Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [10]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunocytochemistry [4]
- Immunoprecipitation [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [3]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [11]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA1-066 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Caveolin 3 Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Synthetic peptide
- Description
- PA1-066 detects Caveolin 3 from rat and mouse tissues. This antibody does not detect caveolin-1 or -2. PA1-066 has been successfully used in Western blot, IF, immunocytochemistry and immunoprecipitation procedures. By Western blot, this antibody detects an ~21 kDa protein representing Caveolin 3 from rat heart homogenate. The PA1-066 immunogen is a synthetic peptide corresponding to residues M(1) M T E E H T D L E A R I I K D I H C(19) C of mouse CAV3. This sequence is ~85% conserved in human Caveolin 3. PA1-066 immunizing peptide (Cat. # PEP-081) is available for use in neutralization and control experiments.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μg
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Submitted references Caveolin-3 is a direct molecular partner of the Cav1.1 subunit of the skeletal muscle L-type calcium channel.
Ca2+ sparks and cellular distribution of ryanodine receptors in developing cardiomyocytes from rat.
Loss of caveolin-3 induced by the dystrophy-associated P104L mutation impairs L-type calcium channel function in mouse skeletal muscle cells.
Expression profiling and identification of novel genes involved in myogenic differentiation.
Role of caveolae in signal-transducing function of cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase.
Phosphofructokinase muscle-specific isoform requires caveolin-3 expression for plasma membrane recruitment and caveolar targeting: implications for the pathogenesis of caveolin-related muscle diseases.
Intracellular retention of glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-linked proteins in caveolin-deficient cells.
Intracellular retention of glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-linked proteins in caveolin-deficient cells.
Synapse-associated protein 97 selectively associates with a subset of AMPA receptors early in their biosynthetic pathway.
Synapse-associated protein 97 selectively associates with a subset of AMPA receptors early in their biosynthetic pathway.
Couchoux H, Bichraoui H, Chouabe C, Altafaj X, Bonvallet R, Allard B, Ronjat M, Berthier C
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2011 May;43(5):713-20
The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2011 May;43(5):713-20
Ca2+ sparks and cellular distribution of ryanodine receptors in developing cardiomyocytes from rat.
Snopko RM, Ramos-Franco J, Di Maio A, Karko KL, Manley C, Piedras-Rentería E, Mejía-Alvarez R
Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology 2008 Jun;44(6):1032-1044
Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology 2008 Jun;44(6):1032-1044
Loss of caveolin-3 induced by the dystrophy-associated P104L mutation impairs L-type calcium channel function in mouse skeletal muscle cells.
Couchoux H, Allard B, Legrand C, Jacquemond V, Berthier C
The Journal of physiology 2007 May 1;580(Pt.3):745-54
The Journal of physiology 2007 May 1;580(Pt.3):745-54
Expression profiling and identification of novel genes involved in myogenic differentiation.
Tomczak KK, Marinescu VD, Ramoni MF, Sanoudou D, Montanaro F, Han M, Kunkel LM, Kohane IS, Beggs AH
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2004 Feb;18(2):403-5
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2004 Feb;18(2):403-5
Role of caveolae in signal-transducing function of cardiac Na+/K+-ATPase.
Liu L, Mohammadi K, Aynafshar B, Wang H, Li D, Liu J, Ivanov AV, Xie Z, Askari A
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2003 Jun;284(6):C1550-60
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2003 Jun;284(6):C1550-60
Phosphofructokinase muscle-specific isoform requires caveolin-3 expression for plasma membrane recruitment and caveolar targeting: implications for the pathogenesis of caveolin-related muscle diseases.
Sotgia F, Bonuccelli G, Minetti C, Woodman SE, Capozza F, Kemp RG, Scherer PE, Lisanti MP
The American journal of pathology 2003 Dec;163(6):2619-34
The American journal of pathology 2003 Dec;163(6):2619-34
Intracellular retention of glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-linked proteins in caveolin-deficient cells.
Sotgia F, Razani B, Bonuccelli G, Schubert W, Battista M, Lee H, Capozza F, Schubert AL, Minetti C, Buckley JT, Lisanti MP
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Jun;22(11):3905-26
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Jun;22(11):3905-26
Intracellular retention of glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-linked proteins in caveolin-deficient cells.
Sotgia F, Razani B, Bonuccelli G, Schubert W, Battista M, Lee H, Capozza F, Schubert AL, Minetti C, Buckley JT, Lisanti MP
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Jun;22(11):3905-26
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Jun;22(11):3905-26
Synapse-associated protein 97 selectively associates with a subset of AMPA receptors early in their biosynthetic pathway.
Sans N, Racca C, Petralia RS, Wang YX, McCallum J, Wenthold RJ
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2001 Oct 1;21(19):7506-16
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2001 Oct 1;21(19):7506-16
Synapse-associated protein 97 selectively associates with a subset of AMPA receptors early in their biosynthetic pathway.
Sans N, Racca C, Petralia RS, Wang YX, McCallum J, Wenthold RJ
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2001 Oct 1;21(19):7506-16
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2001 Oct 1;21(19):7506-16
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
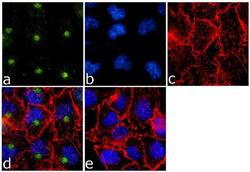
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Caveolin 3 was done on 70% confluent log phase A-375 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-066) at 1 µg/mL in 1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d is a merged image showing cytoplasmic localization. Panel e is a no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
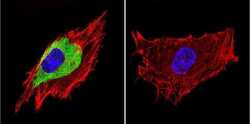
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Caveolin 3 in C2C11 Cells. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with a Caveolin 3 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA1-066) at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4 C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552). Caveolin 3 staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
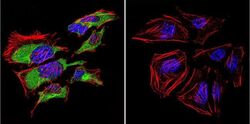
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Caveolin 3 in HeLa Cells. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with a Caveolin 3 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA1-066) at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4 C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552). Caveolin 3 staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
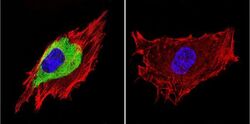
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Caveolin 3 in C2C11 Cells. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with a Caveolin 3 polyclonal antibody (Product # PA1-066) at a dilution of 1:20 overnight at 4 C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35552). Caveolin 3 staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Images were taken at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
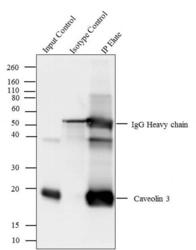
- Experimental details
- Caveolin 3 was immunoprecipitated using 5 µg of the Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-066) from lysate of Mouse Heart (Lane 3) using the Dynabeads® Protein A Immunoprecipitation Kit (Product # 10006D). Normal Rabbit IgG was used as a Isotype control (Lane 2). 10 % input represents the cell extract used for immunoprecipitation (Lane 1). Western blot analysis was performed using Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-066) and Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (Heavy Chain) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, HRP conjugate (Product # A27036, 0.4 µg/mL, 1:2500 dilution). Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Product # 32106).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
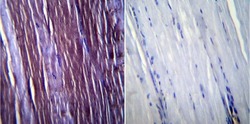
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal biopsies of deparaffinized Mouse skeletal muscle tissue. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:100 with a rabbit polyclonal antibody recognizing Caveolin 3 (Product # PA1-066) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
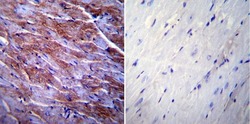
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal biopsies of deparaffinized Mouse heart tissue. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a rabbit polyclonal antibody recognizing Caveolin 3 (Product # PA1-066) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
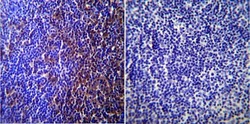
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal biopsies of deparaffinized Mouse lymph node tissue. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a rabbit polyclonal antibody recognizing Caveolin 3 (Product # PA1-066) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
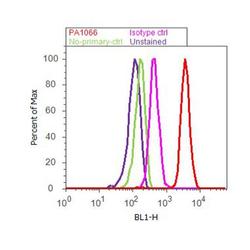
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Caveolin 3 was done on U-87 MG cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (PA1066, red histogram) or with rabbit isotype control (pink histogram) at 3-5 ug/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Goat Anti-Rabbit Secondary Antibody (A11008) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
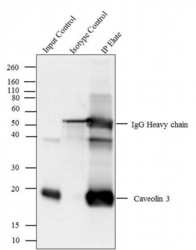
- Experimental details
- Caveolin 3 was immunoprecipitated using 5 æg of the Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-066) from lysate of Mouse Heart (Lane 3) using the Dynabeads® Protein A Immunoprecipitation Kit (Product # 10006D). Normal Rabbit IgG was used as a Isotype control (Lane 2). 10 % input represents the cell extract used for immunoprecipitation (Lane 1). Western blot analysis was performed using Caveolin 3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Product # PA1-066) and Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, HRP conjugate (Product # A27036, 0.4 æg/mL, 1:2500 dilution). Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Product # 32106).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
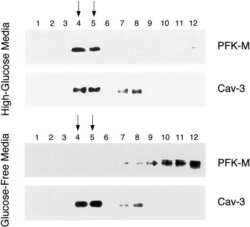
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
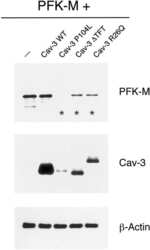
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
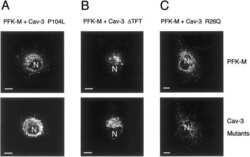
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
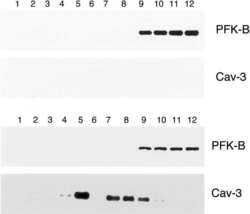
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
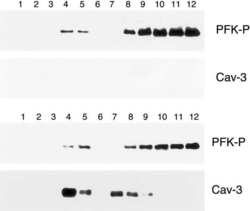
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
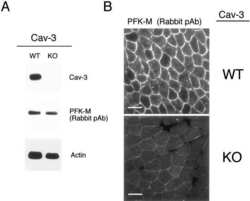
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
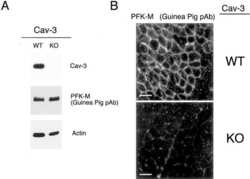
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
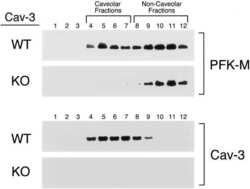
- Experimental details
- NULL
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry