14-7096-81
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: CCL2
GDCF-2, HC11, MCAF, MCP-1, MCP1, MGC9434, SCYA2, SMC-CF
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [8]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [3]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-7096-81 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CCL2 (MCP-1) Monoclonal Antibody (2H5), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The 2H5 monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse, rat, and human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), also known as CCL2 and MCAF. Applications Reported: The 2H5 antibody has been reported for use in ELISA, intracellular staining for flow cytometric analysis, and cytokine neutralization. (Please use Functional Grade purified 2H5 antibody, Product # 16-7096, in functional assays). Applications Tested: Mouse MCP-1 ELISA: The biotinylated 2H5 antibody has been tested as the detection antibody in a sandwich ELISA for analysis of mouse MCP-1 in combination with the affinity purified 4E2/MCP (Product # 14-7091-81) antibody for capture and recombinant mouse MCP-1 as the standard. A suitable range of concentrations of this antibody for ELISA detection is 0.5-2.0 µg/mL. A standard curve consisting of doubling dilutions of the recombinant standard over the range of 2000 pg/mL - 15 pg/mL should be included in each ELISA plate. Human MCP-1 ELISA: The biotinylated 2H5 antibody has been tested as the detection antibody in a sandwich ELISA for analysis of human MCP-1 in combination with the affinity purified 5D3-F7 (Product # 14-7099-81) antibody for capture and recombinant human MCP-1 as the standard. A suitable range of concentrations of this antibody for ELISA detection is 0.5-2.0 µg/mL. A standard curve consisting of doubling dilutions of the recombinant standard over the range of 2000 pg/mL - 15 pg/mL should be included in each ELISA plate. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 2H5
- Vial size
- 50 μg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4°C
Submitted references Apoptotic vesicles restore liver macrophage homeostasis to counteract type 2 diabetes.
Conditioned medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis.
Influence of fatty acids in maternal diet on atherogenesis in offspring of LDL receptor-deficient mice.
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PhoP-PhoQ two-component regulatory system is induced upon interaction with epithelial cells and controls cytotoxicity and inflammation.
Chemokine-mediated recruitment of NK cells is a critical host defense mechanism in invasive aspergillosis.
Mechanisms underlying renoprotection during renin-angiotensin system blockade.
Mechanisms underlying renoprotection during renin-angiotensin system blockade.
Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and KC induce chemokine production by mouse astrocytes.
Zheng C, Sui B, Zhang X, Hu J, Chen J, Liu J, Wu D, Ye Q, Xiang L, Qiu X, Liu S, Deng Z, Zhou J, Liu S, Shi S, Jin Y
Journal of extracellular vesicles 2021 May;10(7):e12109
Journal of extracellular vesicles 2021 May;10(7):e12109
Conditioned medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis.
Shen C, Lie P, Miao T, Yu M, Lu Q, Feng T, Li J, Zu T, Liu X, Li H
Molecular medicine reports 2015 Jul;12(1):20-30
Molecular medicine reports 2015 Jul;12(1):20-30
Influence of fatty acids in maternal diet on atherogenesis in offspring of LDL receptor-deficient mice.
de Oliveira Cipriano Torres D, Santos AC, Silva AK, de Moura PM, Beltrão EI, Peixoto CA
International journal of clinical and experimental medicine 2012;5(1):56-63
International journal of clinical and experimental medicine 2012;5(1):56-63
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa PhoP-PhoQ two-component regulatory system is induced upon interaction with epithelial cells and controls cytotoxicity and inflammation.
Gellatly SL, Needham B, Madera L, Trent MS, Hancock RE
Infection and immunity 2012 Sep;80(9):3122-31
Infection and immunity 2012 Sep;80(9):3122-31
Chemokine-mediated recruitment of NK cells is a critical host defense mechanism in invasive aspergillosis.
Morrison BE, Park SJ, Mooney JM, Mehrad B
The Journal of clinical investigation 2003 Dec;112(12):1862-70
The Journal of clinical investigation 2003 Dec;112(12):1862-70
Mechanisms underlying renoprotection during renin-angiotensin system blockade.
Taal MW, Chertow GM, Rennke HG, Gurnani A, Jiang T, Shahsafaei A, Troy JL, Brenner BM, Mackenzie HS
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2001 Feb;280(2):F343-55
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2001 Feb;280(2):F343-55
Mechanisms underlying renoprotection during renin-angiotensin system blockade.
Taal MW, Chertow GM, Rennke HG, Gurnani A, Jiang T, Shahsafaei A, Troy JL, Brenner BM, Mackenzie HS
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2001 Feb;280(2):F343-55
American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 2001 Feb;280(2):F343-55
Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and KC induce chemokine production by mouse astrocytes.
Luo Y, Fischer FR, Hancock WW, Dorf ME
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2000 Oct 1;165(7):4015-23
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2000 Oct 1;165(7):4015-23
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
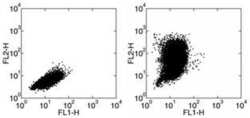
- Experimental details
- Staining of mouse thioglycolate-induced peritoneal exudate cells (PECs) stimulated with LPS in the presence of Brefeldin A for 24 hours with Anti-Mouse F4/80 Antigen FITC and intracellularly stained with Rat IgG2a kappa Isotype Control (Product # 12-4321-82) (left) or with Anti-CCL2 (MCP-1) PE (right).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
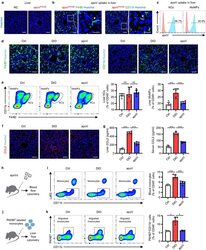
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 3 Efferocytosis of MSC-derived apoVs by liver macrophages alleviates macrophage infiltration in the type 2 diabetes (T2D) liver. (a) Representative confocal microscopy images showing distribution of PKH26-labeled apoVs (red) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). After removal of unbound PKH, the stained apoVs were resuspended in PBS and underwent centrifugation, after which the supernatant was used as the negative control (NC) and injected. Scale bars, 50 mum. (b) Representative confocal microscopy images showing uptake of apoVs (red) by macrophages (green) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 50 mum in low magnification images and 25 mum in high magnification images. (c) Flow cytometric analysis showing the uptake of apoVs by macrophages in the liver. KCs, Kupffer cells; MoMFs, monocyte-derived macrophages. (d) Representative immunofluorescent (IF) staining images of F4/80 (green) and CD11b (green) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). Ctrl, control mice; DIO, mice with diet-induced obesity; apoV, DIO mice treated by apoVs. Scale bars, 50 mum. (e) Flow cytometric analysis and the corresponding quantification of the percentages of KCs and MoMFs in hepatic CD45 + cells. N = 6 per group. (f) Representative IF staining images of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) (red) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 50 mum. (g) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of CCL2 in liver lysate and serum. N
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
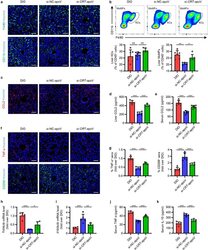
- Experimental details
- FIGURE 8 CRT mediates efferocytosis of MSC-derived apoVs to modulate T2D liver macrophages in vivo. (a) Representative immunofluorescent (IF) staining images of F4/80 (green) and CD11b (green) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). DIO, mice with diet-induced obesity; si-NC-apoV, DIO mice treated by apoVs derived from MSCs transfected by siRNA-negative control; si- CRT -apoV, DIO mice treated by apoVs derived from MSCs transfected by siRNA- CRT . Scale bars, 50 mum. (b) Flow cytometric analysis and the corresponding quantification of the percentages of KCs and MoMFs in hepatic CD45 + cells. KCs, Kupffer cells; MoMFs, monocyte-derived macrophages. N = 5-6 per group. (c) Representative IF staining images of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) (red) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 50 mum. (d and e) ELISA analysis of CCL2 in liver lysate (d) and serum (e). N = 6 per group. (f and g) Representative IF staining images of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) (red) and CD206 (green) in the liver, counterstained by Hoechst (blue), and the corresponding quantification of fold changes over the DIO group. Scale bars, 50 mum. N = 5-6 per group. (h and i) Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis of mRNA expression levels of Tnf (h) and interleukin 10 ( Il10 ) (i) in the liver, normalized to beta-actin ( Actb ), and quantification of fold changes over the DIO group. N = 5 per group. (j and k) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent as
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
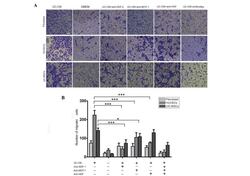
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 Migration of fibroblasts, HUVECs and UC-MSCs in response to UC-CM. (A) A total of 5x10 4 cells were collected and allowed to migrate. Lane 1, UC-CM; lane 2, DMEM; lanes 3-6, in the presence or absence of anti-SDF-1 (20 mu g/ml), anti-MCP-1 (20 mu g/ml) or anti-HGF (20 mu g/ml), respectively. Results are from a representative experiment and are expressed as the mean number of migrated cells in three random fields, scale bar=200 mu m. Cells that crossed the matrigel membrane were stained with crystal violet (magnification, x40). (B) Graphical presentation of the quantified data, presented as the number of migrated cells and expressed as the mean +- standard error of the mean. HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; UC-MSCs, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; UC-CM, UC-MSCs conditioned medium; DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry