Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [3]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [4]
- Immunohistochemistry [3]
- Other assay [4]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-31965 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- VCAM-1 (CD106) Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (SA05-04)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies are produced using in vitro expression systems. The expression systems are developed by cloning in the specific antibody DNA sequences from immunoreactive rabbits. Then, individual clones are screened to select the best candidates for production. The advantages of using recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies include: better specificity and sensitivity, lot-to-lot consistency, animal origin-free formulations, and broader immunoreactivity to diverse targets due to larger rabbit immune repertoire.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- SA05-04
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Complement Inhibition Alleviates Cholestatic Liver Injury Through Mediating Macrophage Infiltration and Function in Mice.
Silencing of lncRNA XIST impairs angiogenesis and exacerbates cerebral vascular injury after ischemic stroke.
KLF4 alleviates cerebral vascular injury by ameliorating vascular endothelial inflammation and regulating tight junction protein expression following ischemic stroke.
Guo Z, Chen J, Zeng Y, Wang Z, Yao M, Tomlinson S, Chen B, Yuan G, He S
Frontiers in immunology 2021;12:785287
Frontiers in immunology 2021;12:785287
Silencing of lncRNA XIST impairs angiogenesis and exacerbates cerebral vascular injury after ischemic stroke.
Wang C, Dong J, Sun J, Huang S, Wu F, Zhang X, Pang D, Fu Y, Li L
Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids 2021 Dec 3;26:148-160
Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids 2021 Dec 3;26:148-160
KLF4 alleviates cerebral vascular injury by ameliorating vascular endothelial inflammation and regulating tight junction protein expression following ischemic stroke.
Zhang X, Wang L, Han Z, Dong J, Pang D, Fu Y, Li L
Journal of neuroinflammation 2020 Apr 7;17(1):107
Journal of neuroinflammation 2020 Apr 7;17(1):107
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
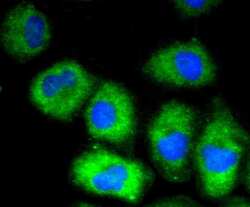
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemical analysis of VCAM-1 (CD106) in HUVEC cells using a VCAM-1 (CD106) Monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-31965) as seen in green. The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
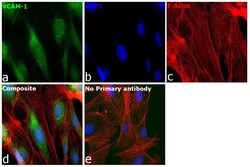
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 was performed using 70% confluent log phase HUVEC cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with VCAM-1 (CD106) Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (SA05-04) (Product # MA5-31965) at 1:100 in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32790), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b:Blue) were stained with ProLong™ Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # P36962). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing Cytoplasmic localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
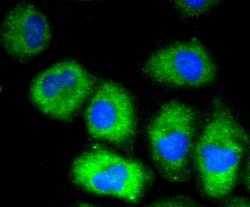
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemical analysis of VCAM-1 (CD106) in HUVEC cells using a VCAM-1 (CD106) Monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-31965) as seen in green. The nuclear counter stain is DAPI (blue). Cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, permeabilised with 0.25% Triton X100/PBS.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
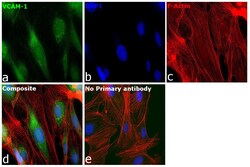
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 was performed using 70% confluent log phase HUVEC cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with VCAM-1 (CD106) Recombinant Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (SA05-04) (Product # MA5-31965) at 1:100 in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32790), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b:Blue) were stained with ProLong™ Diamond Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # P36962). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing Cytoplasmic localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
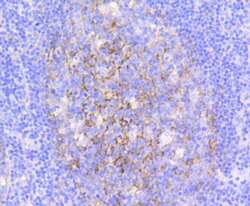
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of VCAM-1 (CD106) of paraffin-embedded Human tonsil tissue using a VCAM-1-CD106 Monoclonal antibody (Product #MA5-31965). Counter stained with hematoxylin.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
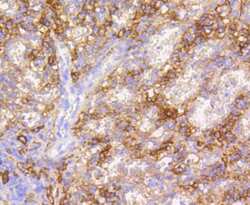
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of VCAM-1 (CD106) of paraffin-embedded Human spleen tissue using a VCAM-1-CD106 Monoclonal antibody (Product #MA5-31965). Counter stained with hematoxylin.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
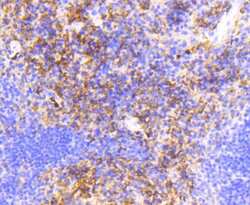
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of VCAM-1 (CD106) of paraffin-embedded Mouse spleen tissue using a VCAM-1-CD106 Monoclonal antibody (Product #MA5-31965). Counter stained with hematoxylin.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
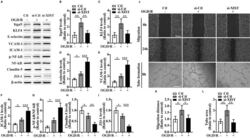
- Experimental details
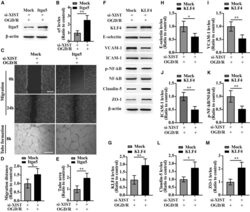
- Figure 4 The influence of silencing of lncRNA XIST on the migration and tube formation and the expression of Itgalpha5, KLF4, three CAMs, phosphorylation of (p)-NF-kappaB, and TJPs of bEnd3 cells under OGD/R conditions (A) Representative images of western blot for the expression of Itgalpha5, KLF4, three CAMs (E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1), p-NF-kappaB, and TJPs (Claudin-5 and ZO-1) in bEnd3 cells transfected with the negative control siRNA (si-Ctl) or siRNA-lncRNA XIST (si-XIST) at 24 h restoration from OGD. The NO-OGD/R cells served as a control. (B-I) Bar graphs show the quantitative analyses of western blots as ratios of Itgalpha5/beta-actin (B), KLF4/beta-actin (C), E-selectin/beta-actin (D), VCAM-1/beta-actin (E), ICAM-1/beta-actin (F), p-NF-kappaB/total NF-kappaB (G), Claudin-5/beta-actin (H), and ZO-1/beta-actin (I) (n = 4 per experimental group). Note that the expressions of Itgalpha5, KLF4, and TJPs (Claudin-5 and ZO-1) in the si-XIST-treated bEnd3 cells were markedly reduced, but the expressions of three CAMs including E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 and the p-NF-kappaB were significantly elevated relative to the si-Ctl-treated group at 24 h restoration from OGD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. (J) Representative images of cell migration and capillary tube formation of bEnd3 cells transfected with si-Ctl or si-XIST after OGD/R treatment. Scale bar, 400 mum for migration; 500 mum for tube formation. (K) Quantification of cell migration of bEnd3 cells. The
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 Overexpression of Itgalpha5 or KLF4 reverses the effect of lncRNA XIST on the migration and tube formation and the expression of three CAMs, p-NF-kappaB, and TJPs of bEnd3 cells under OGD/R conditions (A) Representative images of western blot for the expression of Itgalpha5 in bEnd3 cells co-transfected with si-XIST and Itgalpha5 overexpression plasmid at 24 h restoration from OGD. (B) Bar graphs show the quantitative analyses of western blots as ratios of Itgalpha5/beta-actin (n = 4 per experimental group). (C) Representative images of cell migration and capillary tube formation of bEnd3 cells co-transfected with si-XIST and Itgalpha5 overexpression plasmid after OGD/R treatment. Scale bar, 400 mum for migration; 500 mum for tube formation. (D and E) Quantification of cell migration (D) and tube formation (E) of bEnd3 cells (n = 4 per experimental group). (F) Representative images of western blot for the expression of KLF4, three CAMs (E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1), p-NF-kappaB, and TJPs (Claudin-5 and ZO-1) in bEnd3 cells co-transfected with si-XIST and KLF4 overexpression plasmid at 24 h restoration from OGD. (G-M) Bar graphs show the quantitative analyses of western blots as ratios of KLF4/beta-actin (G), E-selectin/beta-actin (H), VCAM-1/beta-actin (I), ICAM-1/beta-actin (J), p-NF-kappaB/total NF-kappaB (K), Claudin-5/beta-actin (L), and ZO-1/beta-actin (M) (n = 4 per experimental group). Note that bEnd3 cells co-transfected with si-XIST and Itgalpha5 displaye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
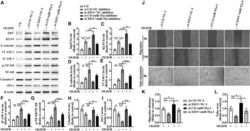
- Experimental details
- Figure 6 lncRNA XIST alleviates a vascular endothelial inflammation response and regulates migration and tube formation of bEnd3 cells under OGD/R conditions by targeting miR-92a (A) Representative images of western blot for the expression of Itgalpha5, KLF4, E-selectin, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, p-NF-kappaB, Claudin-5, and ZO-1 in bEnd3 cells co-transfected with the si-Ctl or si-XIST and/or miR-92a inhibitor (miR-92a-I) at 24 h restoration from OGD. (B-I) Bar graphs show the quantitative analyses of western blots as ratios of Itgalpha5/beta-actin (B), KLF4/beta-actin (C), E-selectin/beta-actin (D), VCAM-1/beta-actin (E), ICAM-1/beta-actin (F), p-NF-kappaB/total NF-kappaB (G), Claudin-5/beta-actin (H), and ZO-1/beta-actin (I) (n = 4 per experimental group). Note that the expressions of Itgalpha5, KLF4, and TJPs (Claudin-5 and ZO-1) in the si-XIST + NC inhibitor (NC-I)-treated bEnd3 cells markedly decreased, but the expressions of three CAMs including E-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 and the p-NF-kappaB were significantly elevated relative to the si-Ctl + NC-I-treated group at 24 h restoration from OGD. However, these effects were significantly rescued by inhibiting the levels of miR-92a in the bEnd3 cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. (J) Representative images of cell migration and capillary tube formation of bEnd3 cells transfected with si-Ctl or si-XIST and/or miR-92a-I after OGD/R treatment. Scale bar, 400 mum for migration; 500 mum for tube formation. (K and L) Quantifica
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
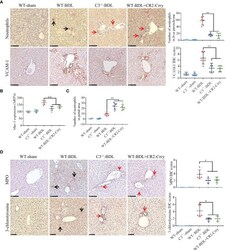
- Figure 3 C3 deficiency or CR2-Crry significantly inhibits the activation of neutrophils and decreases the expression of VCAM-1 and Mac-1 in mice with CLI. Wild-type and C3 deficient mice were subjected to BDL or sham operations. WT-BDL mice were injected i.p. with PBS or CR2-Crry and sacrificed 3 days later. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded liver sections were stained for specific esterase or immunostained for MPO, 3-chlorotyrosine and VCAM-1. Anticoagulated blood was subjected to flow cytometry for Mac-1 detection. (A) Specific esterase staining for neutrophils and immunohistochemical staining for VCAM-1 in liver parenchyma. (B) Expression of Mac-1 on neutrophils. (C) Assessment of neutrophils in the liver portal area. (D) Immunohistochemical staining for MPO and 3-chlorotyrosine. Scale bars for all, 100 mum; n = 5-6 per group. Black arrows, positive staining in the liver parenchyma; red arrows, positive staining in the portal area. Results are expressed as mean +- SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry