Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- PA5-29678 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- PPAR delta Polyclonal Antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Antigen
- Recombinant full-length protein
- Description
- Recommended positive controls: K562, HL-60, DDDDK-tagged PPARD delta-transfected 293T. Predicted reactivity: Mouse (95%), Rat (94%), Japanese Medaka (80%), Dog (98%), Pig (95%), Rabbit (95%), Chicken (90%), Bovine (96%). Store product as a concentrated solution. Centrifuge briefly prior to opening the vial.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 0.44 mg/mL
- Storage
- Store at 4°C short term. For long term storage, store at -20°C, avoiding freeze/thaw cycles.
Submitted references Enhancement of anaerobic glycolysis - a role of PGC-1α4 in resistance exercise.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle contributes to the development of acute insulin resistance in mice.
Mitochondrial Utilization of Competing Fuels Is Altered in Insulin Resistant Skeletal Muscle of Non-obese Rats (Goto-Kakizaki).
PPARβ Is Essential for Maintaining Normal Levels of PGC-1α and Mitochondria and for the Increase in Muscle Mitochondria Induced by Exercise.
Deubiquitinase DUBA is a post-translational brake on interleukin-17 production in T cells.
Koh JH, Pataky MW, Dasari S, Klaus KA, Vuckovic I, Ruegsegger GN, Kumar AP, Robinson MM, Nair KS
Nature communications 2022 Apr 28;13(1):2324
Nature communications 2022 Apr 28;13(1):2324
Mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle contributes to the development of acute insulin resistance in mice.
Lee H, Ha TY, Jung CH, Nirmala FS, Park SY, Huh YH, Ahn J
Journal of cachexia, sarcopenia and muscle 2021 Dec;12(6):1925-1939
Journal of cachexia, sarcopenia and muscle 2021 Dec;12(6):1925-1939
Mitochondrial Utilization of Competing Fuels Is Altered in Insulin Resistant Skeletal Muscle of Non-obese Rats (Goto-Kakizaki).
Lai N, Fealy CE, Kummitha CM, Cabras S, Kirwan JP, Hoppel CL
Frontiers in physiology 2020;11:677
Frontiers in physiology 2020;11:677
PPARβ Is Essential for Maintaining Normal Levels of PGC-1α and Mitochondria and for the Increase in Muscle Mitochondria Induced by Exercise.
Koh JH, Hancock CR, Terada S, Higashida K, Holloszy JO, Han DH
Cell metabolism 2017 May 2;25(5):1176-1185.e5
Cell metabolism 2017 May 2;25(5):1176-1185.e5
Deubiquitinase DUBA is a post-translational brake on interleukin-17 production in T cells.
Rutz S, Kayagaki N, Phung QT, Eidenschenk C, Noubade R, Wang X, Lesch J, Lu R, Newton K, Huang OW, Cochran AG, Vasser M, Fauber BP, DeVoss J, Webster J, Diehl L, Modrusan Z, Kirkpatrick DS, Lill JR, Ouyang W, Dixit VM
Nature 2015 Feb 19;518(7539):417-21
Nature 2015 Feb 19;518(7539):417-21
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
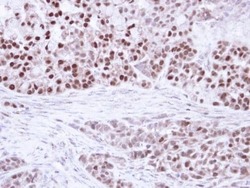
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded A549 Xenograft, using PPAR delta (beta) (Product # PA5-29678) antibody at 1:100 dilution. Antigen Retrieval: EDTA based buffer, pH 8.0, 15 min.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
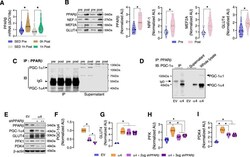
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
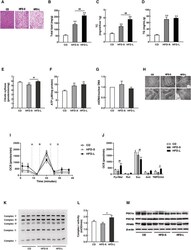
- Experimental details
- Figure 3 Hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction was not observed in acute IR. (A) Representative haematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-liver sections from CD, HFD-S, and HFD-L mice. Hepatic lipid profiles, including total lipid content (B), total cholesterol (TC, C), and triglyceride (TG, D). (E) Citrate synthase activity in liver tissues from CD, HFD-S, and HFD-L groups. (F) Total ATP content in liver tissues. (G) The mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) content calculated as the ratio of COX5 to Cyclophilin A DNA levels measured by quantitative PCR in liver tissues. (H) Mitochondrial morphology imaged by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). (I) Complex-dependent respiration determined by electron flow assay in mitochondrial proteins. (J) OCR quantification to measure complex-dependent respiration. (K) OXPHOS complex expression in liver tissues. (L) Complex I activity in liver tissues. (M) Expressions of PGC1 and PPARdelta measured by western blot.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
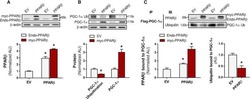
- Experimental details
- Resistance exercise training-induced PGC-1a4 cooperates with PPARbeta to regulate glycolysis. A PPARbeta mRNA was determined by qPCR in muscle biopsy samples of healthy participants before (SED Pre), within 10 min after (0 h Post), and 1 h after (1 h Post) a one-legged resistance exercise (RE) bout ( n = 16). Time-matched control muscle samples were obtained from the non-exercised leg at 1 h post-RE (SED 1 h Post) ( n = 16 per group). One-way ANOVA was used with multiple comparisons. B Protein abundance of PPARbeta and its downstream related proteins was determined in muscle before (Pre) and after (Post) RET. Representative immunoblots for each protein and quantification of the relative change after training for PPARbeta, NRF-1, MEF2A, and GLUT4 are displayed ( n = 16). Paired two-tailed t -tests were used. C PPARbeta was immunoprecipitated from pooled muscle samples before (pre) and after (post) RET, then the immunoprecipitate was immunoblotted for PGC-1alpha1 and PGC-1alpha4 to determine binding between PPARbeta with PGC-1alpha1 and PGC-1alpha4. Owing to the large amount of protein required to immunoprecipitate enough PPARbeta for immunoblot detection of PGC-1alpha1 and PGC-1alpha4, samples of multiple participants before and after training were pooled together, resulting in a smaller n for PGC-1alpha isoform quantification ( n = 2). D The binding between PPARbeta and PGC-1alpha isoforms was confirmed using cells overexpressing PGC-1alpha4. Experiment shown in panel D was p
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry