MA5-15218
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: MAPK14
CSBP1, CSBP2, CSPB1, Mxi2, p38, PRKM14, PRKM15
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [2]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-15218 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Phospho-p38 MAPK (Thr180, Tyr182) Monoclonal Antibody (C.7.8)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- Antibodies to this protein (and modification) were previously sold as part of a Thermo Scientific Cellomics High Content Screening Kit. This replacement antibody is now recommended for researchers who need an antibody for high content cell based assays. It has been thoroughly tested and validated for cellular immunofluorescence (IF) applications. Further optimization including the selection of the most appropriate fluorescent Dylight conjugated secondary antibody may have to be performed for your high content assay. It is not recommended to aliquot this antibody.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Yeast
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- C.7.8
- Vial size
- 100 µL
- Concentration
- 156 µg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Alterations of the renin angiotensin system in human end-stage heart failure before and after mechanical cardiac unloading by LVAD support.
Roxatidine inhibits fibrosis by inhibiting NF‑κB and MAPK signaling in macrophages sensing breast implant surface materials.
Messmann R, Dietl A, Wagner S, Domenig O, Jungbauer C, Luchner A, Maier LS, Schopka S, Hirt S, Schmid C, Birner C
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2020 Sep;472(1-2):79-94
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2020 Sep;472(1-2):79-94
Roxatidine inhibits fibrosis by inhibiting NF‑κB and MAPK signaling in macrophages sensing breast implant surface materials.
Ji L, Wang T, Tian L, Song H, Gao M
Molecular medicine reports 2020 Jan;21(1):161-172
Molecular medicine reports 2020 Jan;21(1):161-172
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
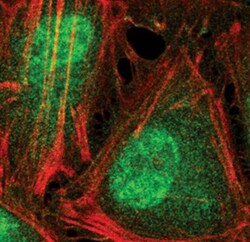
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 in HeLa cells using a Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-15218) (green). Actin filaments are labeled with a fluorescent red phalloidin.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
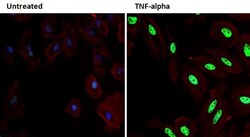
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 (green) in HeLa cells either left untreated (left panel) or treated with 100 ng/mL TNF-alpha for 15 minutes (right panel). Formalin fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in TBS for 10 minutes at room temperature and blocked with 1% Blocker BSA (Product # 37525) for 15 minutes at room temperature. Cells were probed with a Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-15218) at a dilution of 1:100 for at least 1 hour at room temperature, washed with PBS, and incubated with DyLight 488 goat-anti mouse IgG secondary antibody (Product # 35502) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. F-Actin (red) was stained with DyLight 554 phalloidin (Product # 21834) and nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ArrayScan or ToxInsight Instrument at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
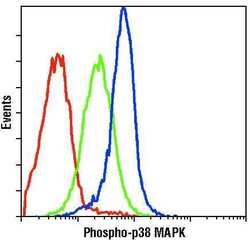
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometric analysis of Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 in untreated (green) or anisomycin-treated (blue) Jurkat cells using a Phospho-p38 MAPK pThr180/Tyr182 monoclonal antibody (Product # MA5-15218) compared to a nonspecific negative control antibody (red).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
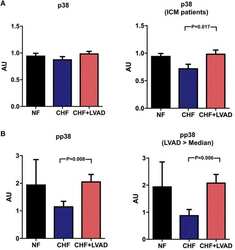
- Experimental details
- Fig. 11 a p38 before (CHF) and after LVAD therapy (CHF+LVAD) as compared to non-failing ventricles (NF), left. The same comparisons in the subgroup of ICM patients, right ( n = 8). P38 expression was determined by immunoblot (Western blot) analysis and referred to a standard, respectively, whose densitometric value was set 1 by default. The value on the y -axis, therefore, reflects the percentage of each parameter's immunoblot band density in relation to this default value. AU arbitrary unit, CHF congestive heart failure, ICM ischemic cardiomyopathy, LVAD left ventricular assist device, NF non-failing myocardial tissue specimen. b Phosphorylated p38 (pp38) before (CHF) and after LVAD therapy (CHF+LVAD) as compared to non-failing ventricles (NF), left. The same comparisons in the subgroup of patients with a duration of LVAD therapy above the median value, right ( n = 10). AU arbitrary unit, CHF congestive heart failure, LVAD left ventricular assist device, NF non-failing myocardial tissue specimen
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
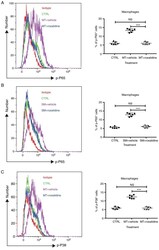
- Experimental details
- Figure 5. Addition of roxatidine to the culture medium of RAW 264.7 macrophages inhibited the activation of the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. RAW 264.7 macrophages were cultured in serum-free media at 37degC. Then, 24 h after cells were seeded, roxatidine (25 µM) was added to the media 1 h prior to stimulation with silicone surface materials. Cells were collected for analysis of phosphorylation of NF-kappaB subunit p65 and p38 MAPK by flow cytometry 15 minutes after adding silicone surface materials to culture media. Administration of roxatidine suppressed p65 activation stimulated by (A) MT and (B) SM, as well as p38 phosphorylation stimulated by (C) MT. p38 phosphorylation stimulated by (D) SM. n=6 wells/group, from one of triplicated experiments. n.s., not significant and ***P
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation