HPA001591
antibody from Atlas Antibodies
Targeting: RBM39
CAPER, CAPERalpha, CC1.3, fSAP59, HCC1, RNPC2
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [14]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- HPA001591 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Atlas Antibodies
- Proper citation
- Atlas Antibodies Cat#HPA001591, RRID:AB_1079749
- Product name
- Anti-RBM39
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Polyclonal Antibody against Human RBM39, Gene description: RNA binding motif protein 39, Alternative Gene Names: CAPER, CAPERalpha, CC1.3, fSAP59, HCC1, RNPC2, Validated applications: WB, IHC, Uniprot ID: Q14498, Storage: Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 100 µl
- Concentration
- 0.1 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at +4°C for short term storage. Long time storage is recommended at -20°C.
- Handling
- The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use.
Submitted references Liver cancer initiation requires translational activation by an oncofetal regulon involving LIN28 proteins
A molecular glue RBM39-degrader induces synthetic lethality in cancer cells with homologous recombination repair deficiency.
Targeted protein degradation via intramolecular bivalent glues.
Overlaid Transcriptional and Proteome Analyses Identify Mitotic Kinesins as Important Targets of Arylsulfonamide-Mediated RBM39 Degradation
Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39
Molecular basis of RNA-binding and autoregulation by the cancer-associated splicing factor RBM39
A proximity biotinylation-based approach to identify protein-E3 ligase interactions induced by PROTACs and molecular glues
Indisulam targets RNA splicing and metabolism to serve as a therapeutic strategy for high-risk neuroblastoma
Genetic and compound screens uncover factors modulating cancer cell response to indisulam.
Pharmacologic modulation of RNA splicing enhances anti-tumor immunity.
The Influenza A Virus Endoribonuclease PA-X Usurps Host mRNA Processing Machinery to Limit Host Gene Expression
UBE2G1 governs the destruction of cereblon neomorphic substrates
Negative autoregulation of BMP dependent transcription by SIN3B splicing reveals a role for RBM39
CSE1L, DIDO1 and RBM39 in colorectal adenoma to carcinoma progression
Hsieh M, Wei Y, Li L, Nguyen L, Lin Y, Yong J, Sun X, Wang X, Luo X, Knutson S, Bracken C, Daley G, Powers J, Zhu H
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2024;134(15)
Journal of Clinical Investigation 2024;134(15)
A molecular glue RBM39-degrader induces synthetic lethality in cancer cells with homologous recombination repair deficiency.
Kohsaka S, Yagishita S, Shirai Y, Matsuno Y, Ueno T, Kojima S, Ikeuchi H, Ikegami M, Kitada R, Yoshioka KI, Toshimitsu K, Tabata K, Yokoi A, Doi T, Yamamoto N, Owa T, Hamada A, Mano H
NPJ precision oncology 2024 May 24;8(1):117
NPJ precision oncology 2024 May 24;8(1):117
Targeted protein degradation via intramolecular bivalent glues.
Hsia O, Hinterndorfer M, Cowan AD, Iso K, Ishida T, Sundaramoorthy R, Nakasone MA, Imrichova H, Schätz C, Rukavina A, Husnjak K, Wegner M, Correa-Sáez A, Craigon C, Casement R, Maniaci C, Testa A, Kaulich M, Dikic I, Winter GE, Ciulli A
Nature 2024 Mar;627(8002):204-211
Nature 2024 Mar;627(8002):204-211
Overlaid Transcriptional and Proteome Analyses Identify Mitotic Kinesins as Important Targets of Arylsulfonamide-Mediated RBM39 Degradation
Coomar S, Mota P, Penson A, Schwaller J, Abdel-Wahab O, Gillingham D
Molecular Cancer Research 2023;21(8):768-778
Molecular Cancer Research 2023;21(8):768-778
Arginine reprograms metabolism in liver cancer via RBM39
Mossmann D, Müller C, Park S, Ryback B, Colombi M, Ritter N, Weißenberger D, Dazert E, Coto-Llerena M, Nuciforo S, Blukacz L, Ercan C, Jimenez V, Piscuoglio S, Bosch F, Terracciano L, Sauer U, Heim M, Hall M
Cell 2023;186(23):5068-5083.e23
Cell 2023;186(23):5068-5083.e23
Molecular basis of RNA-binding and autoregulation by the cancer-associated splicing factor RBM39
Campagne S, Jutzi D, Malard F, Matoga M, Romane K, Feldmuller M, Colombo M, Ruepp M, Allain F
Nature Communications 2023;14(1)
Nature Communications 2023;14(1)
A proximity biotinylation-based approach to identify protein-E3 ligase interactions induced by PROTACs and molecular glues
Yamanaka S, Horiuchi Y, Matsuoka S, Kido K, Nishino K, Maeno M, Shibata N, Kosako H, Sawasaki T
Nature Communications 2022;13(1)
Nature Communications 2022;13(1)
Indisulam targets RNA splicing and metabolism to serve as a therapeutic strategy for high-risk neuroblastoma
Nijhuis A, Sikka A, Yogev O, Herendi L, Balcells C, Ma Y, Poon E, Eckold C, Valbuena G, Xu Y, Liu Y, da Costa B, Gruet M, Wickremesinghe C, Benito A, Kramer H, Montoya A, Carling D, Want E, Jamin Y, Chesler L, Keun H
Nature Communications 2022;13(1)
Nature Communications 2022;13(1)
Genetic and compound screens uncover factors modulating cancer cell response to indisulam.
Pogacar Z, Groot K, Jochems F, Dos Santos Dias M, Mulero-Sánchez A, Morris B, Roosen M, Wardak L, De Conti G, Velds A, Lieftink C, Thijssen B, Beijersbergen RL, Bernards R, Leite de Oliveira R
Life science alliance 2022 Sep;5(9)
Life science alliance 2022 Sep;5(9)
Pharmacologic modulation of RNA splicing enhances anti-tumor immunity.
Lu SX, De Neef E, Thomas JD, Sabio E, Rousseau B, Gigoux M, Knorr DA, Greenbaum B, Elhanati Y, Hogg SJ, Chow A, Ghosh A, Xie A, Zamarin D, Cui D, Erickson C, Singer M, Cho H, Wang E, Lu B, Durham BH, Shah H, Chowell D, Gabel AM, Shen Y, Liu J, Jin J, Rhodes MC, Taylor RE, Molina H, Wolchok JD, Merghoub T, Diaz LA Jr, Abdel-Wahab O, Bradley RK
Cell 2021 Jul 22;184(15):4032-4047.e31
Cell 2021 Jul 22;184(15):4032-4047.e31
The Influenza A Virus Endoribonuclease PA-X Usurps Host mRNA Processing Machinery to Limit Host Gene Expression
Gaucherand L, Porter B, Levene R, Price E, Schmaling S, Rycroft C, Kevorkian Y, McCormick C, Khaperskyy D, Gaglia M
Cell Reports 2019;27(3):776-792.e7
Cell Reports 2019;27(3):776-792.e7
UBE2G1 governs the destruction of cereblon neomorphic substrates
Lu G, Weng S, Matyskiela M, Zheng X, Fang W, Wood S, Surka C, Mizukoshi R, Lu C, Mendy D, Jang I, Wang K, Marella M, Couto S, Cathers B, Carmichael J, Chamberlain P, Rolfe M
eLife 2018;7
eLife 2018;7
Negative autoregulation of BMP dependent transcription by SIN3B splicing reveals a role for RBM39
Faherty N, Benson M, Sharma E, Lee A, Howarth A, Lockstone H, Ebner D, Bhattacharya S
Scientific Reports 2016;6(1)
Scientific Reports 2016;6(1)
CSE1L, DIDO1 and RBM39 in colorectal adenoma to carcinoma progression
Sillars-Hardebol A, Carvalho B, Beliën J, de Wit M, Delis-van Diemen P, Tijssen M, van de Wiel M, Pontén F, Meijer G, Fijneman R
Cellular Oncology 2012;35(4):293-300
Cellular Oncology 2012;35(4):293-300
No comments: Submit comment
Enhanced validation
- Submitted by
- Atlas Antibodies (provider)
- Enhanced method
- Genetic validation
- Main image
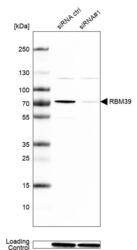
- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis in Caco-2 cells transfected with control siRNA, target specific siRNA probe #1, using Anti-RBM39 antibody. Remaining relative intensity is presented. Loading control: Anti-GAPDH.
- Sample type
- Human
- Protocol
- Protocol
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry