Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [17]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- ELISA [1]
- Other assay [5]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-7052-81 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- IL-5 Monoclonal Antibody (TRFK5), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The TRFK5 antibody reacts with mouse and human interleukin-5 (IL-5). The TRFK5 antibody is a neutralizing antibody. Mouse IL-5 is a disulfide-linked homodimer, containing two 113 amino acid peptides; these resolve as 32-34 kDa bands in SDS-PAGE. IL-5 is produced by T cells and has been known as eosinophil-differentiating factor (EDF), B cell growth factor II (BCGFII), and T cell-replacing factor (TRF). IL-5 induces eosinophil differentiation and promotes eosinophil survival and activation. In mice, IL-5 has been shown to stimulate B cell proliferation and antibody production. Applications Reported: The TRFK5 antibody has been reported for use in ELISA capture, ELISPOT capture, neutralization of IL-5 bioactivity, IHC, and intracellular staining for flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: The TRFK5 antibody has been tested as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA for analysis of mouse IL-5 in combination with the biotin TRFK4 (13-7051) antibody for detection and recombinant mouse IL-5 (14-8051) as the standard. A suitable range of concentrations of this antibody for ELISA capture is 1-4 µg/mL. A standard curve consisting of doubling dilutions of the recombinant standard over the range of 1000 pg/mL - 8 pg/mL should be included in each ELISA plate. The TRFK5 antibody has been tested as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA for analysis of human IL-5 in combination with the biotinylated JES1-5A10 (13-7059) antibody for detection and recombinant human IL-5 (14-80591) as the standard. A suitable range of concentrations of this antibody for ELISA capture is 1-4 µg/mL. A standard curve consisting of doubling dilutions of the recombinant standard over the range of 1000 pg/mL - 8 pg/mL should be included in each ELISA plate. The Functional Grade purified TRFK5 antibody has been tested for neutralization of IL-5 bioactivity. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse
- Host
- Rat
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- TRFK5
- Vial size
- 50 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Il4ra-independent vaginal eosinophil accumulation following helminth infection exacerbates epithelial ulcerative pathology of HSV-2 infection.
Bcl11b is essential for licensing Th2 differentiation during helminth infection and allergic asthma.
Rab6-dependent retrograde traffic of LAT controls immune synapse formation and T cell activation.
Intratracheal myriocin enhances allergen-induced Th2 inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness.
Concerted activity of IgG1 antibodies and IL-4/IL-25-dependent effector cells trap helminth larvae in the tissues following vaccination with defined secreted antigens, providing sterile immunity to challenge infection.
Fiber composite slices for multiplexed immunoassays.
Allergic airway inflammation decreases lung bacterial burden following acute Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a neutrophil- and CCL8-dependent manner.
Group 2 innate lymphoid cell production of IL-5 is regulated by NKT cells during influenza virus infection.
The Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit protects from allergic airway disease development by inducing CD4+ regulatory T cells.
Rapid, multiparameter profiling of cellular secretion using silicon photonic microring resonator arrays.
The essential role of single Ig IL-1 receptor-related molecule/Toll IL-1R8 in regulation of Th2 immune response.
MHC class II-dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote T(H)2 cytokine-dependent immunity.
Differential role of gamma interferon in inhibiting pulmonary eosinophilia and exacerbating systemic disease in fusion protein-immunized mice undergoing challenge infection with respiratory syncytial virus.
Pertussis toxin-induced cytokine differentiation and clonal expansion of T cells is mediated predominantly via costimulation.
Pathogenic role for virus-specific CD4 T cells in mice with coronavirus-induced acute encephalitis.
Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples.
The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent.
Chetty A, Darby MG, Vornewald PM, Martín-Alonso M, Filz A, Ritter M, McSorley HJ, Masson L, Smith K, Brombacher F, O'Shea MK, Cunningham AF, Ryffel B, Oudhoff MJ, Dewals BG, Layland LE, Horsnell WGC
Cell host & microbe 2021 Apr 14;29(4):579-593.e5
Cell host & microbe 2021 Apr 14;29(4):579-593.e5
Bcl11b is essential for licensing Th2 differentiation during helminth infection and allergic asthma.
Lorentsen KJ, Cho JJ, Luo X, Zuniga AN, Urban JF Jr, Zhou L, Gharaibeh R, Jobin C, Kladde MP, Avram D
Nature communications 2018 Apr 26;9(1):1679
Nature communications 2018 Apr 26;9(1):1679
Rab6-dependent retrograde traffic of LAT controls immune synapse formation and T cell activation.
Carpier JM, Zucchetti AE, Bataille L, Dogniaux S, Shafaq-Zadah M, Bardin S, Lucchino M, Maurin M, Joannas LD, Magalhaes JG, Johannes L, Galli T, Goud B, Hivroz C
The Journal of experimental medicine 2018 Apr 2;215(4):1245-1265
The Journal of experimental medicine 2018 Apr 2;215(4):1245-1265
Intratracheal myriocin enhances allergen-induced Th2 inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness.
Edukulla R, Rehn KL, Liu B, McAlees JW, Hershey GK, Wang YH, Lewkowich I, Lindsley AW
Immunity, inflammation and disease 2016 Sep;4(3):248-62
Immunity, inflammation and disease 2016 Sep;4(3):248-62
Concerted activity of IgG1 antibodies and IL-4/IL-25-dependent effector cells trap helminth larvae in the tissues following vaccination with defined secreted antigens, providing sterile immunity to challenge infection.
Hewitson JP, Filbey KJ, Esser-von Bieren J, Camberis M, Schwartz C, Murray J, Reynolds LA, Blair N, Robertson E, Harcus Y, Boon L, Huang SC, Yang L, Tu Y, Miller MJ, Voehringer D, Le Gros G, Harris N, Maizels RM
PLoS pathogens 2015 Mar;11(3):e1004676
PLoS pathogens 2015 Mar;11(3):e1004676
Fiber composite slices for multiplexed immunoassays.
Kim J, Bae S, Song S, Chung K, Kwon S
Biomicrofluidics 2015 Jul;9(4):044109
Biomicrofluidics 2015 Jul;9(4):044109
Allergic airway inflammation decreases lung bacterial burden following acute Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a neutrophil- and CCL8-dependent manner.
Dulek DE, Newcomb DC, Goleniewska K, Cephus J, Zhou W, Reiss S, Toki S, Ye F, Zaynagetdinov R, Sherrill TP, Blackwell TS, Moore ML, Boyd KL, Kolls JK, Peebles RS Jr
Infection and immunity 2014 Sep;82(9):3723-39
Infection and immunity 2014 Sep;82(9):3723-39
Group 2 innate lymphoid cell production of IL-5 is regulated by NKT cells during influenza virus infection.
Gorski SA, Hahn YS, Braciale TJ
PLoS pathogens 2013 Sep;9(9):e1003615
PLoS pathogens 2013 Sep;9(9):e1003615
The Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit protects from allergic airway disease development by inducing CD4+ regulatory T cells.
Donaldson DS, Apostolaki M, Bone HK, Richards CM, Williams NA
Mucosal immunology 2013 May;6(3):535-46
Mucosal immunology 2013 May;6(3):535-46
Rapid, multiparameter profiling of cellular secretion using silicon photonic microring resonator arrays.
Luchansky MS, Bailey RC
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2011 Dec 21;133(50):20500-6
Journal of the American Chemical Society 2011 Dec 21;133(50):20500-6
The essential role of single Ig IL-1 receptor-related molecule/Toll IL-1R8 in regulation of Th2 immune response.
Bulek K, Swaidani S, Qin J, Lu Y, Gulen MF, Herjan T, Min B, Kastelein RA, Aronica M, Kosz-Vnenchak M, Li X
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2009 Mar 1;182(5):2601-9
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2009 Mar 1;182(5):2601-9
MHC class II-dependent basophil-CD4+ T cell interactions promote T(H)2 cytokine-dependent immunity.
Perrigoue JG, Saenz SA, Siracusa MC, Allenspach EJ, Taylor BC, Giacomin PR, Nair MG, Du Y, Zaph C, van Rooijen N, Comeau MR, Pearce EJ, Laufer TM, Artis D
Nature immunology 2009 Jul;10(7):697-705
Nature immunology 2009 Jul;10(7):697-705
Differential role of gamma interferon in inhibiting pulmonary eosinophilia and exacerbating systemic disease in fusion protein-immunized mice undergoing challenge infection with respiratory syncytial virus.
Castilow EM, Olson MR, Meyerholz DK, Varga SM
Journal of virology 2008 Mar;82(5):2196-207
Journal of virology 2008 Mar;82(5):2196-207
Pertussis toxin-induced cytokine differentiation and clonal expansion of T cells is mediated predominantly via costimulation.
Denkinger CM, Denkinger MD, Forsthuber TG
Cellular immunology 2007 Mar;246(1):46-54
Cellular immunology 2007 Mar;246(1):46-54
Pathogenic role for virus-specific CD4 T cells in mice with coronavirus-induced acute encephalitis.
Anghelina D, Pewe L, Perlman S
The American journal of pathology 2006 Jul;169(1):209-22
The American journal of pathology 2006 Jul;169(1):209-22
Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples.
Abrams JS, Roncarolo MG, Yssel H, Andersson U, Gleich GJ, Silver JE
Immunological reviews 1992 Jun;127:5-24
Immunological reviews 1992 Jun;127:5-24
The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent.
Schumacher JH, O'Garra A, Shrader B, van Kimmenade A, Bond MW, Mosmann TR, Coffman RL
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576-81
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576-81
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
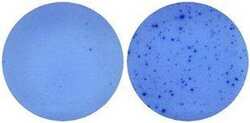
- Experimental details
- Naive mouse splenocytes (SJL/J strain) were stimulated with 2 µg/mL ConA in HL-1 media for 48 hours (right well) in a Mouse IL-5 ELISPOT assay plate. Left well is medium alone control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
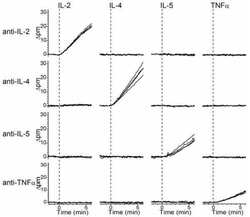
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Fig. 4 Frequencies of CD4 + T-cells expressing Gata3 and Th2 cytokines in asthma and helminth infection are reduced in Bcl11b fl/fl dLck-iCre mice by an intrinsic defect. a Flow cytometry analysis of IL-4 (left column), IL-5 (middle column), and IL-13 (right column) against GATA3 in the CD4 + T-cell population of the lung parenchyma of HDM asthma-induced mice. b Frequencies of IL-4 + ( n = 4), IL-5 + ( n = 4), and IL-13 + ( n = 8) (top panel) and GATA3 + ( n = 10) (bottom panel) CD4 + T-cells from the lungs of the indicated groups. Data are derived from two (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 data) or five (GATA3 data) independent experiments. c Flow cytometry analysis of IL-4 (left column), IL-5 (middle column), and IL-13 (right column) against GATA3 in the CD4 + T-cell population from the mesenteric (m)LNs of H. polygyrus infected mice. d Frequencies of IL-4 + ( n = 4), IL-5 + ( n = 4), and IL-13 + ( n = 4) (top panel) and GATA3 + ( n = 8) (bottom panel) CD4 + T-cells from mLNs of the indicated groups. Data are derived from two (IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13) or four (GATA3) independent experiments. e Flow cytometry analysis of GATA3 in CD4 + T-cells (left column) and IL-4 (middle and right columns) in the GATA3 hi (middle column) and GATA3 lo (right column) CD4 + T-cells from the mLNs of H. polygyrus bakeri infected mice. f The ratio of GATA3 hi /GATA3 lo CD4 + T-cells (top) and frequencies of IL-4 secreting cells within the GATA3 hi and GATA3 lo CD4 + T-cells (bottom) from the mLNs of H. poly
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
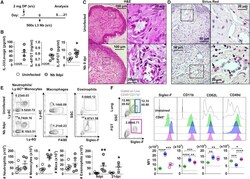
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 Influence of N. brasiliensis exposure on uncolonized FGT, increase in FGT eosinophils following Nb exposure (A) Female mice were hormone-synchronized 7 days prior to Nb infection. (B) At day 9 post-Nb infection (Nb 9dpi), levels of IL-33, IL-4, and IL-5 in FGT homogenates or lavages were assessed by ELISA or Luminex.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
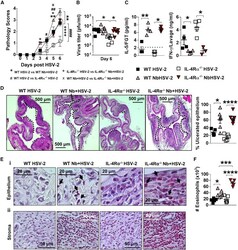
- Experimental details
- Figure 4 Nb-exacerbated HSV-2 pathology and FGT eosinophil infiltration is Il4ra independent WT and Il4ra -/- mice were infected with HSV-2 following Nb exposure as previously described. (A) HSV-2 progression was determined by daily pathology scoring. (B) Viral shedding was measured by plaque assay of day 6 vaginal washes. (C) Genital levels of IL-5 and IFN-gamma at day 2 post-HSV-2 infection, determined by Luminex and ELISA, respectively. Dotted line represents LLOQ of Luminex analysis. At 6 dpi, vaginal tissue was analyzed by H&E staining. (D) Representative sections (n = 3-4), displaying ulceration and inflammation of vaginal tissue. Images were taken at x50 magnification. HSV-2-ulcerated vaginal epithelium is indicated by black dotted lines and qualified as percentage (%) of ulcerated epithelium. (E) Representative Sirius-red-stained sections (n = 3-4) of virus-induced (Ei) epithelial ulcers and (Eii) stromal inflammation. Black arrows indicate eosinophil presence in the vaginal epithelial layer. Images were taken at x400 and x1,000 magnification. (F) Numbers (x10 3 ) of FGT eosinophils in WT and Il4ra -/- co-infected mice compared with HSV-2-only controls. Data are representative of two independent experiments with 3-6 mice per group (mean +- SEM). Statistical significance was calculated by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. * p
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
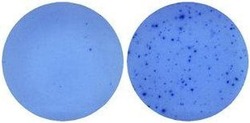
- Experimental details
- Naive mouse splenocytes (SJL/J strain) were stimulated with 2 µg/mL ConA in HL-1 media for 48 hours (right well) in a Mouse IL-5 ELISPOT assay plate. Left well is medium alone control.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn ELISA
ELISA Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry