Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [0]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 692204 - Provider product page

- Provider
- BioLegend
- Proper citation
- BioLegend Cat#692204, RRID:AB_2632762
- Product name
- Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-VEGF-121
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Description
- VEGF was initially identified in conditioned medium from bovine pituitary follicular cells. VEGF-A belongs to the VEGF family, which has the following members: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, and PlGF (placental growth factor). In addition, viral VEGF homologs (collectively called VEGF-E) and snake venom VEGFs such as T.f. (Trimeresurus flavoviridis) and svVEGF (called VEGF-F) have been described. VEGFA is alternatively spliced to generate variants with different number of amino acids such as VEGF-121, VEGF-145, VEGF-165, and VEGF-189. While VEGF-121 is freely diffusible and does not bind to heparin sulphate, VEGF-165 and VEGF-189 bind to heparin sulfate, resulting in retention on the cell surface or in the extracellular matrix. VEGF-A is highly expressed in solid tumors generated in breast, lung, renal, colorectal and liver tissues. VEGF has strong vascular permeability activity and significantly contributes to the formation of ascites tumors. VEGF can act as a direct proinflammatory mediator during the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and protect rheumatoid synoviocytes from apoptosis, which contributes to synovial hyperplasia. VEGF is expressed in synovial macrophages and synovial fibroblasts in RA patients. Also, VEGF is associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). AMD is due to neovascularization that originates from endothelial cells in the choroid that grow into neurosensory retina as choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Antibody clone number
- A15136B
- Vial size
- 1 mg
- Concentration
- 1.0 mg/ml
- Storage
- 2°C-8°C
- Handling
- Ambient RT
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- BioLegend (provider)
- Main image
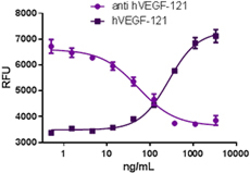
- Experimental details
- Recombinant human VEGF-121 stimulates proliferation of HUVEC in a dose-dependent manner (dark purple squares). Proliferation induced by recombinant human VEGF-121 (15 ng/mL) is neutralized (purple circles) by increasing concentrations of anti-VEGF-121 (clone A15136B) antibody. The ND50 is typically 25 – 100 ng/mL.
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Blocking/Neutralizing
Blocking/Neutralizing Other assay
Other assay