Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [4]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 35-9100 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- TTK Monoclonal Antibody (N1)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- N1
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Characterisation of CCT271850, a selective, oral and potent MPS1 inhibitor, used to directly measure in vivo MPS1 inhibition vs therapeutic efficacy.
Structure-based design of orally bioavailable 1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine inhibitors of mitotic kinase monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1).
High frequency of TTK mutations in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer and evaluation of their effect on spindle assembly checkpoint.
Human Mps1 protein kinase is required for centrosome duplication and normal mitotic progression.
Faisal A, Mak GWY, Gurden MD, Xavier CPR, Anderhub SJ, Innocenti P, Westwood IM, Naud S, Hayes A, Box G, Valenti MR, De Haven Brandon AK, O'Fee L, Schmitt J, Woodward HL, Burke R, vanMontfort RLM, Blagg J, Raynaud FI, Eccles SA, Hoelder S, Linardopoulos S
British journal of cancer 2017 Apr 25;116(9):1166-1176
British journal of cancer 2017 Apr 25;116(9):1166-1176
Structure-based design of orally bioavailable 1H-pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine inhibitors of mitotic kinase monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1).
Naud S, Westwood IM, Faisal A, Sheldrake P, Bavetsias V, Atrash B, Cheung KM, Liu M, Hayes A, Schmitt J, Wood A, Choi V, Boxall K, Mak G, Gurden M, Valenti M, de Haven Brandon A, Henley A, Baker R, McAndrew C, Matijssen B, Burke R, Hoelder S, Eccles SA, Raynaud FI, Linardopoulos S, van Montfort RL, Blagg J
Journal of medicinal chemistry 2013 Dec 27;56(24):10045-65
Journal of medicinal chemistry 2013 Dec 27;56(24):10045-65
High frequency of TTK mutations in microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer and evaluation of their effect on spindle assembly checkpoint.
Niittymäki I, Gylfe A, Laine L, Laakso M, Lehtonen HJ, Kondelin J, Tolvanen J, Nousiainen K, Pouwels J, Järvinen H, Nuorva K, Mecklin JP, Mäkinen M, Ristimäki A, Ørntoft TF, Hautaniemi S, Karhu A, Kallio MJ, Aaltonen LA
Carcinogenesis 2011 Mar;32(3):305-11
Carcinogenesis 2011 Mar;32(3):305-11
Human Mps1 protein kinase is required for centrosome duplication and normal mitotic progression.
Fisk HA, Mattison CP, Winey M
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003 Dec 9;100(25):14875-80
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003 Dec 9;100(25):14875-80
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
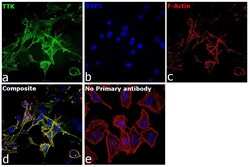
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Dual specificity protein kinase TTK was performed using 70% confluent log phase U-87 MG cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with TTK Monoclonal Antibody (N1) (Product # 35-9100) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32766), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b:Blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 (Product # H1399). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 40X magnification in CellInsight CX7 LZR High-Content Screening (HCS) Platform (Product # CX7C1115LZR).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
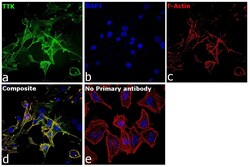
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Dual specificity protein kinase TTK was performed using 70% confluent log phase U-87 MG cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 45 minutes at room temperature. The cells were labeled with TTK Monoclonal Antibody (N1) (Product # 35-9100) at 1:100 dilution in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree celsius overnight and then labeled with Donkey anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 (Product # A32766), (1:2000 dilution), for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: Green). Nuclei (Panel b:Blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 (Product # H1399). F-actin (Panel c: Red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing cytoskeletal and cytoplasmic localization. Panel e represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 40X magnification in CellInsight CX7 LZR High-Content Screening (HCS) Platform (Product # CX7C1115LZR).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
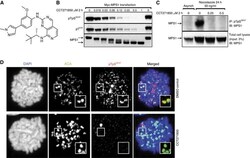
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 CCT271850 inhibits MPS1 autophosphorylation in cells. ( A ) Structure of CCT271850. ( B ) HCT116 cells transiently expressing Myc-tagged MPS1 were treated with increasing concentrations of CCT271850 for 2 h. Cell lysates were analysed for MPS1 autophosphorylation (at pT33pS37 and pT676 sites) and gel shift using immunoblotting. ( C ) HCT116 cells were synchronised with nocodazole for 24 h followed by treatment with indicated concentrations of CCT271850 for 2 h in the presence of MG132. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated for endogenous MPS1 with phospho-specific anti-pT33pS37 antibodies and immunoblotted with anti-MPS1 antibodies. Total cell lysates were also immunoblotted with anti-MPS1 antibodies as a control for immunoprecipitation input (lower panel). ( D ) Immunofluorescence for MPS1 pT33pS37 localisation at kinetochores with and without treatment with CCT271850. Cells were treated with CCT271850 for 1 h, followed by treatment with nocodazole, MG132 and CCT271850 for an additional hour. Cells were fixed and stained as indicated.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
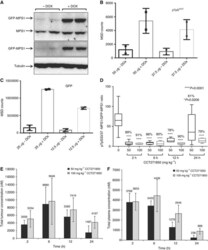
- Experimental details
- Figure 4 Development of a PD biomarker assay for measuring direct inhibition of MPS1 in DLD1 GFP-MPS1 Dox-inducible xenografts. ( A ) Five million DLD1 cells, stably expressing Dox-inducible GFP-MPS1, were used to grow tumours in athymic mice. Mice were dosed with ~6 mg of Dox per day for 3 days. Tumours were lysed and equal amount of protein was used for immunoblotting with GFP and MPS1 antibodies. ( B ) MSD assay for detection of MPS1 phosphorylation in xenograft tumours. Cell lysates (37.5 and 50 mu g) from non-induced and induced tumours were used for MSD assay with pTpS 33/37 antibodies. ( C ) Two concentrations (12.5 and 25 mu g) of cell lysates were also used for MSD with GFP antibodies. ( D ) PK/PD studies in DLD1 GFP-MPS1 Dox-inducible xenografts treated with CCT271850. Mice bearing bilateral DLD1 (GFP-MPS1 Dox inducible) xenografts were placed on Dox diet for 3 days (~6 mg/day). Twenty-four hours prior to harvest, mice were given a single 10 mg oral gavage bolus of Dox, followed by a single dose of 50 or 100 mg/kg of CCT271850. Tumours and plasma samples were collected at 2, 6, 12 and 24 h after CCT271850 dosing and followed with PK and PD examination. Samples were lysed and analysed by MSD for pTpS 33/37 and GFP. Ratio of phospho-MPS1 (pTpS 33/37 )/Total-MPS1 (GFP) in tumour samples at various time points after 50 and 100 mg/kg CCT271850 dosing was calculated. Concentration of CCT271850 in tumours ( E ) and plasma ( F ) was measured.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry