, Alternative Gene Names: DFNA23, Validated applications: WB, IHC, ICC, Uniprot ID: Q15475, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.4 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references AAV‐mediated Gene Cocktails Enhance Supporting Cell Reprogramming and Hair Cell Regeneration
Overlapping functions of SIX homeoproteins during embryonic myogenesis
All-trans retinoic acid changes muscle fiber type via increasing GADD34 dependent on MAPK signal
Loss of Elp1 disrupts trigeminal ganglion neurodevelopment in a model of familial dysautonomia
SIX1/EYA1 are novel liver damage biomarkers in chronic hepatitis B and other liver diseases
Chromatin Remodelers Interact with Eya1 and Six2 to Target Enhancers to Control Nephron Progenitor Cell Maintenance
Six1 promotes skeletal muscle thyroid hormone response through regulation of the MCT10 transporter
Dynamic changes in cis-regulatory occupancy by Six1 and its cooperative interactions with distinct cofactors drive lineage-specific gene expression programs during progressive differentiation of the auditory sensory epithelium
Blastula stage specification of avian neural crest
SIX1 cooperates with RUNX1 and SMAD4 in cell fate commitment of Müllerian duct epithelium
SIX1 represses senescence and promotes SOX2-mediated cellular plasticity during tumorigenesis
BORIS promotes chromatin regulatory interactions in treatment-resistant cancer cells
Eya3 partners with PP2A to induce c-Myc stabilization and tumor progression
Dynamic transcriptional signature and cell fate analysis reveals plasticity of individual neural plate border cells
A Modular Platform for Differentiation of Human PSCs into All Major Ectodermal Lineages
Respective contribution of the cephalic neural crest and mesoderm to SIX1-expressing head territories in the avian embryo
Six1 is essential for differentiation and patterning of the mammalian auditory sensory epithelium
Increased Six1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma.
Six1 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with glioma.
Six1 homeoprotein drives myofiber type IIA specialization in soleus muscle
SIX1 Oncoprotein as a Biomarker in a Model of Hormonal Carcinogenesis and in Human Endometrial Cancer
SIX1 coordinates with TGFβ signals to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer
The Six1 oncoprotein downregulates p53 via concomitant regulation of RPL26 and microRNA-27a-3p
The homeoprotein SIX1 controls cellular senescence through the regulation of p16INK4A and differentiation-related genes
Axud1 Integrates Wnt Signaling and Transcriptional Inputs to Drive Neural Crest Formation
3D mouse embryonic stem cell culture for generating inner ear organoids
Overexpression of sineoculis homeobox homolog 1 predicts poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Six Homeoproteins and a linc-RNA at the Fast MYH Locus Lock Fast Myofiber Terminal Phenotype
Persistently Altered Epigenetic Marks in the Mouse Uterus After Neonatal Estrogen Exposure
The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer
SIX1 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through ZEB1 activation
Six1 regulates stem cell repair potential and self-renewal during skeletal muscle regeneration
Expression of Six1 in luminal breast cancers predicts poor prognosis and promotes increases in tumor initiating cells by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways
Eya2 is required to mediate the pro-metastatic functions of Six1 via the induction of TGF-β signaling, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and cancer stem cell properties
The Six1 homeoprotein induces human mammary carcinoma cells to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in mice through increasing TGF-β signaling
Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Gene expression changes during HPV-mediated carcinogenesis: a comparison between an in vitro cell model and cervical cancer.
Zhang L, Chen X, Wang X, Zhou Y, Fang Y, Gu X, Zhang Z, Sun Q, Li N, Xu L, Tan F, Chai R, Qi J
Advanced Science 2024;11(29)
Advanced Science 2024;11(29)
Overlapping functions of SIX homeoproteins during embryonic myogenesis
Cox G, Wurmser M, Madani R, Chaverot N, Backer S, Borok M, Dos Santos M, Comai G, Tajbakhsh S, Relaix F, Santolini M, Sambasivan R, Jiang R, Maire P
PLOS Genetics 2023;19(6):e1010781
PLOS Genetics 2023;19(6):e1010781
All-trans retinoic acid changes muscle fiber type via increasing GADD34 dependent on MAPK signal
Adachi Y, Masuda M, Sakakibara I, Uchida T, Niida Y, Mori Y, Kamei Y, Okumura Y, Ohminami H, Ohnishi K, Yamanaka-Okumura H, Nikawa T, Taketani Y
Life Science Alliance 2022;5(7):e202101345
Life Science Alliance 2022;5(7):e202101345
Loss of Elp1 disrupts trigeminal ganglion neurodevelopment in a model of familial dysautonomia
Leonard C, Quiros J, Lefcort F, Taneyhill L
eLife 2022;11
eLife 2022;11
SIX1/EYA1 are novel liver damage biomarkers in chronic hepatitis B and other liver diseases
Xu B, Yang Q, Tang Y, Tan Z, Fu H, Peng J, Xiang X, Gan L, Deng G, Mao Q, Xu P, Jiang Y, Ding J
Annals of Translational Medicine 2021;9(12):992-992
Annals of Translational Medicine 2021;9(12):992-992
Chromatin Remodelers Interact with Eya1 and Six2 to Target Enhancers to Control Nephron Progenitor Cell Maintenance
Li J, Xu J, Jiang H, Zhang T, Ramakrishnan A, Shen L, Xu P
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2021;32(11):2815-2833
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2021;32(11):2815-2833
Six1 promotes skeletal muscle thyroid hormone response through regulation of the MCT10 transporter
Girgis J, Yang D, Chakroun I, Liu Y, Blais A
Skeletal Muscle 2021;11(1)
Skeletal Muscle 2021;11(1)
Dynamic changes in cis-regulatory occupancy by Six1 and its cooperative interactions with distinct cofactors drive lineage-specific gene expression programs during progressive differentiation of the auditory sensory epithelium
Xu P, Shen L, Ding J, Loh Y, Wong E, Xu J, Fritzsch B, Ramakrishnan A, Zhang T, Li J
Nucleic Acids Research 2020;48(6):2880-2896
Nucleic Acids Research 2020;48(6):2880-2896
Blastula stage specification of avian neural crest
Prasad M, Uribe-Querol E, Marquez J, Vadasz S, Yardley N, Shelar P, Charney R, García-Castro M
Developmental Biology 2020;458(1):64-74
Developmental Biology 2020;458(1):64-74
SIX1 cooperates with RUNX1 and SMAD4 in cell fate commitment of Müllerian duct epithelium
Terakawa J, Serna V, Nair D, Sato S, Kawakami K, Radovick S, Maire P, Kurita T
Cell Death & Differentiation 2020;27(12):3307-3320
Cell Death & Differentiation 2020;27(12):3307-3320
SIX1 represses senescence and promotes SOX2-mediated cellular plasticity during tumorigenesis
De Lope C, Martín-Alonso S, Auzmendi-Iriarte J, Escudero C, Mulet I, Larrasa-Alonso J, López-Antona I, Matheu A, Palmero I
Scientific Reports 2019;9(1)
Scientific Reports 2019;9(1)
BORIS promotes chromatin regulatory interactions in treatment-resistant cancer cells
Debruyne D, Dries R, Sengupta S, Seruggia D, Gao Y, Sharma B, Huang H, Moreau L, McLane M, Day D, Marco E, Chen T, Gray N, Wong K, Orkin S, Yuan G, Young R, George R
Nature 2019;572(7771):676-680
Nature 2019;572(7771):676-680
Eya3 partners with PP2A to induce c-Myc stabilization and tumor progression
Zhang L, Zhou H, Li X, Vartuli R, Rowse M, Xing Y, Rudra P, Ghosh D, Zhao R, Ford H
Nature Communications 2018;9(1)
Nature Communications 2018;9(1)
Dynamic transcriptional signature and cell fate analysis reveals plasticity of individual neural plate border cells
Roellig D, Tan-Cabugao J, Esaian S, Bronner M
eLife 2017;6
eLife 2017;6
A Modular Platform for Differentiation of Human PSCs into All Major Ectodermal Lineages
Tchieu J, Zimmer B, Fattahi F, Amin S, Zeltner N, Chen S, Studer L
Cell Stem Cell 2017;21(3):399-410.e7
Cell Stem Cell 2017;21(3):399-410.e7
Respective contribution of the cephalic neural crest and mesoderm to SIX1-expressing head territories in the avian embryo
Fonseca B, Couly G, Dupin E
BMC Developmental Biology 2017;17(1)
BMC Developmental Biology 2017;17(1)
Six1 is essential for differentiation and patterning of the mammalian auditory sensory epithelium
Chen P, Zhang T, Xu J, Maire P, Xu P
PLOS Genetics 2017;13(9):e1006967
PLOS Genetics 2017;13(9):e1006967
Increased Six1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma.
Chao L, Liu J, Zhao D
Oncology letters 2017 May;13(5):2891-2896
Oncology letters 2017 May;13(5):2891-2896
Six1 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with glioma.
Zhang X, Xu R
Oncology letters 2017 Mar;13(3):1293-1298
Oncology letters 2017 Mar;13(3):1293-1298
Six1 homeoprotein drives myofiber type IIA specialization in soleus muscle
Sakakibara I, Wurmser M, Dos Santos M, Santolini M, Ducommun S, Davaze R, Guernec A, Sakamoto K, Maire P
Skeletal Muscle 2016;6(1)
Skeletal Muscle 2016;6(1)
SIX1 Oncoprotein as a Biomarker in a Model of Hormonal Carcinogenesis and in Human Endometrial Cancer
Suen A, Jefferson W, Wood C, Padilla-Banks E, Bae-Jump V, Williams C
Molecular Cancer Research 2016;14(9):849-858
Molecular Cancer Research 2016;14(9):849-858
SIX1 coordinates with TGFβ signals to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer
Sun S, Liu D, Deng Y, Zhang X, Wan D, Xi B, Huang W, Chen Q, Li M, Wang M, Yang F, Shu P, Wu K, Gao Q
Oncology Letters 2016;12(2):1271-1278
Oncology Letters 2016;12(2):1271-1278
The Six1 oncoprotein downregulates p53 via concomitant regulation of RPL26 and microRNA-27a-3p
Towers C, Guarnieri A, Micalizzi D, Harrell J, Gillen A, Kim J, Wang C, Oliphant M, Drasin D, Guney M, Kabos P, Sartorius C, Tan A, Perou C, Espinosa J, Ford H
Nature Communications 2015;6(1)
Nature Communications 2015;6(1)
The homeoprotein SIX1 controls cellular senescence through the regulation of p16INK4A and differentiation-related genes
Adrados I, Larrasa-Alonso J, Galarreta A, López-Antona I, Menéndez C, Abad M, Gil J, Moreno-Bueno G, Palmero I
Oncogene 2015;35(27):3485-3494
Oncogene 2015;35(27):3485-3494
Axud1 Integrates Wnt Signaling and Transcriptional Inputs to Drive Neural Crest Formation
Simões-Costa M, Stone M, Bronner M
Developmental Cell 2015;34(5):544-554
Developmental Cell 2015;34(5):544-554
3D mouse embryonic stem cell culture for generating inner ear organoids
Koehler K, Hashino E
Nature Protocols 2014;9(6):1229-1244
Nature Protocols 2014;9(6):1229-1244
Overexpression of sineoculis homeobox homolog 1 predicts poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Kong J, Zhou X, Liu S, Jin T, Piao Y, Liu C, Lin Z
International journal of clinical and experimental pathology 2014;7(6):3018-27
International journal of clinical and experimental pathology 2014;7(6):3018-27
Six Homeoproteins and a linc-RNA at the Fast MYH Locus Lock Fast Myofiber Terminal Phenotype
Dawn C, Sakakibara I, Santolini M, Ferry A, Hakim V, Maire P
PLoS Genetics 2014;10(5):e1004386
PLoS Genetics 2014;10(5):e1004386
Persistently Altered Epigenetic Marks in the Mouse Uterus After Neonatal Estrogen Exposure
Jefferson W, Chevalier D, Phelps J, Cantor A, Padilla-Banks E, Newbold R, Archer T, Kinyamu H, Williams C
Molecular Endocrinology 2013;27(10):1666-1677
Molecular Endocrinology 2013;27(10):1666-1677
The miR-106b-25 cluster targets Smad7, activates TGF-β signaling, and induces EMT and tumor initiating cell characteristics downstream of Six1 in human breast cancer
Smith A, Iwanaga R, Drasin D, Micalizzi D, Vartuli R, Tan A, Ford H
Oncogene 2012;31(50):5162-5171
Oncogene 2012;31(50):5162-5171
SIX1 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer through ZEB1 activation
Ono H, Imoto I, Kozaki K, Tsuda H, Matsui T, Kurasawa Y, Muramatsu T, Sugihara K, Inazawa J
Oncogene 2012;31(47):4923-4934
Oncogene 2012;31(47):4923-4934
Six1 regulates stem cell repair potential and self-renewal during skeletal muscle regeneration
Le Grand F, Grifone R, Mourikis P, Houbron C, Gigaud C, Pujol J, Maillet M, Pagès G, Rudnicki M, Tajbakhsh S, Maire P
Journal of Cell Biology 2012;198(5):815-832
Journal of Cell Biology 2012;198(5):815-832
Expression of Six1 in luminal breast cancers predicts poor prognosis and promotes increases in tumor initiating cells by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways
Iwanaga R, Wang C, Micalizzi D, Harrell J, Jedlicka P, Sartorius C, Kabos P, Farabaugh S, Bradford A, Ford H
Breast Cancer Research 2012;14(4)
Breast Cancer Research 2012;14(4)
Eya2 is required to mediate the pro-metastatic functions of Six1 via the induction of TGF-β signaling, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and cancer stem cell properties
Farabaugh S, Micalizzi D, Jedlicka P, Zhao R, Ford H
Oncogene 2011;31(5):552-562
Oncogene 2011;31(5):552-562
The Six1 homeoprotein induces human mammary carcinoma cells to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in mice through increasing TGF-β signaling
Micalizzi D, Christensen K, Jedlicka P, Coletta R, Barón A, Harrell J, Horwitz K, Billheimer D, Heichman K, Welm A, Schiemann W, Ford H
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2009;119(9):2678-2690
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2009;119(9):2678-2690
Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition
McCoy E, Iwanaga R, Jedlicka P, Abbey N, Chodosh L, Heichman K, Welm A, Ford H
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2009;119(9):2663-2677
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2009;119(9):2663-2677
Gene expression changes during HPV-mediated carcinogenesis: a comparison between an in vitro cell model and cervical cancer.
Wan F, Miao X, Quraishi I, Kennedy V, Creek KE, Pirisi L
International journal of cancer 2008 Jul 1;123(1):32-40
International journal of cancer 2008 Jul 1;123(1):32-40
No comments: Submit comment
Enhanced validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Genetic validation
- Main image
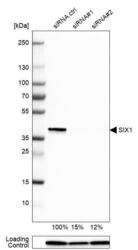
- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis in Rh30 cells transfected with control siRNA, target specific siRNA probe #1 and #2, using Anti-SIX1 antibody. Remaining relative intensity is presented. Loading control: Anti-PPIB.
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
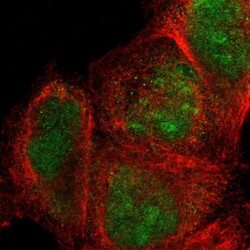
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent staining of human cell line A-431 shows localization to nucleus & nucleoli.
- Sample type
- Human
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Orthogonal validation
- Main image
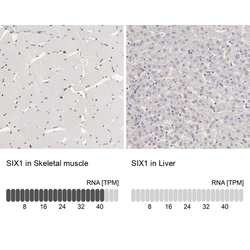
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry analysis in human skeletal muscle and liver tissues using HPA001893 antibody. Corresponding SIX1 RNA-seq data are presented for the same tissues.
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry